Alimentary allergy – What is this disease, symptoms, treatment prevention

Food allergy is a pathological reaction of the body to a certain food., based on immunological mechanisms.
First of all, we are talking about the production of immunoglobulin E (IgE) - squirrel, playing a key role in the occurrence of allergic manifestations from the skin and mucous membranes. IgE is not always involved in the allergic process, therefore isolated IgE-mediated, non-IgE mediated (for which cellular mechanisms are responsible, eg, T lymphocytes) and mixed allergic reactions. To start the allergic process, exposure to an allergen is necessary - a component of food, capable of inducing IgE production or activating a cellular allergic reaction. Allergens are usually food proteins..
Symptoms of food allergies
European Academy of Allergology and Clinical Immunology (Earaci) subdivides the manifestations of food allergy depending on the mechanism, underlying. IgE-mediated allergy can occur as:
- pollen food allergy syndrome / oral allergic syndrome, which is accompanied by itching and swelling of the oral mucosa. Usually, first occurs in adulthood and then depends on the season;
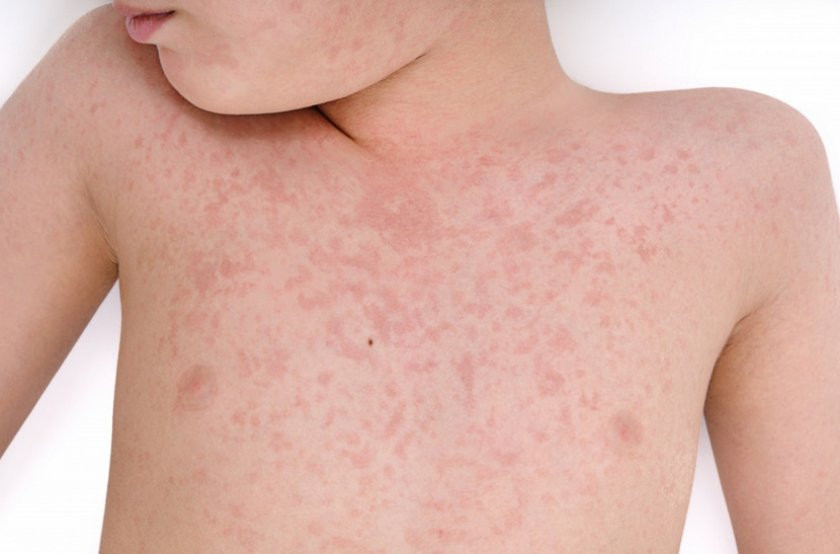
- urticaria is a reddening of the skin with the formation of flat-raised blisters, similar topics, what happens after contact with nettles, that itch;
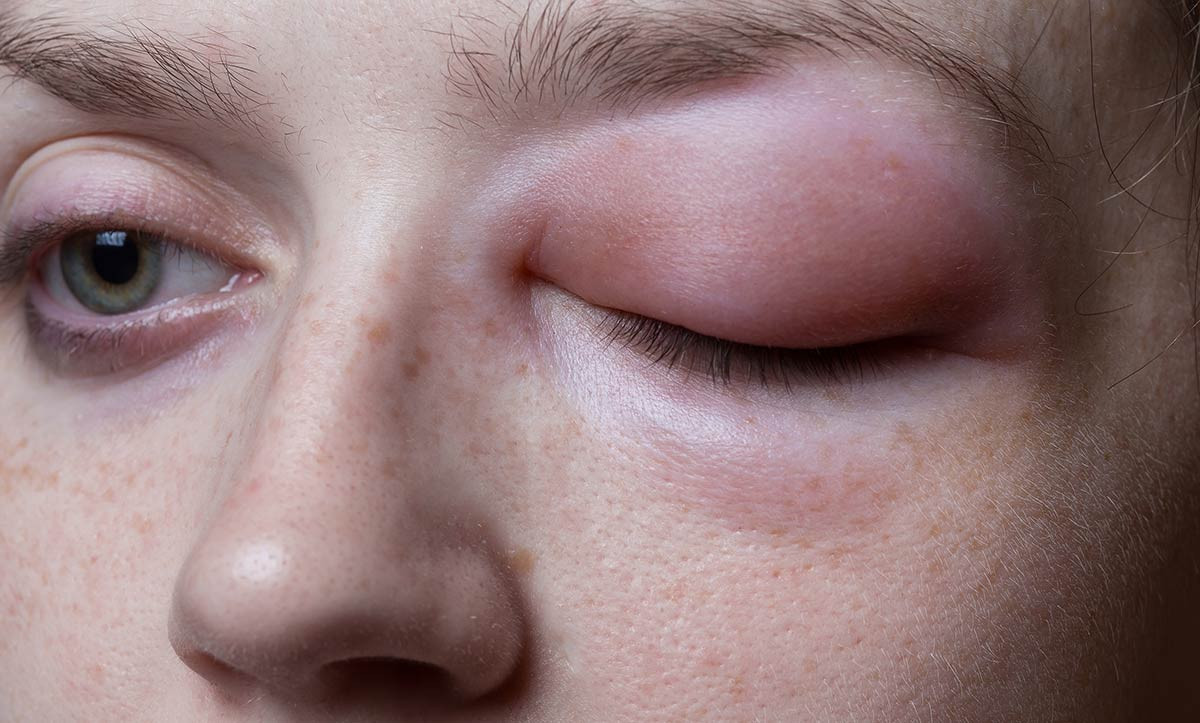
- angioedema is a puffiness of the face, sharp swelling of the lips, language, areas around the eyes (a photo 2). This condition is dangerous by the transition of edema to the upper respiratory tract, difficulty breathing and stopping it. Angioedema due to food allergies is often accompanied by urticaria;
- rhino-conjunctivitis - runny nose (rhinitis), lacrimation, which can be caused by inhalation of aerosolized food protein. As an isolated syndrome, it is rare and usually associated with other food allergy symptoms.;
- bronchial asthma similar to rhinoconjunctivitis, Rarely is an independent manifestation of a food allergy.;
- set of gastrointestinal symptoms (GI) quite diverse. It's a pain in the stomach, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea (diarrhea), less often constipation. They are always associated with the consumption of certain foods.. Food allergies should not be confused with lactose intolerance, a condition, associated with deficiency of the enzyme lactase in the intestine. It is also important to timely distinguish manifestations of food allergies from infectious gastroenteritis., usually accompanied by a rise in temperature;
- anaphylaxis - rapidly progressive, multisystem response, which is independent of the age of the patient. This is a dangerous manifestation of a food allergy in the form of sharp wheezing., shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, as well as a rapid drop in blood pressure, leading to dizziness and loss of consciousness (fainting);
- anaphylaxis, exercise-related condition, when manifestations of anaphylaxis occur only if after eating a food allergen, man puts himself under physical strain.
Non-IgE mediated food allergy often develops in infants. Therefore, food allergies in children are often accompanied by:
- food protein-induced proctitis/mucosal proctocolitis, bloody stool;
- food protein enterocolitis syndrome, which is characterized by vomiting, diarrhea, growth retardation, slackness, drop in blood pressure a few hours after eating.
