Pylonidal disease, Pylonidal pitch cyst: What's it, causes, symptoms, diagnostics, treatment, prevention
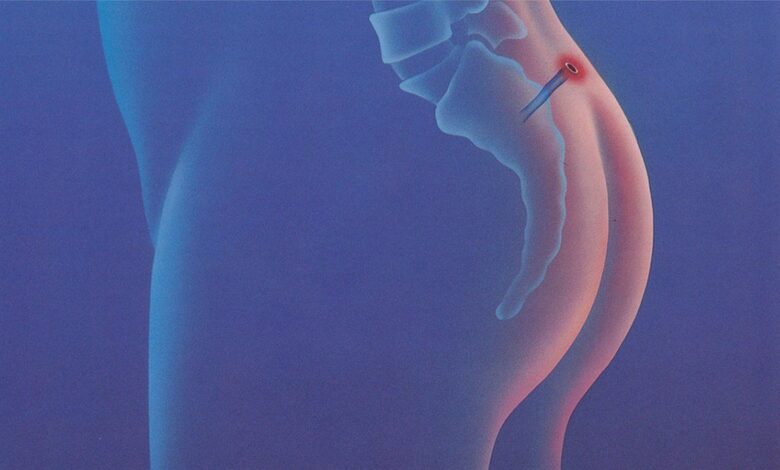
Pylonidal disease (Pilonidal sinus, Pylonidal cyst, Pylonidal abscess) - This is an inflammatory disease, follicle, which most often occurs in the area, Starting from the sacrum and ending with the anus. This is a benign condition, which is not related to cancer, However, in the absence of treatment, it can cause significant discomfort, Pain and even complications. In this article, we will examine in detail the reasons, symptoms, Methods of treatment and prevention of pylonidal disease.
What is pylonidal disease?
Pylonidal disease is a chronic inflammatory disease, which is developing in the area of the coccyx and the inter -enclosure fold. It can manifest itself in several forms:
- Pylonidal abscess - Acute state, in which the hair follicle is infected, which leads to the accumulation of pus in the subcutaneous fat.
- Pilonidal cyst - the formation of a cavity or hole in the skin, which occurs with a prolonged existence of the abscess.
- Pilonidal sinus - Formation of the subcutaneous channel (tract), which can delve into the hair follicle and cause chronic inflammation.
- Small hole or time in the skin, darling, which may be the only sign of the disease in the early stages.
Symptoms of pylonidal disease
Symptoms of pylonidal disease can vary depending on the stage and form of the disease. The most common features include:
- Purulent discharge from a small hole in the skin, which may have an unpleasant odor.
- Soreness in the sacrum, especially after physical activity or prolonged sitting.
- Redness, swelling and increasing skin temperature in the coccyx area.
- The formation of the abscess, which can be painful when touching.
- Rarely - an increase in body temperature, which indicates the spread of infection.
Sometimes the disease proceeds asymptomatic, And the only sign is a small hollow (The hole) In the inter -one -year fold. However, even in such cases, it is important to consult a doctor to prevent complications.
Causes of pylonidal disease
The exact cause of pylonidal disease has not been fully studied, However, it is considered, that the disease occurs due to the growth of hair in the skin in the area. This leads to inflammation, the formation of cysts and, in some cases, To the abscess. Factors, increasing the risk of the development of the disease, include:
- Obesity - overweight increases pressure on the coccyx and helps to grow hair.
- Injuries or irritation in the sacrum, eg, Due to friction of clothes or long-term seats.
- Excess hair growth, especially hard and curly, which more often grow into the skin.
- Prolonged sitting - Drivers are at risk, Office workers and people, leading sedentary lifestyle.
- Hereditary predisposition - in some people, the skin is more prone to the formation of cysts and inflammation.
Diagnosis of pylonidal disease
Diagnosis of pylonidal disease usually includes:
- Inspection of the doctor - The specialist assesses the condition of the skin in the coccyx area, The presence of abscesses, Cyst or sinus.
- Anamnesis - The doctor may ask about the symptoms, duration of the disease and risk factors.
- Ultrasonography (US) - in some cases it is used to assess the depth and prevalence of inflammation.
- Laboratory tests - if an infection is suspected, a blood test or a study of purulent secretions may be prescribed.
Treatment of pylonidal disease
Treatment of pylonidal disease depends on the stage and severity of the disease. The main methods include:
1. Conservative treatment
In the early stages, In the absence of an abscess, They may be assigned:
- Antibiotics - to combat infection.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs - to reduce pain and edema.
- Local funds - ointments or creams to accelerate healing.
2. Surgical treatment
In the presence of an abscess or chronic sinus, an operation may be required:
- Opening and drainage of the abscess - The procedure, in which the doctor removes pus and rinses the cavity.
- Removing the affected area (Exception) - surgical excision of a cyst or sinus.
- Skin plastic - used to close the wound after removing the cyst.
- Patchwork operations - Modern methods, which allow minimizing the risk of relapse.
3. Postoperative care
After the operation, it is important to follow the doctor's recommendations:
- Change the bandages regularly.
- Avoid prolonged sitting.
- Monitor the hygiene of the wound area.
Prevention of pylonidal disease
To prevent the development of pylonidal disease and its relapses, it is recommended:
- Follow hygiene - regularly wash the area of the inter -enclosure folds with soft soap and thoroughly dry.
- Remove hair - maintain a short hair length in this area with shaving, laser hair removal or depilation creams.
- Avoid injuries - use soft seats and avoid prolonged pressure on the coccyx area.
- Maintain a healthy weight - obesity is one of the main risk factors.
- To live an active lifestyle - regular physical activity improve blood circulation and reduce the risk of inflammation.
Complications of pylonidal disease
In the absence of treatment, pylonidal disease can lead to the following complications:
- Chronic abscesses - repeated clusters of pus, which require constant treatment.
- The formation of multiple sinuses - Subcutaneous channels, which can apply to neighboring fabrics.
- Sepsis - Rare, But a dangerous complication, in which the infection spreads throughout the body.
Conclusion
Pylonidal disease is unpleasant, but treating the disease. With timely seeking a doctor and compliance with the care recommendations, complications and relapses can be avoided. If you notice the symptoms, such as pain, redness or purulent discharge in the coccyx area, Do not postpone a visit to a specialist. Early diagnosis and treatment will help maintain your health and comfort.
Sources
Gunter RL, Johnson i, Steele SR. Anorectal: management of pilonidal disease. In: Cameron J, ed. Current Surgical Therapy. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:287-350.
Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Bloom NJ, et al. Surgical conditions of the anus and rectum. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Bloom NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 392.
Surrell ja. Pilonidal cyst and abscess: current management. In: Fowler GC, ed. Pfenninger and Fowler’s Procedures for Primary Care. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 31.
