Tumors of the stomach – The cytological diagnosis of diseases of the alimentary canal
According to the International histological classification of tumors of the stomach, the following types of tumors.
Epithelial tumors
Benign
- Adenoma (papillary, or villeznaya; tubular, papillary, tubular)
Malignant
- Adenocarcinoma (papillary, tubular, mucinous, signet ring cell)
- Nedifferentsirovannыy cancer
- Adenokankroid
- Ploskokletochnыy cancer
- Neklassifitsiruemыy cancer
Karцinoid
Non-epithelial tumors
Tumors of smooth muscle
- Leyomyoma
- Leiomyoblastoma
- Leiomyosarcoma
Other
Hematopoietic and lymphoid tumors
- Lymphosarcoma
- Retikulosarkoma
- Hodgkin's disease
- Myeloma
- Other
Enclavoma
Secondary tumors
To carry tumor-like lesions of the stomach polyps, lymphoid hyperplasia, geterotopii, hamartoma, etc..
Polyposis of the gastric mucosa - The concept of collective. Every swelling on leg, issuing from the mucosa and disposed in the lumen of the stomach, regarded as a polyp. Histological polyp consists of connective tissue framework and hypertrophic mucosa with the growth of glands and surface epithelium.
Polyp malignancy occurs without the typical symptoms. Valuable for the diagnosis data obtained via fibergastroscope. It is mandatory cytology prints fibergastroscope tip and wash water.
Microscopically can find layers of epithelial cells of the gastric mucosa with drives proliferation and some atypia. Among evenly spaced columnar epithelial cells found two, tricyclic enlarged cells, which is located in the nuclei of several nucleoli. The uniformity of the structure of the nucleus, chromatin and arrangement of cells indicates the absence of malignancy.
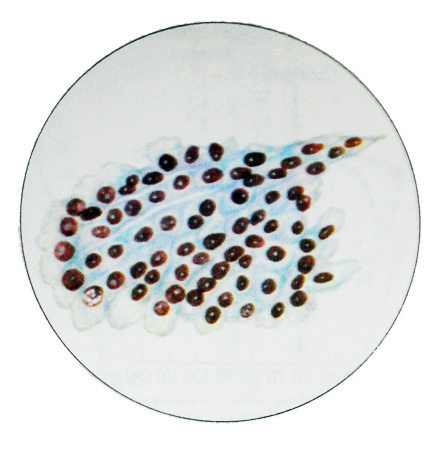

Suspected it only allows the identification of abrupt changes hyperchromatic cells with enlarged nuclei and nucleoli hypertrophied.
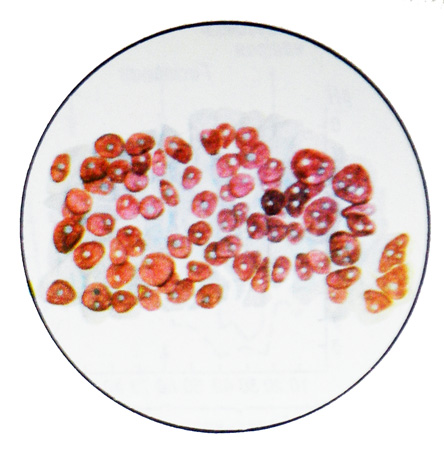
Adenoma of the stomach - Epithelial benign tumor, often turning into cancer; quite rare. Cytologically for adenomas are characterized by high cylindrical epithelium cells, often with symptoms of intestinal metaplasia, located zhelezistopodobnymi, Tubular, papillary structures, clusters and layers. In cases of pronounced proliferation and cell atypia revealed cellular and nuclear polymorphism, enlarged nuclei, uneven pattern of chromatin, there may hyperchromia cores, hypertrophied nucleoli, goloyadernyh structures, mitotic figures. With such a cytological picture adenoma must be differentiated from high-grade adenocarcinoma.
