Pseudogout – Xondrokalьцinoz
Description pseudogout
Pseudogout is a type of arthritis, which can affect any joint in the body. The disease occurs, when calcium crystals (calcium pyrophosphate), accumulate a fluid, surrounding the joints. The accumulation of these crystals causes inflammation in cartilage, material, which softens the bones and allows the joint to move smoothly. In this weakened cartilage, there is swelling and pain in the affected joints, which can lead to chronic disability.
Pseudogout occurs most often in the knees, and can be very severe. Also, the disease can affect the joints of the wrist, hips, Shoulder, elbows, Ankle, toes and hands. Pseudogout usually only occurs in one joint, but sometimes it can affect several joints at the same time.
The disease is called pseudogout (pseudo means false), because it causes symptoms, similar to gout. Nonetheless, the cause is the deposition of calcium pyrophosphate crystals, and gout is caused by the deposition of uric acid crystals. Gout also has a more severe disease course and often a poor prognosis.
As soon as possible is important to correctly identify the disease, because if left untreated, pseudogout can lead to chronic disability. Pseudogout is a potentially dangerous disease, which requires medical supervision. The sooner treatment begins pseudogout, the more favorable outcome. If you suspect, that you have this disease, consult a physician immediately.
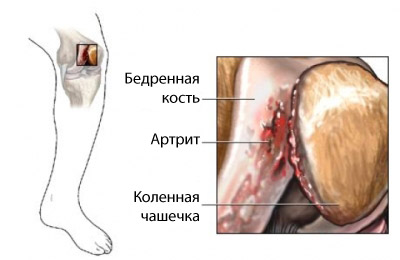
Reasons pseudogout
Pseudogout occurs, when calcium crystals, called calcium pyrophosphate, accumulate in joints. The accumulation of these crystals causes swelling and pain, that may cause damage to cartilage in joints.
The reasons for the accumulation of crystals of calcium are not yet known. The probability of accumulation of crystals increases with age, may play a role as genetic factors.
Risk Factors pseudogout
Anyone can get pseudogout. Nonetheless, Some factors increase the risk of disease:
- Age:
- The risk increases with age pseudogout;
- Attacks of pain can occur more frequently and become more severe with age;
- The presence of family members with pseudogout;
- Gipotireoz – underactive thyroid;
- Gemoxromatoz – an excess of iron in the body;
- Hyperactivity parathyroid – one of four endocrine glands located above or within the thyroid, that increases the level of calcium in the blood;
- Hypercalcemia – Too much calcium in the blood;
- Renal failure;
- Diabetes;
- Recent surgery – pseudogout sometimes develops after surgery;
- Trauma – damage to the joint, especially in the elderly, can cause the accumulation of crystals of calcium.
The symptoms of pseudogout
Pseudogout especially strongly affects knee joints, but also can affect the wrist joints, shoulders, Ankle, elbows and hands.
These symptoms, except pseudogout, They may be caused by other disorders. If you experience any of them, consult a doctor.
- Pain or tenderness in joints;
- Pain, similar to the attack of arthritis;
- Very high sensitivity joint pressure;
- Stiffness in joints;
- Swollen joints, warm to the touch;
- Redness of the skin around the joint.
Left untreated, pseudogout can last attack 5-12 days.
Diagnosing pseudogout
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history, a physical exam.
To correctly identify and diagnose pseudogout, the doctor must analyze the type of crystals, which are in fluid affected joint.
- Aspiration sustava – the doctor may use a needle, to remove some of the fluid around the affected joint and to determine the presence therein of crystals of calcium pyrophosphate;
- Roentgen – the doctor may perform an X-ray of the affected joint / joints to determine whether calcium crystals;
- Blood tests – tests are used, to rule out other diseases, Taki how gout, rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis, which can cause swelling and pain in joints.
Treatment of pseudogout
Treatment of pseudogout – question of the treatment of the discomfort during active pseudogout attacks. There are no treatments for the most pseudogout, because it is impossible to dissolve the crystal deposits, that already exist.
Without treatment the pain and discomfort of pseudogout attack are themselves within 5-12 days. But, in the treatment of symptoms can take place within 24 hours.
Treatment options include the following:
Drugs in pseudogout
Reducing inflammation can help slow the deterioration of joints.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (eg, aspirin) – are used to reduce inflammation;
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) – (eg, Ibuprofen, naproxen, Indomethacin) apply, to quickly stop the attacks of pain and reduce inflammation;
- Corticosteroids – They are used to reduce inflammation. They can be introduced into the affected joint or provided in the form of tablets;
- Colchicine – another kind of anti-inflammatory drugs. Studies have shown, Colchicine may be used to prevent attacks pseudogout.
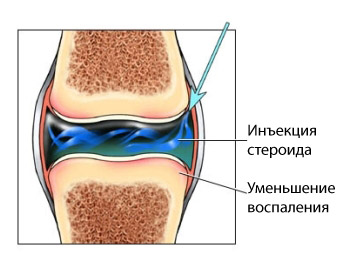
Procedures
- Injections of cortisone – your doctor may prescribe cortisone injections into the affected joint. Cortisone is a powerful anti-inflammatory drug. It is a synthetic steroid, which is naturally produced by the adrenal glands;
- Artrotsentez – the procedure includes the removal of liquid and crystals from the joint using a needle. Removal of the liquid can relieve pain;
- Operation – sometimes performed, to repair or replace damaged joints.
Peace
It is important to protect joints, keeping them at rest and not putting loads.
Prevention pseudogout
To date, there are no methods, allowing to prevent pseudogout.
To reduce the likelihood of pseudogout or to stop the progression of the disease, proceed as follows:
- Talk to your doctor about taking anti-inflammatory drugs, to prevent the symptoms;
- Protect joints – do not expose them to heavy loads:
- Do not lift heavy objects;
- Lift and carry heavy objects need, properly distribute the weight on your hands, legs, back;
- Maintain a healthy body weight, not to expose additional stress joints;
- Relax your muscles, to reduce pain.
