Lung cancer – status and sputum
Approximately lung cancer is divided into three types:
- Squamous;
- Undifferentiated;
- Adenocarcinoma.
Nedifferentsirovannыy cancer, in turn, divided into small- and large-. Between three main types of lung cancer are often no clear distinction, since 30 % cases there is a mixed structure.
The most common squamous cell carcinoma of the lung (45-60 %), in second place is the frequency of undifferentiated carcinoma (20-40%), on tretem- adenocarcinoma (9-12 %); However, quite often there are mixed type, therefore, in each individual case of cancer, it is advisable to specify its histological form.
There are exophytic tumor growth, when it grows in the form of a polyp in the lumen of the bronchus, and endophytic, when the tumor infiltrates the wall of the bronchus.
Cytological diagnosis of cancer of the bronchi based on the study of sputum, scourages bronchi or smears, taken directly from the modified portions of the mucous membrane of the bronchi during bronchoscopy. Comparative studies have shown, that the greatest number of positive results obtained in the study of sputum, especially repeated. Research wash water and smears from bronchi produce fewer positive results.
Easy to obtain material for study and a high percentage of positive diagnoses do sputum cytology one of the main methods of diagnosis of lung cancer, and even in the early stages of its development.
Therefore, in the sputum in cases of its occurrence in a patient of particular diagnostic value.
Tumor cells in the sputum of lung cancer patients with squamous were first found and described in 1887 g.
For the microscopic study used mostly native products from carefully selected particles of sputum, followed by coloring them in Pappenheim, Romanovsky et al.
Squamous (epidermoid) cancer
According to the degree of differentiation of squamous cell carcinoma may be high, moderately- and low-grade.
In determining the level of differentiation of squamous cell carcinoma is necessary to consider not only the morphological changes in the cells, but also the degree of keratinization, t. it is. keratinization of the cytoplasm and the cell as a whole compared with the normal flat oro- goveyuschim epithelium.
Vыsokodifferentsirovannыy ploskokletochnыy cancer orogoveniem It consists of epithelial polygonal or rounded shape, similar to the flat surface epithelium cells. The cytoplasm of cells, soderzhashtih keratin, clearly delineated, in nativnыh preparatah opaque. In preparations stained by Pappenheim it basophilic, The color intensity is proportional to the degree of keratinization of the cytoplasm. The rounded shape large nuclei in stained hyperchromic.
A characteristic feature of this form of squamous histology of lung cancer is the formation of keratin and squamous cells of cancer (horny) "Pearls" and rod-shaped structures.
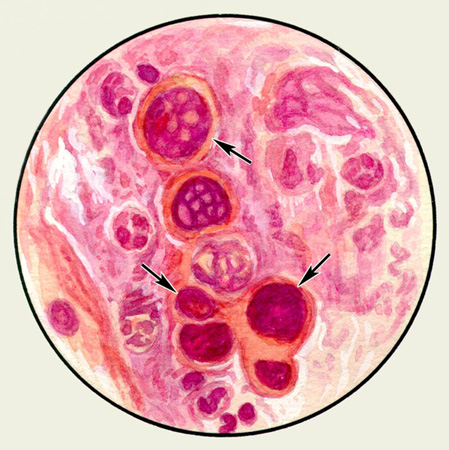
The latter may contain two or three cancers "pearls" of different sizes and more. In some cells showing signs of steatosis. This tumor grows slowly and easily verified cytology native preparations, since in stained cancer "pearls" are losing their morphological features. In this form of squamous cell carcinoma in sputum often found dense patches of tissue tumor, which are often covered with bacteria, scraps can be found inside the crystals gematoidina and elastic fibers, which are particles of necrotic tissue. Detection in native preparations along with the tumor cells elastic fibers confirms the accuracy of the diagnosis of cancer and evidence of tissue destruction.
For a moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma characterized polymorphism partially stratum cells of different shapes and sizes with a fairly large, sharply hyperchromatic nuclei round, oval or rod-shaped. The kernels are often wrong wavy contours, sometimes with deep angular cuts and awl-shaped protrusions. Nucleoli are often not visible. Cytoplasm and sharply delineated fairly evenly surrounds the nucleus. Cytoplasmic rim width is usually less, than the diameter of the core, however, this is not the rule, as in SCC also found cells with abundant cytoplasm.