Stomach cancer
Stomach cancer It ranks first among malignant tumors of other sites. Develops, usually, in abnormal mucosa in various pathological processes result (gastritis, polyposis, and others.). Usually it localized in the pyloric part on the lesser curvature, at least - in a large part of the cardiac curvature, on the front and rear walls, in the body of the stomach. In connection with the collapse of a tumor characterized by functional disorders of gastric motility, axlorgidrija, axilija, development of fermentation and putrefaction.
Cytological picture depends on the histological forms of cancer.
Diffyeryentsirovannaya adenocarcinoma
When differentiated adenocarcinoma tumor cells in cytological preparations, the prints are placed in small groups, Have zhelezistopodobnuyu papillary structure, and characterized by chaotic jumble of cores.
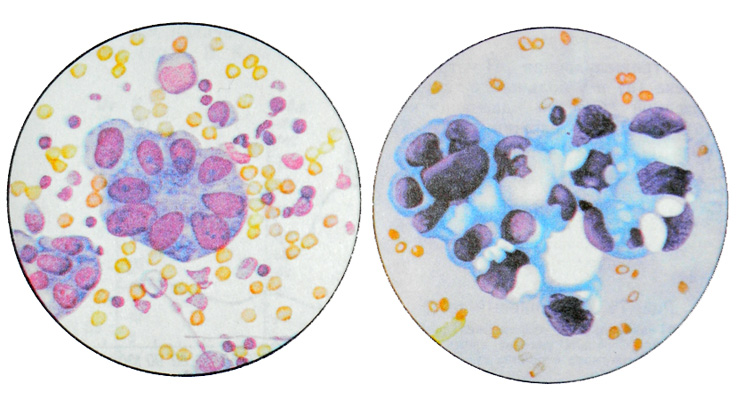
The cells do not differ the expressed polymorphism, may have a cubic, cylindrical, irregular round or oval. The nuclei are eccentrically. In some cases, they are enlarged, bright, with uneven contours and chromatin pattern setchatotyazhistym, It does not contain very large nucleoli. In other parts of the kernel hyperchromic, small or medium size, with a rough figure compact chromatin and single, sharply hypertrophied nucleoli. The cytoplasm of these cells pale, basophilic, inhomogeneous, clearly outlined.
In some cases, cancerous changes are detected epithelial cells of the intestinal type inhomogeneous, strongly vacuolated cytoplasm. In contrast, cells of intestinal metaplasia, intestinal-type tumor cells contain large hyperchromatic nucleus are characterized by marked and nuclear and cellular polymorphism.
Nizkodiffyeryentsirovannaya adenocarcinoma
When poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma tumor cells are pronounced signs of malignancy, located in cytological preparations often large clusters or solid fields, in which randomly arranged nuclei of different size and structure. Chromatin their thin, soft mesh, There are hypertrophied nucleoli. The cytoplasm of individual cells with signs of secretion.
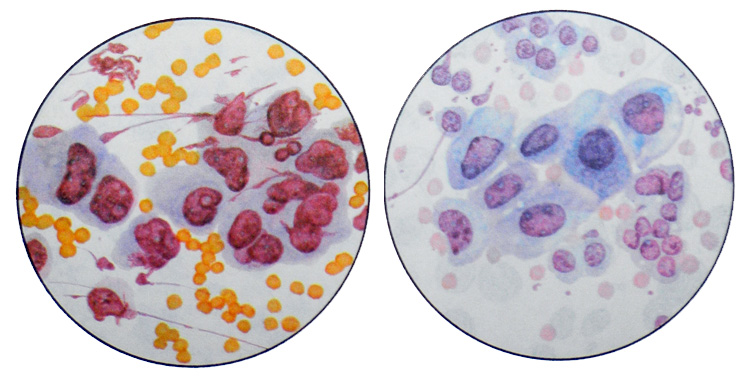
The cytoplasm of tumor cells can be filled with mucus - slizeobrazuyushtiy cancer.
