Peripheral vascular disease
Description of peripheral vascular disease
Peripheral vascular disease (LPP) – This is a general term for any disease of the blood vessels, not related to the heart or brain. Arterial the form is usually caused by fatty deposits (ateromami) in the arteries of the legs. Arteries deliver oxygenated blood to the body's cells, and the restriction of blood flow can lead to diseases of the internal organs.
This is a potentially dangerous disease, that requires early treatment. When early treatment outcome favorable. If you suspect the presence of peripheral vascular disease should consult a doctor.
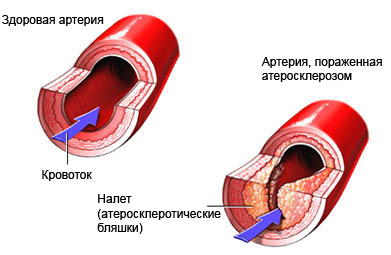
Causes of peripheral vascular disease
LPP is usually caused by a gradual build-up of deposits in the arteries (atherosclerosis). Other causes may include blood clots (blood clots) or embolism, congenital heart disease, and inflammation of the blood vessels (vasculitis).
LPP may be hereditary. Most often, the LPP suffer from overweight people, obesity, high blood pressure, diabetes, or high cholesterol. Unhealthy lifestyle (smoking, eating foods with high fat diet) quite often lead to LPP.
Risk factors
Factors, that increase the likelihood of peripheral vascular disease:
- Diabetes;
- Cigarette smoking;
- High blood pressure;
- Coronary artery disease;
- Stroke;
- High cholesterol;
- Age: senior 50 years;
- High levels of homocysteine in the blood;
- Paul: male;
- Family history of peripheral vascular disease.
Symptoms of peripheral vascular disease
Symptoms of PSA are associated with organ or body part, devoid of corresponding circulation and include:
- Claudication, pain, fatigue, the severity of the, weakness, cramping or tingling in your leg (legs) under load, which take place during the rest (with mild disease);
- Numbness and pain in the leg or legs in the absence of physical load in more severe disease;
- Cold hands, legs, or feet;
- Hair loss on legs;
- Pale or blue legs;
- Weak or absent pulse in the legs;
- Wounds, ulcers, or infection of feet and legs, slow healing;
- Erectile dysfunction;
- Edema of the lower limbs;
- Atorofija muscles.
Diagnosis of peripheral vascular disease
The doctor asks about the symptoms and medical history, performs a physical exam. Tests may include the following:
- Check the pulse in the arteries of the legs;
- Listening to the arteries using stethoscope;
- Check the pressure at various points in the feet and its comparison with normal blood pressure in the hands;
- Blood lipids, homocysteine, blood sugar, hemoglobin HbA1c, oxidative stress marker (eg, 8-ISO-PGF 2 Alfa);
- Test on a treadmill;
- Ultrasound and Doppler analysis of arteries, especially the carotid arteries in the neck, that supply blood to the brain;
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) – test, that records heart activity by measuring electrical current, passing through the heart muscle;
- Angiography of the arteries in the legs – x-rays of blood vessels, performed after the introduction of contrast dye;
- MRT – test, which uses magnetic waves, to make pictures of blood vessels.
Treatment of peripheral vascular disease
Early treatment can slow or halt the progression of the disease. Treatment options include the following:
Lifestyle Changes
- Smoking cessation;
- Treatment of diabetes;
- Control blood pressure;
- Increased physical activity (eg, athletics);
- Weight reduction, if you are overweight;
- Low consumption of saturated fat, low cholesterol diet;
- Chiropody (It is important for people with diabetes);
- Wearing comfortable shoes;
- Proper care of foot injuries.
Medication
- Reception antitrombocitarnyh funds, such as aspirin and Clopidogrel;
- Supplementation, to relieve pain in legs (eg, pentoxifylline);
- Preparations for hypercholesterolemia (cilostazol, simvastatin);
- Taking medications for cholesterol-lowering drugs (Statins);
- Medication, widening the artery.
Invasive procedures
- Ballonnaя angioplasty – a balloon is inserted into the artery and inflates, to stretch it;
- Stent implant – tubular mesh is placed into the artery, sutured and stays in place, preventing the narrowing of arteries;
- Laser therapy;
- Atherectomy.
Surgery
Operation, to widen the narrowed artery is performed in severe cases.
- Endartyerektomiya – removed the inner part of the artery, that impressed with atherosclerotic plaques;
- Bypass – Vienna from another part of the body or synthetic graft replaces the damaged vessel.
Prevention of peripheral vascular disease
To reduce the likelihood of ZPA, You must live a healthy lifestyle and perform the procedures, prescribed by a doctor.
