The content of cellular elements in the serous fluid
The main morphological elements, which can be found in the serous cavities of punctates, are:
- blood cells (erythrocytes and leucocytes);
- mezoteliotsity;
- gistiocitы.
Red blood cells in serous liquids
Red blood cells detected in the serous fluid in different quantities depending on the cause, caused by their appearance (trauma, malignancy, infection, and others.). They can be detected by degenerative changes, are important in determining the statute of limitations hemorrhage, its intensity and duration.
White blood cells in serous fluid
Neutrophilic granulocytes
With the penetration of infection in serous cavities inflammatory reaction occurs with the emergence of primarily segmented neutrophils, exudates which may be characterized by a number of degenerative changes: toksogennoy grit, hypersegmentation, vacuolization of cytoplasm, etc..
The presence of neutrophils in the stage of a degenerative collapse of detritus on the background and abundant flora (intra-, and extracellular) It indicates the severity of the process. The appearance of this background mononuclear cells of the tissue of origin indicates favorable prognosis of the inflammatory process.
Eosinophilic granulocytes
Single eosinophil granulocytes can be detected in any of serous fluid, Sometimes, however,, in particular in allergic reactions, they can be very (to 90 %). Morphologically, they did not differ from eosinophilic granulocytes blood.
Lymphocytes
Lymphocytes are more resistant, than segmented neutrophilic granulocytes, they are less exposed to degenerative changes and are in any serous fluid. Sometimes degenerative changed, shriveled neutrophilic granulocytes mistaken for lymphocytes. In difficult cases, the differentiation of these cells should pay attention to the chromatin structure of the nucleus. For lymphocytes characterized by specific structure gruboglybchataya.
Monocytes
Monocytes in serous fluid is also more resistant, than segmented neutrophilic granulocytes. Morphologically, they usually do not differ from blood monocytes. Their appearance or quantitative increase in inflammatory reactions is a welcome sign.
Plasma cells in serous fluid
Plasma cells (plasmacytes) if protracted inflammation in serous cavities can be detected in large quantities.
Histiocytes in serous fluid
Histiocytes varied in size, shape and color. Their diameter ranges from 10-30 microns. The color of the cytoplasm in some cells light blue, others - darker. Kernels histiocytes are delicate structure of chromatin network, oval or bean-shaped (monocytoid), located centrally or eccentrically. At the core are 1-2 nucleoli, are often not visible due to degenerative changes. The cytoplasm is often vacuolated.
Giant multinucleated cells in chronic inflammation of serous fluid
Giant multinucleated cells of chronic inflammation (cells of foreign bodies) found in serous fluid rarely, It results from amitotic fission histiocytes and characterized by the following features:
- large sizes;
- round or oval shape;
- small, round, monomorphic, compact, randomly arranged nuclei without nucleoli;
- basophilic cytoplasm without inclusions.
Macrophages in serous fluid
Macrophages are morphologically extremely similar to monocytes.. Their cytoplasm basophilic, pale colored, mesh, contains vacuoles and azurophilic granularity. The nuclei are quite large, most often wrong, sometimes bizarre shape, the chromatin of the nuclei is located in the form of a more dense and uneven, then a gentle and uniform network. The nucleoli are not always clearly visible. Often these cells contain inclusions in the form of erythrocytes., nuclei of leukocytes and other more or less preserved cells or only cellular remnants, etc.. d.
Mesotheliocytes in serous fluid
Mesotheliocytes are single-layered squamous epithelial cells, lining the serous membranes of the pleural, pericardial and abdominal cavities. The diameter of mesotheliocytes reaches 25-30 microns. Kernels their round shape, less oval, located centrally, sometimes a bit eccentric. The chromatin network is delicate, uniform. Sometimes a small nucleolus is visible in the nucleus. The cytoplasm is large, most often round, painted according to Pappenheim in soft blue tones.
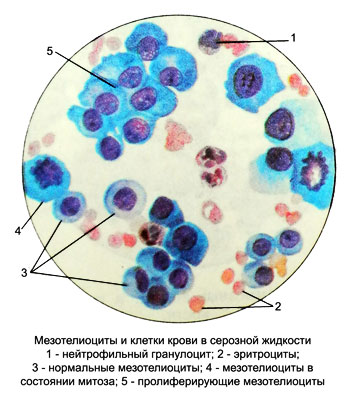
Under the influence of various stimuli (infection, injury, drugs) mesothelial proliferation may increase. This increases the cells, their nuclei and nucleoli, increased basophilia of the cytoplasm and nucleoli, as the content of RNA is increased in intensively proliferating cells. The cytoplasm acquires uneven contours, its quantity increases. Mitotic division of mesothelial nuclei is often determined. With proliferation, the total number of mesotheliocytes increases significantly. In the results of the study, there is no need to reflect in detail the morphology of proliferating mesotheliocytes., because it is specific; it is enough to indicate their number.
Various pathological processes are accompanied by the same type of dystrophic changes in mesotheliocytes.. Characterized by a variety of cell sizes and shapes. Their nuclei are pycnotic or with a sparse chromatin pattern., may undergo lysis. There are multi-cell. The cytoplasm of mesotheliocytes can have a different color, contain coarse granular inclusions and undergo vacuolization (frothy, cricoid cells).
Cytomorphological changes in mesotheliocytes proliferative and dystrophic nature are especially pronounced in chronic heart and kidney failure. At the same time, accumulations of cells in the form of layers and glandular structures are found in the serous fluid.. Sometimes there are giant round or polygonal symplasts with a large number of differently colored enlarged monomorphic nuclei., arranged crowded or in the form of a ring.
In acute inflammation, mesotheliocytes become atypical and look like cancer cells. Large cells with enlarged hyperchromic nuclei appear, hypertrophied nucleoli and intensely colored, basophilic cytoplasm. There are giant multinucleated cells with figures of mitosis and amitosis.
With mechanical and chemical irritation of the serous membranes (surgery, entry into the serous cavity of a contrasting mass, etc.) an increase in the total number of mesotheliocytes, polymorphism of their nuclei is revealed (bizarrely wrong, horseshoe shape, hourglass, etc.).
For benign tumors of the uterus and ovaries in the serous fluid from the uterine-rectal space, mesotheliocytes are located in the form of extensive clusters. Large hyperchromic nuclei and pronounced basophilia of the cytoplasm are noted.. Nuclear and cellular polymorphism is absent. Cages, detached from the loosened layers of mesothelium, resemble histiocytes (elongated, with cytoplasmic processes).
With tumor lesions of the serous membranes dystrophic changes are usually expressed in mesotheliocytes: signs of proliferation (many glandular structures, synthial formations, etc.) characteristic of a pronounced adhesive process, accompanying tumor.
Changes in mesotheliocytes of regenerative and degenerative nature create diagnostic difficulties and often lead to erroneous conclusions, especially in the diagnosis of malignant neoplasms.