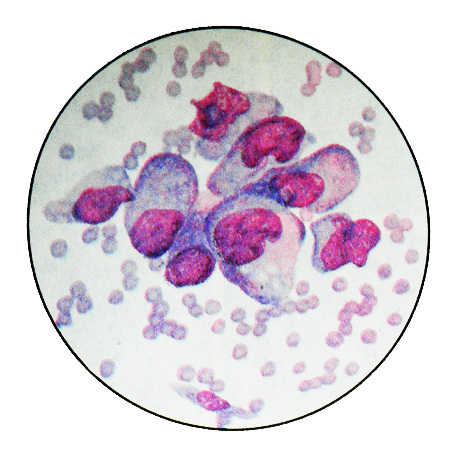
Sometimes, tumor cells acquire the signet ring shape - mucinous carcinoma.
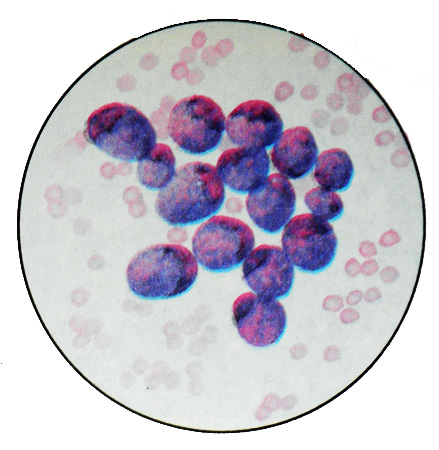
Undifferentiated gastric cancer
A characteristic feature is the presence of large cells dramatically anaplazirovaniyh (30-40 M) with very large round or irregularly shaped nuclei, containing chromatin pale reticulation, and often hypertrophied nucleoli. In some nuclei and cytoplasm vacuolization found. The cytoplasm has a narrow rim without clear borders. Often identified Blues- tsitialnye Education. Perhaps the presence of mitotic figures.
Squamous cell cancer of the stomach
Squamous (epidermoid) Stomach cancer is very rare. It can be the stratum and neorogovevayuschy. Last cytologically characterized by clusters of cells with enlarged nuclei, containing hypertrophied nucleoli and basophilic cytoplasm clearly contoured different widths. Less commonly detected tumor cells with marked polymorphism and hyperchromatic nuclei, characteristic of epi- dermoid cancer with moderate differentiation. When mixed form of cancer, combined epidermoid cancers and adenocarcinomas (adenokankroid) in cytological preparations revealed the tumor cells of both types.
In cytological preparations from the wash water of the stomach often can be found in the smallest scraps of tissue elastic fibers, evidence of underlying tissue destruction. Sometimes small pieces of necrotic with elastic fibers and fiber-based, covered with bacteria, Brown revealed blood pigment - hemosiderin, sometimes with crystals gematoidina and groups of tumor cells. The presence of these elements indicates the decay of cancer. Identified these elements mainly in native preparations.
Karцinoid
Carcinoid is rare, It develops from the basal parts of the mucous membrane, It is localized mainly in the pyloric cave. Tumor cells of average size, monomorphic, rounded, polygonal, sometimes cylindrical shape. Kernels round, cytoplasm nechetkaya. The cells are arranged seams, strands or glandular structures.
Non-epithelial tumors
Non-epithelial tumors of the stomach are very rare. These include leiomyoma, LMS and other, cytological picture which is similar to the same tumors other sites.
From the hematopoietic and lymphoid tumors in the stomach is most common lymphosarcoma (prolimfocitarnaâ, limfoplazmocitarnaâ, lymphoblastic, immunoblastic). Prolymphocytic lymphosarcoma is necessary to differentiate the cells of lymphoid hyperplasia with formation of stomach. Sometimes the stomach develops lymphogranulomatous node; cytology in such cases are detected Berezovsky-Sternberg cells.