With simultaneous exposure to IgE and cellular mechanisms, symptoms include:
- atopic eczema / dermatitis, which is a rash of any nature and localization. In 30-40% children, atopic eczema and dermatitis become moderate or severe;
- eosinophilic disorders of the gastrointestinal tract are accompanied by lesions of any part of the gastrointestinal tract from the esophagus (eosinophilic esophagitis) to the colon (eosinophilic colitis).
Talking about the frequency of symptoms, food allergy in infants in the classic version is accompanied by dermatitis or symptoms from the gastrointestinal tract. Food allergies in older children are very diverse in their manifestations.. Food allergies in children (not a baby) often associated with asthma and rhinoconjunctivitis. In adults, any of the above syndromes and their combinations may occur..
Patients with anaphylaxis, severe bronchial asthma, taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), exercising after meals, suffering from infectious diseases,have a higher risk of severe allergic reactions, than other patients.
Causes of food allergies
The onset of food allergies and the first symptoms usually occur in childhood. Person, suffering from other allergic diseases or having close relatives, who have allergies, are at high risk for food allergies. In violation of the response of the immune system to food entering the body, heredity plays a significant role.. Among the factors, contributing to food allergies, also called vitamin D deficiency.
You don't have to eat any food to develop a food allergy.. The reaction can develop by inhalation of its microparticles or contact with the skin. An allergic reaction does not occur when you first encounter an allergen.. Necessary sensitization - period, during which an increased sensitivity of the body to the food component is formed. There is a hypothesis, which suggests, that allergic food sensitization occurs through skin sensitization at low doses.
Food allergies can be triggered by absolutely any component of food., the most common of which: various types of nuts (mostly peanuts), pulse, Fish and seafood (shrimp, oysters, crustaceans), eggs, cereals (wheat, barley), soy, cow's milk, honey, chocolate, some fruits (most often citrus and kiwi) and vegetables. It is also believed, that alcohol consumption increases IgE levels and triggers allergic reactions. There is an opinion, that food additives and flavor enhancers can cause food allergies, such as monosodium glutamate, metabisulphite, tartrazine, however, the reaction to these substances is isolated into a separate group of diseases..
Diagnosis of food allergy
The first step is to collect patient data. (the time of onset and the nature of the symptoms play an important role, the presence of other allergopathology and information about the diseases of close relatives, in children, it is important to assess the indicators of their physical and mental development). To identify the allergen, allergic, may be carried out: skin tests or so-called prick tests. To do this, various allergens in liquid form are applied to the skin in the area of u200bu200bthe forearm or back.. Next, the skin at the site of application is pierced and the reaction of the body is analyzed. (photo.3). Another way is to determine specific serum IgE, Why is a blood test done?. samples, testing the body's response to an allergen, should be carried out in specialized departments due to the possible development of an anaphylactic reaction!
