Acute leukemia myeloblastnыy and myelomonoblastnыy
Both forms of leukemia are sensitive histochemical differences: no regular morphology, no clinical picture are practically indistinguishable.
Acute leukemia Myelomonoblastnыy It can be presented by cells, each of which carries histochemical features monocytic cells both, and granulocytic series; however, there are cases, when one of the blasts belongs to mieloblastov, and the other - to monoblastam. This group of leukemia is often combined in the literature the term "nonlymphoblastic" (with promyelocytic, monoblastic leukemia and erythroleukemia).
Among nelimfoblastnyh acute myeloid leukemia in adults and account for about 80-90 myelomonoblastic %, and all nonlymphoblastic acute leukemia in adults - about 85 % all acute leukemias. Children, opposite, about 85 % up lymphoblastic acute leukemia.
Age peaks and acute myelogenous leukemia are observed myelomonoblastic 1-2 and after 10-12 years. According to the literature, the average age of patients with myeloid acute leukemia - 38 years, and myelomonoblastic acute leukemia - 50 years.
Forms of acute myeloid leukemia and myelomonoblastic
Currently we allocated some form of acute myeloid leukemia and myelomonoblastic. The principles of their selection is different.
For Example, allocated Acute leukemia with myelomonoblastnыy translokatsyey 8-, 21-and chromosomes. This form is mostly found in people younger than 50 years and refers to the spontaneous neindutsiruemym leukemia. The disease is characterized by a relatively favorable course. Red sprout in this form of normal, t. it is. neleykemichesky. The blood is often found eosinophilia. More than 50 % Patients with this form of acute leukemia can be obtained remission.
Besides, morphologically abnormal cells, and DIC is highlighted a special form of leukemia myelomonoblastic, podobnaya Island promyelotsytarnomu leukemia. Cytochemical characterization of cells, despite the abundant grain azurophil, It corresponds to the acute form myelomonoblastic. Cells that do not contain any leukemia promyelocytic leukemia characteristic acidic sulfated mucopolysaccharides. Bone marrow fibroblasts in this form of leukemia myeloblastic promyelocytic leukemia contrast grow well in monolayer culture.
The clinical picture of acute myeloid leukemia and myelomonoblastic
The clinical picture of acute myeloid leukemia and is usually characterized by myelomonoblastic hematological disorders. Heavy onset with high fever, necrosis throat typical for cases with deep primary granulocytopenia (T in less than 0,75-0,5 1 liters of blood).
In adults,, usually, the first manifestation of leukemia is not associated with lesions vnekostnomozgovymi: no lymphadenopathy, liver, spleen. Children vnekostnomozgovye lesions are more often. Opposite, congenital forms of leukemia skin and internal organs are fairly common. Neuroleukemia rarely in early disease, but if it is not carried out prevention, observed approximately 1/4 as in the cases of remission, and at relapse.
Blasts in vnekostnomozgovyh outbreaks often lose granularity when stained with Romanovsky-Giemsa, peroksidazopolozhitelnost but retain the ability of the tumor tissue on the cut to give color, which was the basis for the name of her chloroma.
The picture of blood and acute myeloid leukemia myelomonoblastic
Picture of blood at the time of the study may be different:
- mild anemia norm- or slightly hyperchromic type;
- leukocytosis with blasts in the blood;
- leukopenia with or without blasts;
- Normal platelet count;
- thrombocytopenia of varying severity.
In some cases, this form of acute leukemia may begin with the so-called stage predleykemicheskoy, characterized by the partial or cytopenia pancytopenia, long absence of blastic cells in blood and low in their content of bone marrow.
When mieloblastnom and mielomonoblastnom lejkozah blastnye cells contain the cytoplasmic azurofilʹnuû zernistostʹ (from single to tens of pellets), often calf Auer, the presence of which is a favorable prognostic sign (often manage to achieve remission).
Taurus Auer in acute myeloid leukemia presented mostly tubular structures, linearly oriented, and have a clear frequency, less often they are contained within the granular formations. Electron microscopy can find transitional forms from azurophilic granules of the calves Auer, containing lysosomal enzymes: acid phosphatase and peroxidase.
The presence of granules in the cytoplasm of myeloblasts in some cases can be identified only cytochemically. The core of blast cells are usually round, sometimes with small or irregularly shaped impression, but in the ratio of nucleus and cytoplasm is always dominated by the core.
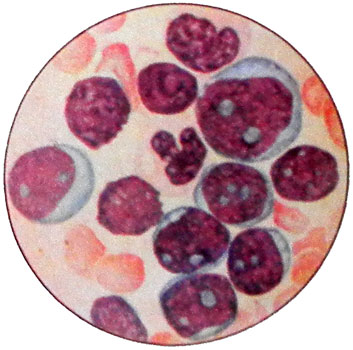
In the course of the disease blasts described forms of leukemia undergo regular changes: the shape of the nucleus becomes irregular round, cytoplasm of a narrow rim is wide and round cells instead of becoming irregular shape. Graininess, detectable early in the disease in a large percentage of cells, many of them becomes invisible and not detectable response peroxidase.
The frequency of remission in acute myeloid leukemia and myelomonoblastic is in modern therapy 60-80 %. The average duration of remission after maintenance treatment up to 12-24 months. Where, If remission is achieved, life expectancy of patients may exceed 3 year.
