Pyelonephritis – state and urinalysis
Pyelonephritis is an inflammation of the renal parenchyma, mainly affecting the interstitial tissue and involvement in the process of the renal pelvis and cups. He is one of the most common kidney disease, often becomes chronic, which is accompanied by hypertension and uremia ends.
The incidence of pyelonephritis, especially acute, in recent years has increased significantly, due to sharply increased virulence of microorganisms, and changes in their qualitative composition (Escherichia coli, Proteus, staphylococcus, Klebsiella, Streptococcus, and others.). Many patients found in the urine mixed flora.
Of great importance in the origin and development of pyelonephritis is a common condition of the body and the condition of his immune system.
The infection spreads mainly through hematogenous.
Urinogenous, t. it is. ascending, route of infection is possible in contact with it from the ureter when disturbed passage of urine. Lymphogenous route of infection is currently being questioned.
Regardless of the route of infection the clinical picture and morphology of urine sediment in acute pyelonephritis same.
Penetration of infection into the renal pelvis does not always cause pyelonephritis. The appearance of it depends on virulence and massive infection, reactivity of the organism and the presence of difficulty of outflow of urine. Chaschee all infectious process affects the right kidney. Apparently, this is due to the fact, that the right kidney is located below the left, whereby it is delayed urine. Pyelonephritis most often occurs in women, than men.
It is considered, pyelonephritis adults that is a continuation of uncured diseases in children.
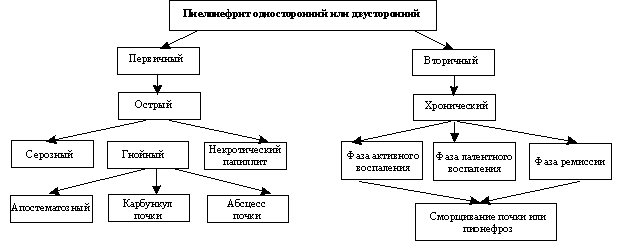
There are primary, uncomplicated, or hematogenous, pyelonephritis and secondary, complicated, or obstructive. Primary pyelonephritis develops in a healthy kidney, secondary - on the background of organic or functional disorders of the kidneys and urinary tract.
Primary and secondary pyelonephritis differ from each other not only in the pathogenesis, but also in the clinical picture of the disease, treatment and outcome.
There are several classifications of pyelonephritis. According to the classification A. I. Pytel, distinguish one- and bilateral pyelonephritis. By the nature of the flow it may be acute (serous, purulent), chronic and recurrent, and on the way of infection - hematogenous (downward) and urinogenous (rising). Depending on the characteristics of the course, due to the age of the patient, changes in its physiological state, the presence of a pathological process, isolated childhood pyelonephritis (including neonatal), Seniors, pregnant, diabetics, patients with spinal cord injury.
In clinical practice, the most frequently used for classification pyelonephritis H. A. Lopatkin and B. E. Rodoman.
Acute pyelonephritis
The disease can occur at any age, but often suffer from two- three year olds, due to reduced resistance to infection of children and the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the renal pelvis and ureter in children. Pyelonephritis in most cases occur in girls, especially over the age of two years, because of their wider and shorter urethra.
Often acute pyelonephritis occurs during pregnancy, what, obviously, due to the stagnation of urine in the renal pelvis, arising in the compression of the ureter enlarged uterus.
In acute pyelonephritis kidney usually somewhat increased, renal pelvis stretched, its mucosa hyperemic, swell, loosening, sometimes ulcerated and covered with purulent discharge, somewhere visible hemorrhage. Histology revealed focal necrosis and infiltration of the wall of the renal pelvis leukocytes. Tubules in the nephrons contain pus; parenchymal kidney formed multiple abscesses. Very severe pyelonephritis is necrosis of renal papillae.
Acute pyelonephritis can be one- and bilateral. In a typical course is manifested symptoms rapidly developing infectious disease (acute onset of high fever, chills, pouring sweat, pain in the lumbar region), and it is usually diagnosed in the clinic as acute pyelitis. Perhaps sluggish for pyelonephritis without clinical manifestations (often in children and pregnant women), when it is revealed only after repeated urine.
Azotemia and uremia are rare. They can occur in pyelonephritis with papillary necrosis (papillary pyelonephritis) most often in patients with diabetes. This severe form of the disease, where necrotic mass and blood clots sometimes clog ureter, causing paroxysmal pain (how much), as in calculous pyelonephritis.