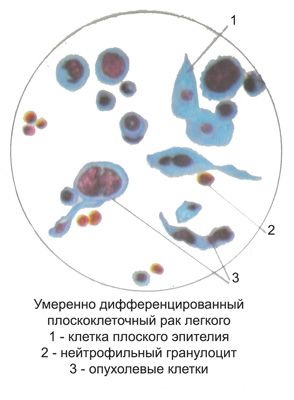
Smears, stained by Pappenheim, cytoplasm sometimes with marked basophilic, opaque, a testament to its Actinic. In some cells can be found in part actinic periphery of the cytoplasm around the nucleus with clearing, resulting in the cytoplasm with double loops.
Sometimes the nucleus of tumor cells is torn and preserved cytoplasm seen scattered small fragments. Due pyknosis of the nucleus of tumor cells can be significantly reduced. As a result of autolytic changes in chromatin structure may completely lose (mist). The cells are moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma are often subject to fatty degeneration, while a drop of fat often completely fill the core; cytoplasm of cells less prone to fatty degeneration. In this histological forms of cancer are found in the sputum macroscopically visible whitish-grayish track, consisting of the above-described cancer cells prlimorfnyh. Verification of tumor is equally easily accomplished both native, and in stained preparations.
Nizkodifferentsirovannыy ploskokletochnыy cancer without keratinization characterized by the presence of polymorphic cells round or more elongated with large round or rod-shaped nuclei and prominent nucleoli more, cells are often found in mitosis.
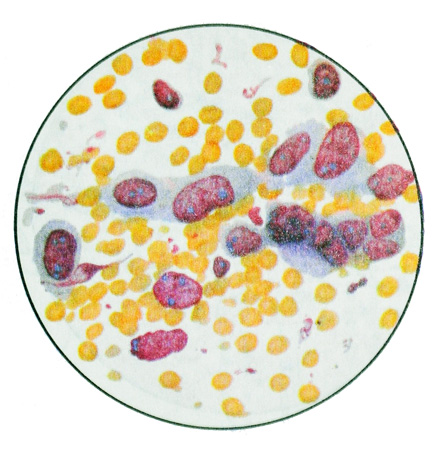
In some cells there is keratin. Sometimes found bottlenecks, spindle-shaped cells with polymorphic nuclei and small steatosis. The combination of these and other cellular elements in a tumor site is often difficult to verify the tumor.
One of the varieties of squamous cell lung cancer is a tumor, cell substrate is small polymorphous epithelium with moderate keratinization and fatty degeneration of the cytoplasm. The size of these cells approach the metaplazirovan- nym (Rar) bronchial epithelial cells. In the sputum, they form a kind of whitish-grayish track, and native specimens under low magnification microscope similar to leukocytes; fat droplets are found not only in cells, extracellularly but. Verifies the tumor in the study of native preparations of sputum at a small and a large increase in their subsequent color.
Adenocarcinoma
When lung adenocarcinoma cell complexes glandular structures have sharp contours. Combination (complexation) rounded cells reflects the structure of glandular and glandular moves bubbles. Very often the tumor cells form a close group.
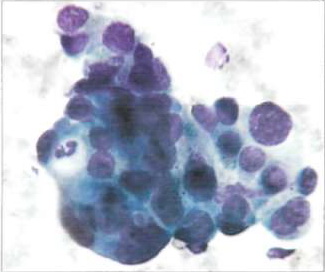
The cell nuclei, Located on the periphery of the group, clearly limit its closed loop, whereby it resembles the structure of the primary glandular bubble. Adenocarcinoma cells from the same patient, even when re-examination is usually have approximately the same dimensions, but sometimes may vary in size.
The cells are highly differentiated adenocarcinoma morphologically similar to secretory gland cells. Most often they are in the form, close to a circular (oval), with some deviation to the side bevel pear. The cytoplasm tenderly painted, usually, inhomogeneous, grained or soft mesh, It recalls the cytoplasm of histiocytes. Often the contours of the cells in the background of the drug clearly visible. The cytoplasm can be detected zones of various sizes enlightenment, reflecting the secretory function of cells. Tumor cells can be arranged in a syncytium.
