Presbiakuzis – Age-related loss of hearing
Description presbycusis
Presbiakuzis – Gradual hearing loss in both ears, which typically occurs with age. Almost half of the people from 75 and older have this form of gradual hearing loss, that It can be mild, moderate or severe. Presbycusis sometimes leads to permanent hearing loss – deafness. Also, hearing loss may cause some diseases. If there is a suspicion of presbycusis, seek medical advice.
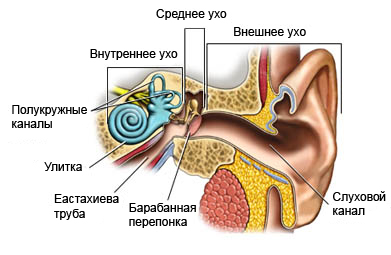
The reasons for presbycusis
- Gradual degeneration of the eardrum and inner ear structures (hair cells) because of age;
- Changes in the hearing nerve terminals, leading to brain;
- Exposure to loud sounds, music, or equipment, which can damage the delicate hair cells in the inner ear;
- Hereditary or genetic causes.
Risk factors for presbycusis
Factors, which increase the likelihood of developing presbycusis:
- The presence of the family of persons with progressive hearing loss with age;
- The use of certain medications, including aspirin, some antibiotics, anti-cancer drugs;
- Health problems, including cardiovascular disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, and other circulatory problems.
The symptoms of presbycusis
These symptoms may be caused by other diseases. For an accurate diagnosis, seek medical advice.
- Noticeable loss of hearing high-pitched sounds, such, how women's voices, phone call, or the birds singing;
- Sounds appear less clear and sharp;
- Difficulty understanding conversations, particularly in noisy places or while speaking on the phone;
- Ringing in one or both ears, noise in ears;
- Background sounds appear overly loud or bothersome.
When hearing loss is presbycusis, usually, It occurs gradually, affecting both ears equally.
Diagnosis of presbycusis
The doctor performs a physical examination of the external auditory canal and tympanic membrane tool, called otoscope. You also need to be examined by an otolaryngologist, doctor, specializing in diseases of the ear, nose, and throat. You must pass the inspection audiologist, which can make a full assessment of hearing, to determine the degree of hearing loss.
Assays may include:
- Rinne Test – a vibrating tuning fork placed on the bone behind the ear (mastoid), and then in air. On the difference in the sound slishimosti determine the nature of hearing loss;
- Analysis of Weber – a tuning fork is placed on the forehead, to determine one-sided hearing loss;
- Audiometria – wearing headphones and listening for different tones, which vary in pitch and volume.
Treatment for presbycusis
Treatment options include the following:
Hearing aids and assistive devices
If it is determined, that the hearing aid may be useful, audiologist will conduct several tests, to determine the type of hearing aid, which is best able to improve hearing. The degree of improvement varies depending on the cause and degree of hearing loss. Sometimes a hearing aid should be replaced by another model, if hearing loss progresses.
Cochlear implants
For some people with very severe hearing loss, Cochlear implants can transmit sound directly to the auditory nerves.
Prevention presbycusis
To reduce the risk of presbycusis, you must take the following steps:
- Avoid exposure to loud noises and sounds of any type, including at work, houses, and during holiday;
- When working with loud machinery or in noisy environments, wear protective plug (Earplugs) or headphones.
