Thyroid Cancer – characteristic punctate
Thyroid cancer develops from adenomas, diffuse or focal hyperplasia, as well as from normal parenchyma.
According to the WHO International Classification, distinguishes the following histological forms thyroid cancer:
- follicular;
- papillary;
- squamous;
- undifferentiated:
- and) spindle cell;
- to) giant;
- in) small cell;
- medullary.
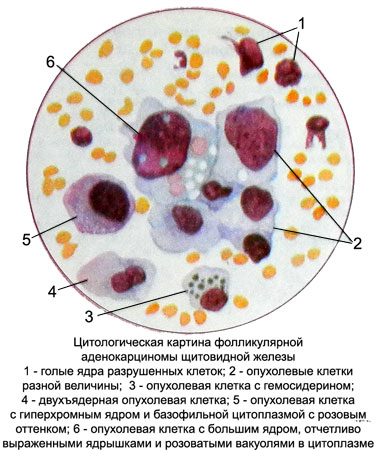
Follicular thyroid cancer
The tumor occurs most often in women aged 60-80 years. Can grow into blood vessels.
Microscopic examination revealed the tumor punctate tumor cells of medium size with a slightly pronounced polymorphism. They are located primarily in the form of complexes, reminiscent of the structure of the follicles. Despite the pronounced nuclear atypia, cytoplasm retains features, characteristic of follicular cells: substantial width, irregular contours, pinkish color and cytoplasmic vacuolization. The cells of this tumor is often observed in colloid form inclusion of bubbles of different sizes, filled with pink contents.
The colloid may be located extracellularly and in the form of a homogeneous mass in follicles or fibrous substance is blocked. Symplast missing. For thyroid cancer is characterized by the emergence of multi-core cell. Sometimes glandular complexes of cancer cells can be detected acervulus. Their presence in cytological specimens is an important feature of follicular thyroid cancer.
Papillary thyroid cancer
Papillary cancer - a tumor, the most common among malignant tumors of the thyroid gland. The substrate can consist of tumors of follicular cells A-, B-cells or from the other and at the same time.
Most often there is papillary carcinoma of the A-cell.
Cytological diagnosis of papillary cancer often presents considerable difficulties, since tumor cells mainly monomorphic, average value, cubic or cylindrical shape.
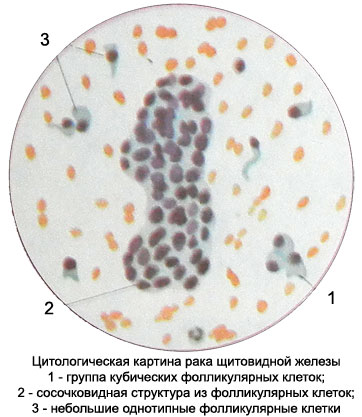
The cell nuclei large, have irregular jagged contours, often hypochromic, some of them contain one or two nucleoli. The light-colored kernels are often rough chromatin structure, glybchataya or in the form of short sticks. The cytoplasm surrounds the nucleus of a small rim, It stained with different intensities and may be slightly frothy appearance. The edges of her clearly konturiruyutsya.
Cells are located mostly in the form of papillary structures, often with signs of atypia.
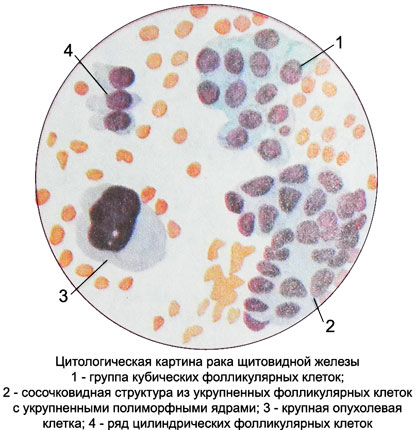
The location of the cells in the papillary structures, two-row.