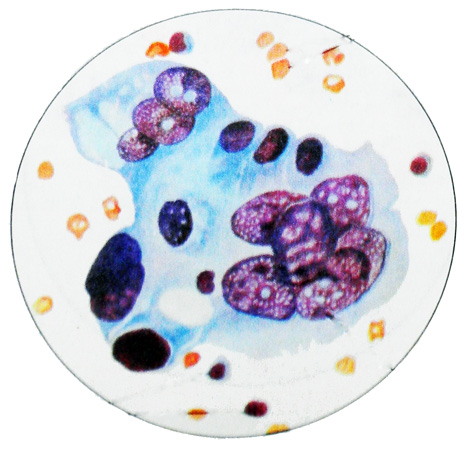
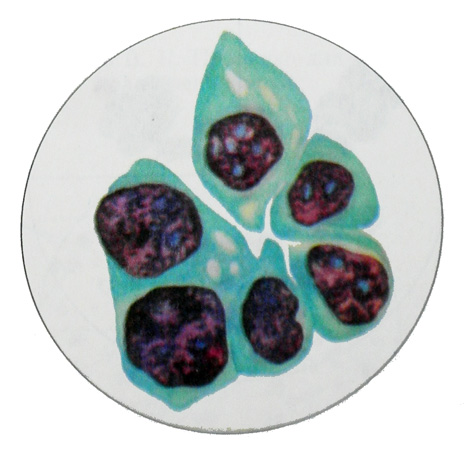
The glandular structure of cancer is most easily recognized by the detection of cell complexes, having the form of rosettes nearly round shape with a slightly scalloped contours.
Cages, forming an outlet, have distinct boundaries only on the periphery thereof, and in the center of the cytoplasm it seems common. Characteristic is the peripheral location of the nuclei, although not expressed, and the formation of papillary structures.

Umyeryenno adenocarcinoma diffyeryentsirovannaya It has a solid structure, glandular. Its cells are characterized by a more pronounced signs of malignancy. They are quite large sizes, round (oval) shape, with abundant cytoplasm and large round (oval) cores.
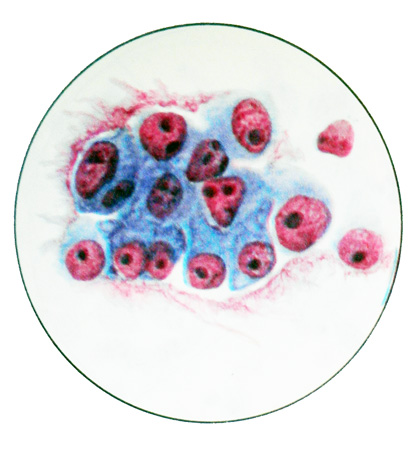
The nuclei are 1-3 rather large nucleolus. There are cells in mitosis. In some places there are huge multi-core and small round-shaped cells with large hyperchromatic nuclei, containing 1-2 nucleoli. Cells are arranged in groups and clusters, mostly in the form of structures zhelezistopodobnyh.
Nizkodiffyeryentsirovannaya adenocarcinoma It consists of large polymorphic cells with pronounced signs of malignancy. Cores of larger, slightly stained, contain large, konturiruemye clear nucleoli. Cytoplasm abundant, often it contains mucous secretion. Located cells in cytological preparations separately and in groups, occasionally forming glandular structures.
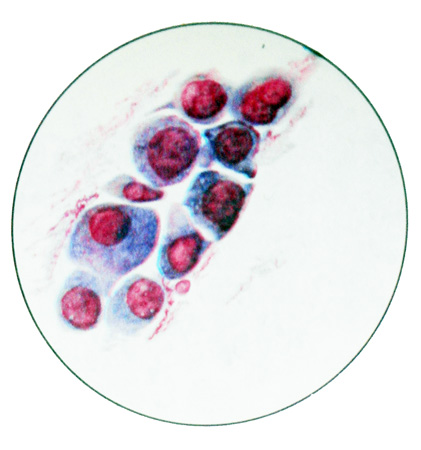
The glandular nature of the tumor can be determined and enlightened in the cytoplasm, eccentric location of nuclei and other features, relating to the structure of the individual cells. Awakening in the cytoplasm sometimes creates the impression of a spherical cell shape. Often, a detailed study syncytial formations, seemingly devoid of structure, reveals the formation of cell-type series in the stockade. In such cases syncytia fragment is assessed as atypical glandular tissue structure. Sputum with adenocarcinoma often contains an admixture of blood.
