Edema, gingivitis: what is this, causes, symptoms, diagnostics, treatment, prevention
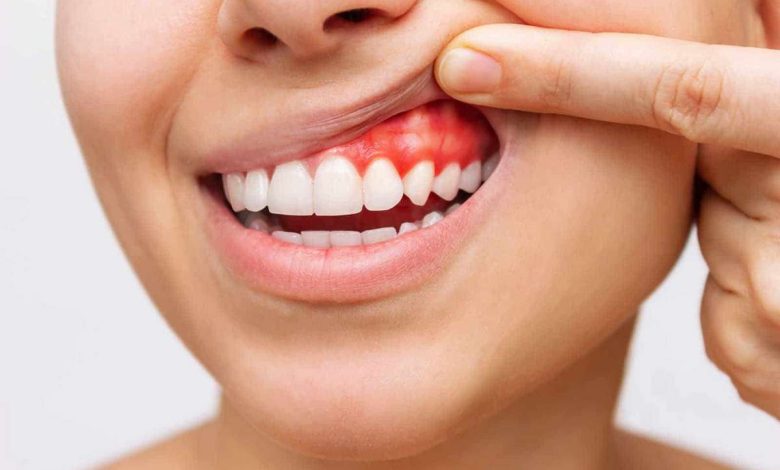
Gums – swell; Swollen gums; Gingival swelling; Bulbous gums; Inflamed gums; Enlarged gums
gum swelling, also known as gum disease, is a common disease, affecting soft tissues, surrounding teeth. Gums play a critical role in maintaining teeth and protecting them from bacteria and other harmful substances.. When the gums become inflamed, they can cause a range of symptoms, including pain, bleeding and discomfort. In this article, we will look at the reasons, symptoms and treatment options for swollen gums.
Causes of swollen gums
Swollen gums can be caused by various factors., including poor oral hygiene, hormonal changes, gingivitis and periodontitis. Other factors, which can contribute to gum swelling, include tobacco use, hormonal imbalance, certain medications and systemic diseases, such as diabetes.
- Poor oral hygiene. Poor oral hygiene, including neglecting regular brushing and flossing, can lead to plaque buildup on teeth and gums. Over time, this plaque can turn into tartar., irritating and inflamed gums.
- Hormonal changes. Hormonal changes, eg, during pregnancy or menopause, may increase the risk of gum swelling. During pregnancy, elevated hormone levels can cause, that the gums will become more sensitive and prone to inflammation.
- Gingivitis: Gingivitis is a mild form of gum disease., which can cause inflammation, redness and swelling of the gums. This condition is caused by a buildup of plaque on the teeth and gums., which can irritate the gums and cause inflammation.
- Periodontitis: Periodontitis is a more severe form of gum disease., in which the gums separate from the teeth, forming pockets, which may become infected. This can lead to swelling of the gums., pain and bleeding.
Symptoms of swollen gums
Symptoms of swollen gums can vary depending on the underlying cause.. Common symptoms of gum swelling include redness, inflammation and soreness of the gums. Other symptoms may include bleeding when brushing or flossing, pain when biting or chewing and bad breath.
When to contact a healthcare professional
If you experience any symptoms of gum swelling, it is important to see a doctor. In some cases, swelling of the gums may be a sign of a more serious underlying condition., such as periodontitis. Your doctor can help determine the cause of your symptoms and recommend appropriate treatment..
Questions, which the doctor can ask for swollen gums
When you visit your doctor for swollen gums, he may ask you some questions, to determine the root cause of your symptoms. Some of these questions may include:
- When did you first start experiencing symptoms?
- Do you have a history of gum disease or other dental problems?
- Have you had any hormonal changes recently, such as pregnancy or menopause?
- You use tobacco products?
- Are you taking any medication, that may contribute to your symptoms?
Diagnosis of swollen right
Diagnosis of swollen gums includes a physical examination of the gums and teeth. Your doctor may also take x-rays or use other imaging tests., to get a better view of the affected area. In some cases, the doctor may take a sample of affected tissue to send to a laboratory for analysis..
Treatment of swollen gums
Treatment for swollen gums depends on the underlying cause. Some common treatments include:
- Improving oral hygiene: regular brushing and flossing, and the use of an antiseptic mouthwash can help reduce plaque formation and prevent further gum disease.
- Antibiotics. If gum swelling is caused by an infection, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics, to get rid of the infection.
- Scaling and polishing the roots: in more severe cases of gum disease, a doctor may recommend a deep cleaning procedure, known as scaling and root polishing. This procedure involves removing plaque and calculus from teeth and gums., as well as smoothing the roots of the teeth, to prevent the formation of plaque in the future.
- Medicines: if hormonal changes contribute to gum swelling, your doctor may prescribe medication, helping regulate hormone levels.
- Surgery: in severe cases of gum disease, surgery may be required to remove damaged tissue and restore the gums.
Home treatment for swollen gums
In addition to therapies, recommended by your doctor, there are several home remedies, which can help reduce swelling and discomfort in the gums. Some of these tools include:
- Salt water rinse: rinsing your mouth with salt water several times a day can help reduce swelling and relieve pain.
- Tea tree oil: tea tree oil has antiseptic properties, which can help reduce inflammation and kill harmful bacteria in the mouth. To use, dilute a few drops of tea tree oil in water and rinse your mouth with the mixture..
- Hydrogen peroxide. Hydrogen peroxide is a natural antiseptic, which can help reduce inflammation and kill bacteria in the mouth. To use, dilute hydrogen peroxide in water and rinse your mouth with the mixture..
Prevention of swollen gums
To prevent gum swelling and other dental problems, it is important to practice oral hygiene. This includes brushing your teeth at least twice a day, daily flossing and use of antiseptic mouthwashes. Besides, it is important to visit the dentist regularly for routine cleanings and check-ups, and avoid tobacco use and excessive alcohol consumption.
Conclusion
Swollen gums can be painful and uncomfortable., but with the right treatment and care, it can be effectively dealt with.
If you experience any symptoms of gum swelling, it is important to consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
By following the tips above and practicing good oral hygiene, you can prevent gum swelling and keep gums healthy.
Used sources and literature
Ball JW, Dains I, Flynn YES, Solomon BS, Stewart RW. Ears, nose, and throat. In: Ball JW, Dains I, Flynn YES, Solomon BS, Stewart RW, eds. Seidel’s Guide to Physical Examination. 10th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2023:chap 13.
Chow AW. Infections of the oral cavity, neck, and head. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 64.
Order RA. Oral medicine. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen’s Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 56.