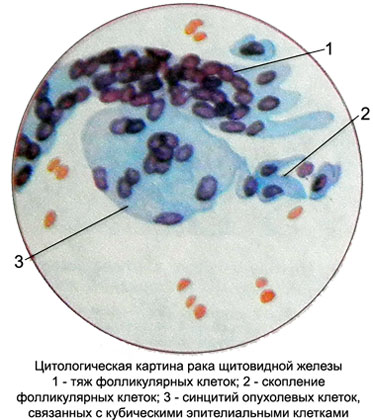
The features of the cytological picture of papillary cancer is the presence of intranuclear cytoplasmic invaginations (intranuclear vacuoles), as well as extensive syncytia without clear boundaries between cells (resembling giant multinucleated cells) and simplastov with a large number of randomly-spaced nuclei.
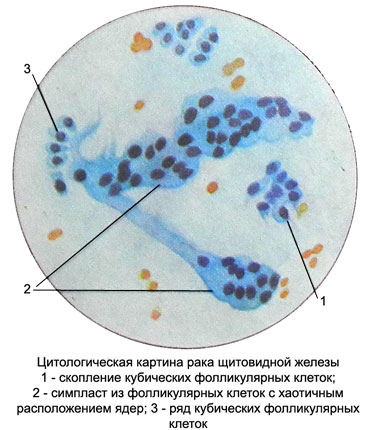
Often such structures are identified long or short projections of cytoplasm in the form of elongated sprouts. The number of cores in them can vary from 2-3 to 15-20 and more. The nuclei of the same medium size, round or oval, It is painted in a reddish-purple tones. The contours of the nuclei clear, smooth, chromatin in the form of small dots arranged compactly. Can detect single small nucleoli. Cores are placed randomly throughout the area symplast or concentrated at one of the poles. The cytoplasm is slightly granular or foamy, with clear contours, painted in light blue tones, sometimes with a pinkish hue. Can meet and individual follicular structures. Often found acervulus. Occasionally punctate tumors of squamous metaplasia observed areas in the form of concentric nests of squamous epithelium and squamous "pearls".
Medullary thyroid cancer – Solid cancer stroma with amyloidosis
It develops from C-cells. The punctate revealed amyloid (stained by Pappenheim, Unlike colloid, in bluish-purple, bluish or yellowish-greenish color) and cancer cells round, oval or spindle-shaped or all of these forms simultaneously. Kernels hyperchromic. There are two- and polynuclear cells. Arranged in isolation cells, forming a solid field, Sometimes they form psevdofollikulyarnye or pseudopapillary structure.
Squamous cell carcinoma and sarcoma, thyroid
Squamous cell carcinoma and sarcoma (primary and metastatic) They do not differ structurally from those of the other tumor localization.
Undifferentiated thyroid cancer
There are small cell, Spindle and giant cell undifferentiated form of thyroid cancer.
Small cell carcinoma of the thyroid gland
When small cell carcinoma found in punctate limfotsitopodobnye small cells with a nucleus, occupying nearly the entire cell, and a narrow rim of cytoplasm. This form of cancer must be differentiated from lymphosarcoma and angiosarcoma. Close, as if cemented, group of cells, arranged in a facet, inherent undifferentiated cell lung cancer.
Giant thyroid cancer
Giant cancer characterized by the presence of large and giant cells round or irregular shape. In stained cell nuclei light or hyperchromic, large, with melkoglybchatym, tyazhistym, annular seats (in the form cut down a tree) arrangement of chromatin. They contain one or more nucleoli. Cytoplasm abundant, with sharp scalloped contours, It is containing secretory vacuoles of various sizes and shapes, colored in pink-red color. The presence of large vacuoles gives cell vesicular. Cells are arranged in isolation or as a large single-layer clusters.
Spindle thyroid cancer
Spindle cell carcinoma is rare. It characterized by the presence of spindle cells in a punctate with large elongated nucleus (oval, rod-shaped, and others.), containing nucleoli. The cytoplasm is more pronounced at the poles of the cell. The most common spindle cell undifferentiated carcinoma combined with giant.
Cancer cells from Askanaz (B-cells)
Microscopic examination of punctate tumor found in the preparation of large and giant cells of various shapes with large and giant, mostly rounded kernels. Can occur in multi-cell. The cytoplasm of tumor cells light, slightly frothy, as if swollen because of the large number of pinkish grit of various sizes, filling the cell and pushes the nucleus to the periphery.