Cadmium poisoning: treatment of disease, symptoms, diagnostics, prevention
Description cadmium poisoning
Cadmium poisoning occurs, when a person breathes in high dose of cadmium from the air, or eating food or drinking water containing high levels of cadmium. Cadmium is a metal, but, usually, present in the environment in conjunction with other elements (oxygen, chlorine, sulfur). Short-term or long-term exposure to cadmium can cause serious health problems. If you suspect, that have been exposed to cadmium, consult a physician immediately.
Causes of cadmium poisoning
Most of the compounds of cadmium is a byproduct of such metals, zinc, lead and copper. It is also found in a variety of consumer products:
- Batteries;
- Pigments;
- Metal coatings;
- Plastics;
- Some metal alloys;
- Fertilizers;
- Cigarettes.
When cadmium enters the air, it binds to it with small particles. Falling to the ground or water as rain or snow, it can infect fish, plants and animals. Improper disposal of waste can lead to leakage of cadmium in water and soil.
Contact with skin cadmium causes health problems, but serious problems may result:
- Inhalation, which contains a high concentration of cadmium;
- Food intake, containing relatively high levels of Cd – clams, liver, kidneys. Also, high levels of cadmium often found in potatoes and vegetables;
- Water Consumption, contaminated by cadmium;
- Inhalation of tobacco smoke. Smoking doubles the average daily dose of cadmium.
Risk Factors cadmium poisoning
Factors, which increase the likelihood of cadmium poisoning:
- Smoking;
- Living near hazardous waste sites or near the industrial emissions of cadmium in the air;
- Work in metallurgy and / or refinery;
- Work at the plant, which produces products containing cadmium (eg, batteries, cover, Plastics, Dyes);
- Nutritional deficiency – Calcium, gland, protein and / or zinc.
Symptoms of poisoning by cadmium
When consuming food or drinking water, contaminated by cadmium, may occur:
- Vomiting / nausea;
- Zheludochnыe colic;
- Diarrhea;
- Kidney damage;
- Brittle bones;
- Death.
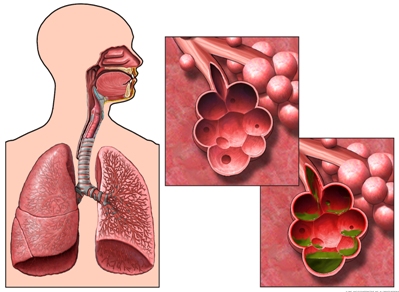
Inhalation of cadmium can cause:
- Damage to the lungs (chest pain or shortness of breath);
- Kidney disease;
- Brittle bones;
- Death.
There is no convincing evidence, that cadmium can cause lung cancer, but as a precaution The US Environmental Protection Agency classifies cadmium as a probable human carcinogen.
Diagnosis of cadmium poisoning
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history, and perform a physical examination.
Tests may include the following:
- Blood tests;
- Urine;
- Analysis of hair and nails;
- Neutron activation analysis – a test to measure the level of cadmium in the liver and kidneys.
Treatment of cadmium poisoning
Also avoid contact with cadmium in the body, there are no other effective treatments for cadmium poisoning. Treatment aimed at, to reduce and relieve the symptoms of poisoning. When bone fragility advised to take vitamin D.
Prevention of cadmium poisoning
To reduce the likelihood of cadmium poisoning:
- Do not smoke. Smoking is the greatest source of exposure to cadmium in the body for most people;
- Identify potential sources of cadmium in and around the house, at work can help prevent poisoning;
- Eat a balanced diet, which provides a sufficient amount of calcium, gland, protein and zinc;
- Pravilyno food (out of reach of children) cadmium-containing items (eg, fungiцidы, Batteries, dye fabrics, glaze for ceramic / glass, fertilizers);
- Keep nickel-cadmium batteries out of the reach of children;
- Read the instructions for the safe use of cadmium-containing fungicides and fertilizers in the garden or in the garden;
- If you have a water well, check for the presence of cadmium water;
- If cadmium is present in well water, is recommended for drinking and cooking, use bottled water or install a water filter, which removes cadmium and other metals from drinking water;
- Do not let small children play around hazardous waste sites.
