Acute leukemia promyelotsytarnыy
It stands out as an independent form acute leukemia in 1957 g.
Characterized by a particular morphology blasts, containing abundant large grain, severe hemorrhagic syndrome and speed currents. The name "promyelocytic" got leukemia because of the resemblance of tumor cells from promyelocytic: The presence of large, abundant grain, filling the cytoplasm and the nucleus is located at.
However, these cells are characterized by a blast of nuclear structure and all other morphological and histochemical characteristics differ from promyelocytic. In children, the leukemia is very rare, In adults - 3,8 % cases.
The clinical picture of acute promielocitarnogo leukemia
Clinical picture of acute promyelocytic leukemia is to express hemorrhagic syndrome, which is often the first sign of disease.
Hemorrhages occur at the site of injury; a number of patients on the background of a moderate (higher 20 T in 1 l), and in some cases, severe thrombocytopenia (higher 100 T in 1 l) marked uterine, nosebleeds, bruising.
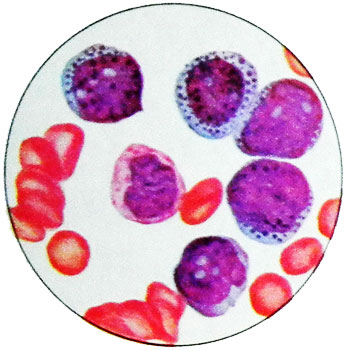
Picture of blood in acute promyelocytic leukemia
The blood picture is characterized by a pronounced polymorphism blasts.
Many cells have cytoplasmic outgrowths, resembling pseudopodia. The cytoplasm is colored in different shades of blue (by Mayu-Grunwald or Romanovsky-Giemsa). Usually it is densely filled with rather large polymorphic violet-brown grit, and large nuclei on the surface. In some cells there are two types of granules: larger - dark purple and smaller - purple and pink.
In the cytoplasm of leukemic cells are often detected calf Auer. In addition Auer cells in this form of leukemia are two types of eosinophilic granuloma: round, homogeneous and with a few figures mielonovymi.
Depending upon the morphological characteristics of leukemic cells isolated Two variants of acute promyelocytic leukemia:
- typical - makrogranulyarny;
- mikrogranulyarny, which occurs in about 20 % of all cases of this form of leukemia.
In a typical, makrohranulyarnom, form the bulk of the leukemia cells of the constituent elements, having a large grain size, napominaющuю in magnitude zernistostь bazofilьnыh granulocytes and basophils tkanevыh, and only a small percentage - elements with fine, Sometimes dust azurophilic granulation.
At mykrohranulyarnom embodiment of the second type cells predominate, fine-grained. They differ, Besides, small size, irregular contours, ugliness cores, Part two- or mnogodolchatyh. When mikrogranulyarnom variant often, than when makrogranulyarnom, observed leukocytosis and out of leukemic cells in blood.
Cytochemical characterization of cells of acute promyelocytic leukemia
Cytochemical characterization makrogranulyarnyh and mikrogranulyarnyh cells of acute promyelocytic leukemia matches: sharply positive reaction to the peroxidase, lipids, High activity hloratsetatesterazy, low, and do not suppress sodium fluoride reaction to α-naftilesterazu. Individual cells with fine azurophilic granulation in a typical form of acute promyelocytic leukemia give the most vivid reaction to acidic sulfated glycosaminoglycans (mukopolisaxaridы).
Mikrogranulyarny variant of acute promyelocytic leukemia has to be differentiated from one myelomonoblastic leukemia, characterized by similar cell morphology and the same, as the promyelocytic leukemia, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome. Differential diagnostic features are cytochemical characteristics of cells: sharply positive reaction to α-naftilesterazu, suppressed sodium fluoride, positive in myelomonocytic cells unlike promyelocytic.
A distinctive feature of abnormal cells in acute promyelocytic leukemia is a nuclear polymorphism. At the same time there are rounded, bean-shaped, bi-lobed (past rarely seen in other forms of leukemia) nuclei with different structures - from soft mesh blast to a relatively dense (almost like a lymphocyte). Often identified nucleoli (from 1 to 3 in various cells). The size of the nuclei relative to the whole cells are widely varied in different cells of the patient.
Diagnosis of acute promyelocytic leukemia already available on the basis of the usual analysis of the morphology of leukemic cells. So, granule cells contain abnormal acidic sulfated mucopolysaccharides. This test is specific for acute promyelocytic leukemia. However, sulfated acidic mucopolysaccharides are not new substrate, peculiar only leukemic cells, in small quantities defined in myeloblasts and promyelocytes normal bone marrow. Specific cell cytogenetics.
Onset of the disease is often characterized by normal or slightly reduced red blood parameters. The content of platelets in the overwhelming majority of significantly reduced. The number of leukocytes, usually, also significantly reduces (less 1 T in 1l).
Important role in the development and hemorrhages, and toxicosis belongs leukemia cells, and comprising on the surface, and in cytoplasmic granules excess thromboplastin. The collapse of these cells, thromboplastin and output of lysosomal proteases provoke disseminated intravascular coagulation. On the role of leukemia cells says a sharp change in the pattern of the disease after the start of effective cytostatic therapy: sometimes on the second day reduced body temperature and stops bleeding, although no hematopoietic recovery yet, and realized only cytostatic effect.
