Detachment of the placenta – Premature separation of the placenta – Placenta
Description detachment of the placenta
Detachment of the placenta – complication, Occurs, when the placenta separates from the uterus before birth in the womb. The placenta is an organ, which provides power fetus, while it develops in the womb. In normal pregnancy, placenta remains attached to the wall of the uterus, while the fetus is developing.
In one form or another delamination occurs in the placenta 0.5-0.8 percent of pregnant, that is, on one occasion 150 – 200 delivery. In very severe placental abruption can cause fetal death. It occurs in about one 500-750 cases of placental abruption. The death of the mother due to placental abruption is very rare. In 40 – 50% children, born when this complication occurs developmental disorders.
Detachment of the placenta can cause the following complications:
- Miscarriage;
- Low birth weight;
- Significant blood loss in the mother.
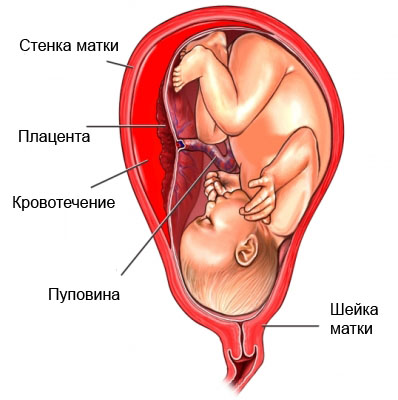
Causes detachment of the placenta
Causes, leading to placental abruption is often difficult to diagnose. The most common reasons are as follows:
- Injuries to the abdomen from an accident or a fall;
- Sudden decrease in the volume of the uterus, from significant loss of amniotic fluid or in connection with the birth of the first twin (in multiple pregnancies);
- Abnormally short umbilical cord;
- The sharp rise in blood pressure (often associated with the use of drugs and drug, in particular cocaine).
Risk factors for placental abruption
Risk factors are conditions, increase the likelihood of developing complications. Factors, increases the likelihood of detachment of the placenta following:
- Placental abruption in a previous pregnancy;
- High blood pressure during pregnancy;
- Pregnancy in older age;
- Polycyesis;
- Rastyanuost uterus;
- Diabetes;
- Drug abuse (cocaine);
- Smoking during pregnancy;
- Alcohol abuse during pregnancy.
The symptoms of placental abruption
In the early stages of detachment symptoms may be invisible. When symptoms occur, They may include:
- Vaginal bleeding;
- Abdominal pain;
- Backache;
- Soreness in the uterus.
Diagnosis of placental abruption
For diagnosis must pass the following examinations:
- Examination by a gynecologist;
- Ultrazvukovvoe study (US);
- Tests for blood clotting.
Treatment of placental abruption
Treatment includes:
- When blood loss is assigned to drip and / or blood transfusions;
- It controls the heart of mother and fetus;
- If there is a health risk to the mother or fetus may be necessary to cesarean. If the minimum risk of complications, birth can take place in the usual way.
Prevention detachment of the placenta
To reduce the risk of placental abruption, you must take the following steps:
- Avoid the use of drugs (especially cocaine), not to abuse alcohol and smoking during pregnancy;
- Receive proper and regular prenatal care throughout the pregnancy period;
- If you have diabetes or elevated pressure is necessary to see a doctor and undergo medical check-up.