Undifferentiated lung cancer
When small cell carcinoma sputum does not have any special features. The drug is made from various parts of the mucous expectoration. The native preparation small cell carcinoma cells are very similar to the white blood cells, but unlike these tumor cells do not have the grit and located close groups or tracks.
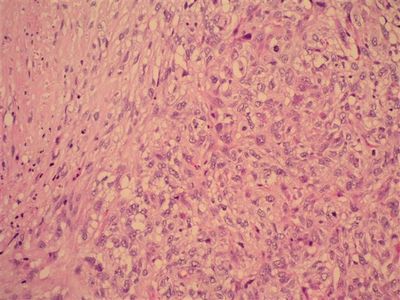
In stained tumor cells resemble cells of the same type limfotsitopodobnye with large nuclei.
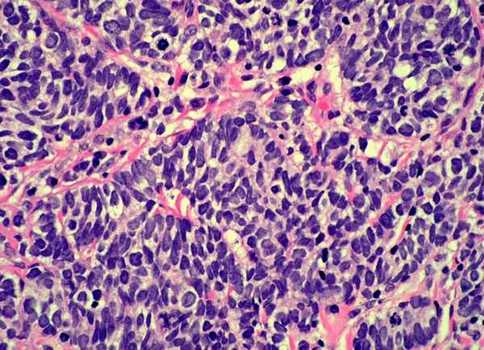
Under low magnification tumor cells can be detected in the course of mucus strands, they are often bare nucleus, hyperchromatic, easily injured. Network chromatin hardly differentiated, hypertrophied nucleoli are uncommon. The contours of the nuclei uneven. The cells are arranged closely, partly in the form of joints, their complexes may also take the form of a bunch of grapes.
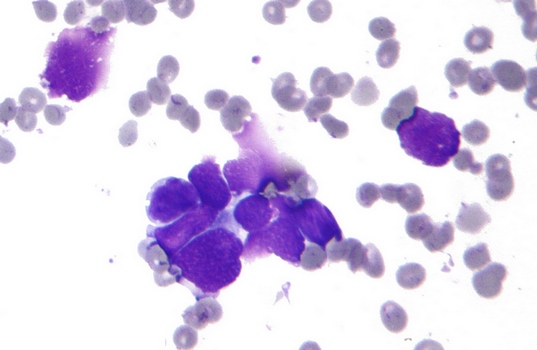
In cytologic preparation, prepared from tumor punctate, small cell carcinoma cells are represented by larger, than in the preparation of sputum. In such cases, the cytologic diagnosis of small cell lung cancer can be difficult. Cells of this type of tumor is not always rounded shape, among them there are and elongated - ovsyanokletochnыy cancer. There is evidence of similarity between the carcinoid cancer ovsyanokletochnogo, because its cells can produce a biologically active substance (Serotonin, vasopressin, calcitonin and others.), what else needs to be confirmed.
Krupnokletochnыy cancer, as melcockletocny, It refers to an undifferentiated. Its cells are polymorphic, different sizes, many of them are large and multi-core.
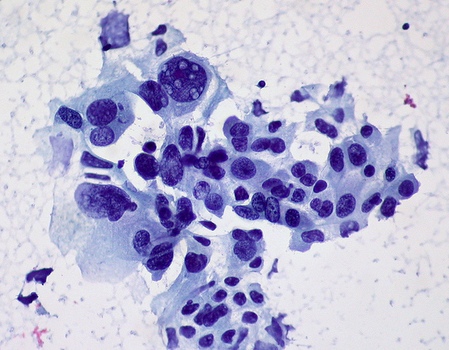
The cell nuclei large, irregular shape, comprise one or several nucleoli. Cytoplasmic wide, basophilic. Cells are arranged separately and in groups. For large-related lung cancer, and the so-called clear cell, consisting of a large light cells with abundant cytoplasm, often containing glycogen, and small cores, located in the cell center or eccentrically. In each case this is necessary to eliminate cancer metastasis from the kidney.
