Acute leukemia monoblastnыy
The clinical picture of acute leukemia monoblastic
The clinical picture of this form of leukemia is not very different from that in acute myeloid leukemia, although most, than with myeloid leukemia, expressed intoxication, hyperthermia, actually caused leukemia cells, in particular through the development of endogenous pyrogen.
Several more frequently observed complications, associated with neutropenia, among them - mostly necrotic lesions of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and pharynx. They are to some extent contributes to the characteristic of this form of acute leukemia leukaemic infiltration of the gums, leading to their hypertrophy. Gingivitis can be caused and most neutropenia.
When monoblastic leukemia acute process is localized mainly in the bone marrow, but individual groups of lymph nodes and spleen may be increased. Often growing infiltration of the tonsils, right, and in the later stages of progression may cause infiltrations in all internal organs and leykemidov - in the skin, on serous membranes.
Picture of blood in acute leukemia acute monoblastic
Monoblastic leukemia represented by large blast cells, Have bean delicate core of the structure with a shallow impression and multiple nucleoli. The cytoplasm of these cells already, than monocyte, but wider, than myeloblasts, its different shades of color - from gray-blue to intense blue, It often contains dust-like lean azurofil- tion graininess.
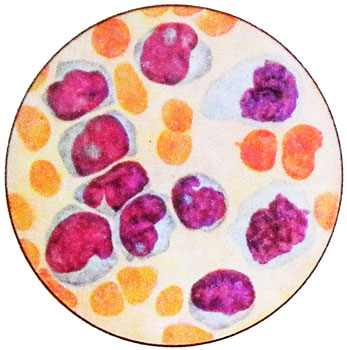
Sometimes such cells are found only in bone marrow, and are more mature blood elements, resembling monocytes and sometimes almost no distinguishable from them. There may be cases with neutrophilia and rejuvenation of the cells to myelocytes. The platelet count usually decreases.
When monoblastic leukemia in the blood and bone marrow blast cells can be detected with a round nucleus and a narrow rim of cytoplasm, and only cytochemical features indicate that they belong to the elements of nature monocytic.
Cytochemical characterization of cells in acute leukemia, acute monoblastic
A special feature of this form of leukemia is acute monocytic cytochemical characteristic elements: they give a positive response to α-nonspecific naftilesterazu, repressed sodium fluoride. Reactions peroxidase and phospholipids in these cells weak.
In some cases, may contain monoblasty hloratsetatesterazu not contain (or may contain a small amount of) a-нафтилэстеразу, indicating the elements of immaturity monocytic series.
Remission in acute leukemia monoblastic
The frequency of complete remission in acute leukemia monoblastic in modern therapy is, as with acute myeloid leukemia, more 60 %.
