Acute leukemia lymfoblastnыy
Picture of blood in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Picture of blood in acute lymphoblastic leukemia is the same, As with other forms of. The clinical onset of the disease may coincide with aleukemic and leukemic phases.
In many nuclei cytoplasm contains grit.
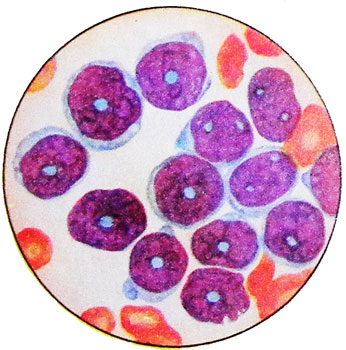
As with other types of acute leukemia, shape of the nucleus in the course of the disease varies: it becomes wrong, its dimensions are increased; and increases the rim of cytoplasm; blast at the structure of the cell nucleus can remind monocyte.
Specific features of this leukemia histochemical consist in, in that the blast cells are not found peroxidase, phospholipids, esterase (or traces of non-specific esterase and hloratsetatesterazy), and glycogen, detectable PAS-reaction, distributed clumps in the cytoplasm in the form of necklaces around the nucleus.
The study of T- and B-markers on blast cells of acute lymphoblastic leukemia possible to distinguish Three forms of leukemia:
- with blast cells, having a B-lymphocyte markers;
- with blast cells, having a T-lymphocyte marker;
- with blasts, non markers T- or B-lymphocytes (This does not mean, we are talking about cells, containing no antigen).
Approximately 2-4 % cases of acute lymphoblastic leukemia observed B-form, in 25 % cases - T-shape; a core group of no T-, neither B- form of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. According to research, the ratio of these forms in children and adults about equal.
K B-form of acute lymphoblastic leukemia often referred leykemiziruyuschiesya stage lymphosarcoma, especially lymphoma (lymphosarcoma) Berkitta, very rare blast crisis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia; cases of actual B-forms of acute lymphoblastic leukemia is very rare. In this form of leukemia cells characterized by a high content density on the surface of IgM.
Clinically more pronounced features T-forms of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. This form is most common among children, average age of 10 years, and mainly boys. It is characterized by T-shape frequency of leukemic variant, high leukocytosis, tumor mass growth in the mediastinum than in 50 % patients, high proliferative activity of cells.
According to research, the average life expectancy of patients with this form of acute leukemia - less 24 months, a relapse in half of cases begins with extramedullary growth - in the CNS or testes. Blast cells of antigenic characteristics resemble thymocytes and pretimotsity, than peripheral T-cells, having at the same time and some of their properties: receptors or FcIgM FcIgG, as a helper or suppressor. These cells retain some functional properties of the suppressor. Cytochemical characteristic of T-blasts is the high activity of acid phosphatase, localization of its cytoplasm and, usually, PAS-negative reaction.
General characteristics of acute lymphoblastic leukemia
General characteristics of acute lymphoblastic leukemia relates mainly to its us T-, us B-form, of about 70 % cases.
Antigen and enzymatic characteristics of cells, representing no T-, nor b-form, deprived of the determinants of peripheral T- and B- lymphocytes, but have features precursors of thymocytes, eg, react with antisera to antigens thymic, antisera with some chronic lymphocytic leukemia, It contains many deoxynucleotidyl.
Currently in addition to the three main forms of acute lymphoblastic leukemia allocated several.
New forms largely separated from any T-, or B-form. So, allocated before-B-shape, representing its blasts are early progenitor cells B-lymphocytes, since they contain cytoplasmic immunoglobulin - and IgM heavy chain immunoglobulins are not on the surface. This form of acute lymphoblastic leukemia has been much more favorable course, than the B-form, it is susceptible to treatment with vincristine and prednisone. On the surface of the cells pre-B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia detected Ia-like antigen, and cytoplasm often - TdT-enzyme - deoxynucleotidyl.
From our T-, or B-form isolated leukemia, submitted immunologically the same antigenic markers lymphoblasts, but containing Ph'-chromosome. This form of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children over the age of 10 years, It has an unfavorable course with a short remission.
In a small percentage of cases occur with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, blasts which immunologically related to the pre-T-lymphocytes, t. it is. progenitor cells to T-lymphocytes.
In contrast, pre-B-forms of acute lymphoblastic leukemia T-pre-form, like T-form, characterized by unfavorable course.
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia forms can occur with high eosinophilia (T cells produce the factor, stimulating eozinofilopoez). The blood thus happens leukocytosis, eosinophils 80-90 %, and blasts may not be available. Therefore, a high eosinophilia requires bone marrow aspiration, in the case where a high percentage of detected leukemia blast cells. When remission eosinophilia disappears and reappears, sometimes the first sign of relapse.
Metastasis of acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Metastasis process in the testes and the meninges, the most common acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children, It is a new stage of tumor progression, often very early.
Vnekostnomozgovye metastases in acute lymphoblastic leukemia in most cases characterized by less malignant forecast, than the myeloid. From inception neuroleukemia to death of a patient may take several years, during which its treatment of the general condition persists satisfactory.
Remission in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
The remission rate in children with this form of leukemia is 94 %, in persons over 15 years - about 80 %. The frequency of recovery of children - more 50 %.
