Edema, swelling: what is this, causes, symptoms, diagnostics, treatment, prevention
Swelling; Edema; Anasarca
Edema is inflammation of the subcutaneous tissue, accompanied by an increase in the volume of fluid in the cells. Edema can occur for various reasons, including as a result of an allergic reaction.
Extra fluid can lead to rapid weight gain over a short period of time. (from days to weeks).
Edema can occur throughout the body (generalized) or only one part of the body (local).
Causes of edema
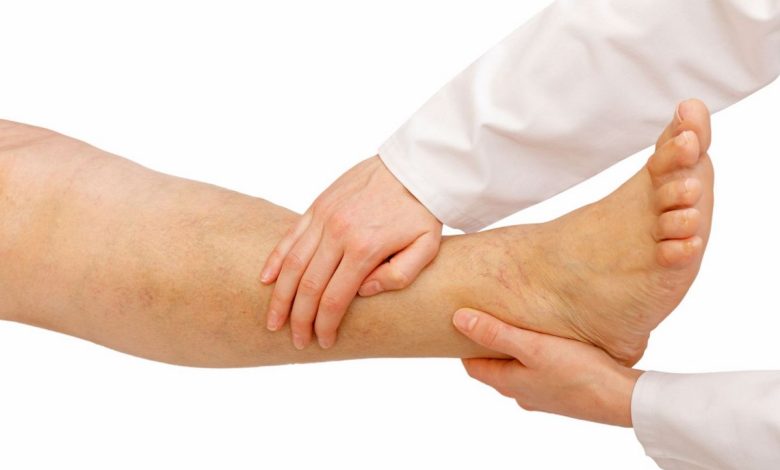
Slight swelling (edema) tibia often seen during warm summer months, especially if a person stands or walks a lot.
General edema or massive edema (also called anasarca) is a common symptom of severely ill people. Although slight swelling may be difficult to detect, large swelling is very noticeable.
Edema may be punctate or non-punctate.
- Pinpoint edema leaves an indentation in the skin after, how do you press this area with your finger for about 5 seconds. The dent will slowly fill back up.
- non-point (nonfocal)edema does not leave such a dent when pressed on a swollen place.
Causes of edema
Swelling can be caused by any of the following factors:
- Acute glomerulonephritis (kidney disease)
- Burns , including solar
- Chronic kidney disease
- Heart failure
- Liver failure due to cirrhosis
- Nephrotic syndrome (kidney disease)
- Poor diet
- Pregnancy
- Thyroid disease
- Too little albumin in the blood (hypoalbuminemia)
- Excess salt intake
- Use of certain medications, such as corticosteroids or medications, used to treat heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes.
Home care for edema
Follow your doctor's advice. If you have long-term edema, ask your doctor about options to prevent skin damage, such as:
- flotation ring
- Sheep wool pillow
- Reduced pressure mattress
Continue with your daily activities. When lying down, keep your arms and legs above heart level if possible., so that the liquid can escape from them. Do not do that, if you are short of breath . Instead, see your doctor.
When to See a Doctor for Edema
If you notice any unexplained swelling, contact your doctor.
What to Expect When Visiting a Doctor for Edema
Except in emergencies (heart failure or pulmonary edema), the doctor will review your medical history and conduct a physical examination . You may be asked about symptoms of edema. Questions may include, when did the swelling start, whether it has spread throughout the body or just in one area, what did you do, to reduce swelling.
Tests, which can be fulfilled, include:
- Albumin blood test
- The level of electrolytes in the blood
- Echocardiography
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Kidney Function Tests
- Liver function tests
- Analysis of urine
- Roentgen
Edema treatment
Treatment for edema depends on its cause.. If the swelling is the result of an allergic reaction, then you need to contact an allergist for the correct diagnosis and treatment. In other cases, drugs or treatment of individual symptoms of edema may be required.. Always follow your doctor's advice.
Treatment may include avoiding salt or taking diuretics (diuretics). Fluid intake and excretion should be monitored and weighed daily.
Avoid alcohol, if you have liver disease.
Used literature and sources
McGee S. Edema and deep vein thrombosis. In: McGee S, ed. Evidence-Based Physical Diagnosis. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 56.
Swartz MH. The peripheral vascular system. In: Swartz MH, ed. Textbook of Physical Diagnosis: History and Examination. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 15.
