Sinusitis – Sinus infection – Ostryi sinusitis – Have chronic sinusitis
Description sinusitis
Sinusitis – inflammation of the sinuses, usually associated with infection. Maxillary sinus cavities in the skull called, filled with air.
Acute sinusitis lasts less than three weeks. Chronic sinusitis is diagnosed, if symptoms last for at least three months. When frequently repeated attacks of acute sinusitis, he could develop into a recurrent sinusitis.
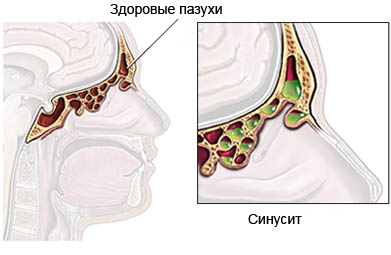
Infectious sinusitis can be caused by a bacterial infection or a fungal infection of the maxillary sinuses. The most common organisms, cause acute sinusitis include:
- Streptococck pneumoniae;
- Haemophilus influenzae;
- Moraxella catarrhalis.
Risk factors for sinusitis
Factors, which increase the risk of sinusitis:
- Recent viral infection;
- Smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke;
- Contaminated air;
- Allergies, especially hay fever.
Abnormalities of the facial bones or nasal passages:
- Deviated nasal septum;
- Nasal polyps;
- Cleft palate;
- Enlarged adenoids in size.
Certain chronic diseases, including:
- Mukovystsydoz;
- Syndrome Kartedzhenera (chronic lung disease);
- Granulematoz Wegener (rare disease, when Kotormo inflamed blood vessel wall);
- Asthma;
- Sarkoidoz;
- HIV infection;
- Diabetes;
- Traumatic brain injury or disease, requiring mechanical ventilation.
Symptoms of sinusitis
Symptoms of sinusitis may include:
- Nasal congestion, not passing using decongestants or antihistamines;
- Nasal discharge;
- Thick yellow, or green mucus;
- Cough, often worse at night;
- Pain or pressure in the ear;
- Headache;
- Fever;
- Toothache;
- Facial pain or a feeling of tightness, which increases when bending or pressing;
- Swollen face;
- Bad Breath;
- Fatigue.
Diagnosis of sinusitis
Sinusitis is diagnosed based on the presence of its symptoms and sinus pain when you press.
Carry out an analysis, which may include:
- Visual inspection of the nasal cavity;
- Computed tomography of the sinuses – X-rays, which uses a computer, to make pictures of structures in the head;
- Tackling sinus fluid through a needle for analysis (rarely);
- Endoscopic examination of the maxillary sinuses – examination of the nasal cavity with a special thin tube with a light source at the end.
Acute sinusitis is most common in the following cases:
- The presence of colored mucus 10 or more days;
- Soreness sinuses;
- The presence of visible mucus in the nose.
Treatment of acute sinusitis
Home Treatment
- Humidification – receiving large quantities of liquid to avoid blockage of the nasal passages and sinuses. Rinsing the nose with salt water and sprays can also weaken nosovyme selection.
- Treatment with steam – We need to fill the capacity of boiling water every two hours, and, covering his head with a towel, breathe steam. For these purposes it is possible to use a special inhaler.
Medication
- Decongestants – the use of tablets, decongestants or nasal sprays, to reduce isolation. Do not use nasal sprays for longer than 3-4 days in a row;
- Intranasal corticosteroids – they are taken directly into the nose through a nasal spray. Corticosteroids can reduce isolation and nasal congestion;
- Antihistamines may help sinusitis, if it is caused by allergies;
- Supplementation, containing guaifenesin – for sputum by coughing;
- Antibiotics taken if it appears, an infection caused by bacteria. Although, as studies have shown, Antibiotics are not effective in treating acute sinusitis;
- Nonprescription drugs – acetaminophen, Ibuprofen, or aspirin can reduce pain in the sinuses; Attention: Aspirin is not recommended for children or teens with a current or recent viral infection due to the risk of Reye's syndrome.
Surgery for acute sinusitis
Surgery – last resort for people with very serious chronic sinusitis. It includes:
- Restoring rejected the nasal septum;
- Removal of nasal polyps;
- Functional endoscopic sinus surgery – used, to increase and improve sinus drainage;
- Balloon (sinuplastika) – a catheter with a balloon attached is inserted into the sinus. The balloon is inflated, to open the maxillary sinus.
Prevention of acute sinusitis
If you have a tendency to get sick sinusitis after a cold or allergies, you need to take the following measures:
- Avoid contact with allergens, to prevent allergies;
- When you use allergy nasal spray with cortisone or antihistamines, to reduce inflammation;
- With a cold should drink plenty of fluids and use a decongestant (tablets or nasal spray);
- Periodically blow your nose, for the release of the nasal passages of mucus;
- Use a humidifier, colds, allergic symptoms, or sinuses;
- Use the filters in the vacuum cleaner, to remove allergens from the air;
- You should avoid cigarette smoke.