Increases the amount of urine (polyuria), especially in the bilateral process, due to violation of reabsorption in the distal tubules of nephrons. Inflammatory edema and cellular infiltration between the tubules with pyelonephritis lead to compression of the epithelium, lining the tubules, primarily in their distal, and damage to blood vessels. In this regard, especially in pyelonephritis decreased reabsorption of water, which causes a decrease in relative density of urine (gipostenuriю).
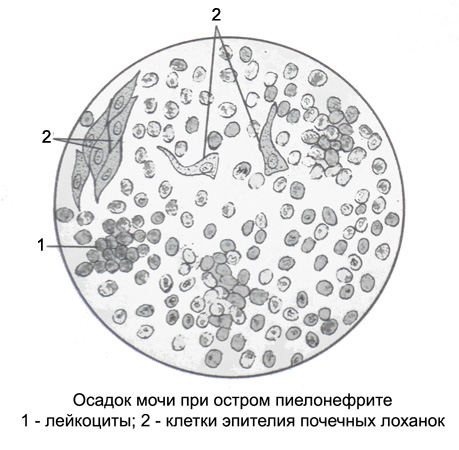
The urine in pyelonephritis pale-colored, with a low relative density and acidic, caused by E. coli. Gross hematuria for this disease is not typical. If a lot of pus in the urine, it is cloudy, and the precipitate purulent. The protein content is typically less than 1 g / l.
Microscopic examination of the drug leukocytes cover the entire field of view and are located separately or, it occurs more often, close Groups (purulent lumps) different sizes.
When a unilateral lesion at the height of the body temperature elevation pus in the urine can not detect, and then reduce the temperature appears Piura. It speaks, that the defeat of the renal pelvis into the process involved and part of the ureter prilohanochnaya. When the attenuation of inflammation and swelling subsides there is pus in the urine (better patient, and the rate of urine worse).
In bilateral kidney disease there may be a temporary anuria. Almost always celebrated microhematuria. The draft identifies mostly leached erythrocytes.
At the beginning of the disease in the urine many epithelial cells of the renal pelvis, and in the midst of disease, when the pelvis covered with pus, epithelial cells isolated, sometimes in the stage of fatty degeneration and rounded. For pyelonephritis is characterized by the emergence of renal epithelial cells in the urine, hyaline and granular cylinders, a small amount of uric acid salts. With prolonged process may develop severe renal failure with oliguria and even azotemia.
Chronic pyelonephritis
Pathogens and ways of infection are the same, as with acute pyelonephritis.
The morphological changes in chronic pyelonephritis It depends on the duration of the process, the degree of inflammation and sclerosis of renal tissue. Chronic pyelonephritis is characterized by the spread of the pathological process of the renal pelvis and medulla in the cortex, that observed for any infection in the way of introduction of a kidney. In addition to the preserved areas or maloizmenennymi renal parenchymal area marked inflammatory infiltrates and festering. With long flowing pyelonephritis areas of purulent inflammation in the kidneys alternating with areas of sclerosis, and between islands may be completely unchanged parenchyma. Therefore, even in advanced pyelonephritis selection indigo when cystochromoscopy normal both in time, and intensity.
In bilateral pyelonephritis the spread of kidney interstitial tissue on is uneven and affected primarily tubules of nephrons. Then there are productive endarteriit, hyperplasia of the tunica media of vessels and arteriolar sclerosis, which is one of the reasons for the further atrophy of the kidney. Only in the final stage of the glomeruli are affected until the development hyalinosis. The slow growth of the morphological changes of the disease explains the peculiar - long-lasting diuresis with iso, and then gipostenuriey (distal tubular syndrome) - And relatively more favorable outlook for life. The more the process progresses, the more pronounced fibrosis and vascular sclerosis, leading to wrinkling of the renal pelvis and reduce kidney (pielonefroticheskaya contracted kidney).
The disease is usually detected after several years of an acute inflammation in the urinary tract - cystitis or pielita. Basically pyelonephritis discovered by chance in the investigation of urine or blood pressure, or when the signs of kidney failure.