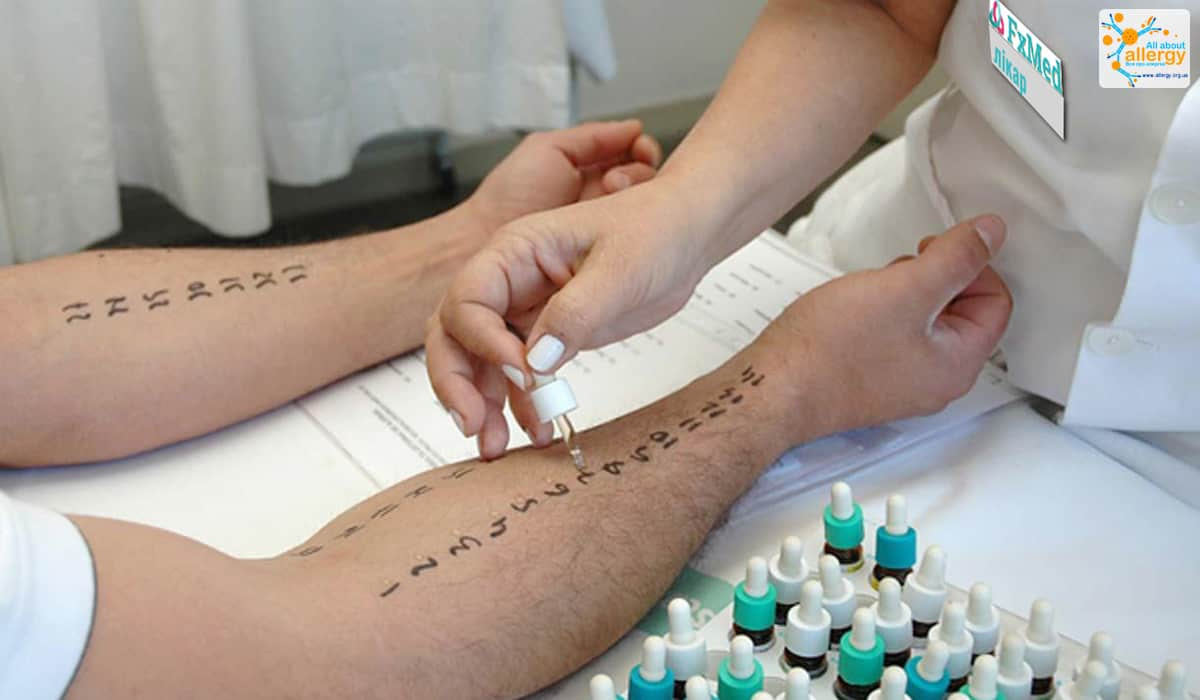
The Elimination Diet is Another Way to Find That Specific Component, which causes food allergies. In this case, a phased elimination of specific products is recommended, followed by clinical and laboratory assessment of the body's response throughout 2-4 weeks. If the result of the elimination diet is a significant improvement in symptoms, should be continued until, until a provocative test is performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Endoscopy with biopsy is used in case of gastrointestinal manifestations to rule out other gastroenteropathology, including celiac disease, and also to confirm eosinophilic esophagitis. As an auxiliary method, if necessary, an ultrasound of the abdominal organs is performed..
Complete blood count required: it can detect an increase in the number of eosinophils, however, this indicator is not specific.
Treatment of food allergy
Treatment includes short-term therapeutic measures to control acute reactions, as well as long-term strategies to minimize the risk of further reactions. The latter is achieved through diet, as well as teaching patients how to, to avoid contact with allergens.
Used to control symptoms:
- antihistamines (suprastin, loratadine, desloratadine, cetirizine, e.g.. tablets);
- mast cell stabilizers (cromolyn);
- glucocorticoids for the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis;
- adrenaline, which is administered during anaphylaxis to relieve a drop in blood pressure, life threatening.
The mainstay of treatment is an elimination diet., i.e. product rejection., containing an allergen. Patients, on a long-term elimination diet, should consult a nutritionist regularly, knowledgeable about food allergies, and children need to be monitored for growth.
There are some methods of desensitization, when the patient is asked to completely eliminate the allergen product for a while, and then use it in a small amount with a constant increase in the dose.
Food allergen-specific immunotherapy for primary food allergy is a promising approach to immunomodulatory treatment., but it is associated with the risk of adverse reactions, including anaphylaxis; therefore not currently recommended for routine clinical use. For patients with respiratory or other symptoms of allergy to inhalant allergens, which can also cause cross food allergies, specific immunotherapy is only recommended for the treatment of respiratory symptoms.
Prevention of food allergy
Few reliable ways to prevent food allergies are known.. However, the early introduction of peanuts (aged around 6 months, but not before 4 months), and, probably, egg white, with their subsequent regular use reduces the chances of food allergies in children, who are at high risk of developing allergies. Medications are not recommended to prevent food allergies..