In the period of acute pyelonephritis increases the amount of urine. Its relative density is 1,005-1,012, the color of pale, acid reaction. The amount of protein and the haze may be different depending on the number of white blood cells. Usually during the relapse protein content increases, and the urine becomes cloudy. Often voluminous precipitate, purulent.
Microscopic examination of drugs are determined leukocytes, located separately and as a festering lumps, covering the entire field of view of the microscope. Number pale leukocytes and leukocyte movement pellets may reach 80-100 %. Often identified eosinophilic granulocytes. There may be microhematuria, at the same time found isolated leached erythrocytes. There are transitional epithelium cells of the renal pelvis, scraps of colored fibrin, bacteria.
The latent period of the disease scanty urine sediment, leukocyte count normal or slightly elevated. There eosinophilic granulocytes, isolated leached erythrocytes, kidney epithelial cells, individual cylinders. Occasionally there are cells of transitional epithelium of the renal pelvis, often in a state of fatty degeneration and vacuolization. In this period of the disease is very difficult diagnosis, therefore it is advisable to determine the number of leukocytes, and erythrocyte cylinders in the urine by Kakovskogo-Addis (in daily urine), Ambyurje (in a urine sample, vыdelivsheysya for 3 h, based on the minute volume of urine), Nechiporenko (in 1 ml of urine).
It is also used rapid method for determining latent leukocyturia (Method Gedholta). The basis of his supposed change of color of white blood cells in the peroxidase reaction. In the study of this method 10 ml of fresh urine is passed through a filter paper, whereupon it deposited three drops of dye. If in 1 l urine contained more 10 leukocytes, is the site of application of the dye appears dark blue spot. The sample is considered negative for the appearance of red spots, and questionable, When the blue spot. This method is simple and reliable enough. The answer can be obtained in a few minutes. Especially valuable is the express method when applied during routine inspections of children in various child care centers (manger, kindergartens, schools).
When unilateral pyelonephritis urine obtained from the renal pelvis and the bladder, count the number of white blood cells, and compare the results. In the differential diagnosis of chronic glomerulonephritis should be remembered, that a large number of white blood cells and red blood cells their predominance over the characteristic of chronic pyelonephritis, chronic glomerulonephritis and renal arteriosclerosis proportion of leukocytes and erythrocytes changes in the opposite direction.
An important diagnostic feature of chronic pyelonephritis is bacteriuria, combined with increased leukocyturia. The presence of bacteria in an amount, exceeding 100000 in 1 ml of urine, It requires determining their specificity and sensitivity to antibiotics and other chemotherapeutic agents.
To determine the degree of bacteriuria in addition to bacteriological methods used colorimetric, among which the most widely test using TTH (trifeniltetrazoliyhlorida). This quantitative test is positive for bacteriuria 85 % cases. He reveals the latent pyelonephritis and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.
Equally informative is nitrite test Grissa, based on determination of nitrite in urine by adding sulfanilic acid and anaftilamina. In the presence of nitrite in a few seconds after the addition of reagents urine stained red. In normal urine does not contain nitrites. A positive nitrite test is observed in 80 % severe cases of bacteriuria and indicates the presence of 1 ml urine least 100000 mikrobnыh wire.
Both tests appropriate to apply on an outpatient basis, where it is not always possible to count the bacteria culture and determination of their resistance.
To determine the degree of bacteriuria recently applied a number of rapid methods, among which deserves special attention dip urine plates, coated with a special nutrient medium. On one side of the plate coated with agar, which grow all kinds of bacteria, on the other - modified agar, which grow only gram-negative bacteria and enterococci. Laminar methods require 12-16 hours of incubation. They are easy technically and in patients with a true bacteriuria yield positive results 95 % cases.
Of great importance in the diagnosis of chronic pyelonephritis is the establishment of the degree of functional ability of the kidneys. Determination of purification of each kidney separately, for example endogenous creatinine, It allows you to set, one- or bilateral disease, and identify back-up capabilities of each kidney. In chronic pyelonephritis violation of renal blood flow and a decrease in glomerular filtration occurs much later, than function disorder tubules of nephrons, in particular their distal parts.
Because of tubular dysfunction in patients with chronic pyelonephritis occur loss of sodium and potassium, hyperphosphatemia and hypocalcemia.
For the diagnosis of chronic pyelonephritis used radionuclide and radiographic methods of investigation, as well as renal biopsy.
