Ovarian tumors – Tsytolohycheskaya description, Diagnosis of tumors
According to its structure ovarian tumors are characterized by considerable diversity, due to multiple sources of origin. There are three groups of ovarian tumors:
- Because of the normal components ovary (basic and rudimentary);
- Embryonic residues and dystopias;
- From postnatal growths (strabismus, purpose- and paraplaziya epithelium).
According to histological classification, the following types of tumors and tumor diseases of the ovaries.
Epithelial tumors
Serous
Benign:
and) kistoma (cystadenoma), papillary cystoma (cystadenoma);
to) Surface papilloma;
in) adenofibroma, cistadenofibroma.
These tumors also belong to the group of "borderline" tumors with potentially low malignancy
Malignant:
and) adenocarcinoma, papillyarnaya adenocarcinoma;
to) Surfacing papillârnaâ cancer;
in) adenofibroma, cistadenofibroma
Mucinous
Benign and borderline (potentially low-grade):
and) pseudomucinous setserniruyuschaya cystoma (cystadenoma);
to) adenofibroma, cistadenofibroma
Malignant:
and) adenocarcinoma, cystadenocarcinoma;
to) adenofibroma, cistadenofibroma
Endometrial
Benign and borderline:
and) adenoma, cystadenoma;
to) adenofibroma, cistadenofibroma
Malignant:
and) cancer (adenocarcinoma, adenoakantoma, adenofibroma and tsistadenofibroma);
to) endometrial stromal sarcoma;
in) mesodermal (Mullerian) mixed tumors, homologous and heterologous
Clear cell (mezonefroidnye)
Benign:
adenofibroma
Border (potentially low-grade)
Malignant:
cancer, adenocarcinoma
Brenner tumor
Benign, Frontier, Malignant
Mixed epithelial
Benign, border, Malignant
Nedifferencirovannaâ cancer
Unclassifiable epithelial
Sex cord stromal tumors
Granulezostromalnokletochnye
Folliculoma
Tecom Group, fibroids:
and) TEKOM;
to) fiʙroma;
in) unclassifiable
Androblastoma: Sertoli cell tumors and Leydig
Highly differentiated
Intermediate (Transition differentiation)
Poorly differentiated (sarkomatoidnye)
With heterologous elements
Ginandroblastoma
Unclassified sex cord stromal tumors
Lipidokletochnye (lipoidnokletochnye) tumor
Germ cell tumors
Disgerminoma
Opuholʹ éntodermalʹnogo sinuses
Émbrionalʹnaâ cancer
Poliembrinoma
Xoriokarцinoma (horionэpitelioma)
Teratomas
Immature
Mature:
and) reputable;
to) cystic (dermoid cyst, dermoid cyst malignancy).
Monodermalnye (highly):
and) ovary Struma;
to) karцinond;
in) Struma and ovarian carcinoid;
g) other
Hybrid
Gonadoblastoma
Soft tissue tumors, nonspecific for ovarian
Unclassified tumors
Secondary (metastatic) tumor
Tumor processes
Lyuteoma pregnancy
Ovarian stromal hyperplasia, gipertekoz
Massive swelling of the ovary
Individual follicular cyst and corpus luteum cyst
Multiple follicular cysts (polycystic ovaries)
Multiple follicular cysts and luteinized (or) lutea
Endometriosis
Surface epithelial inclusion cysts (germinal inclusion cysts)
Simple cysts
Inflammatory processes
Parovarian cyst
Epithelial tumors
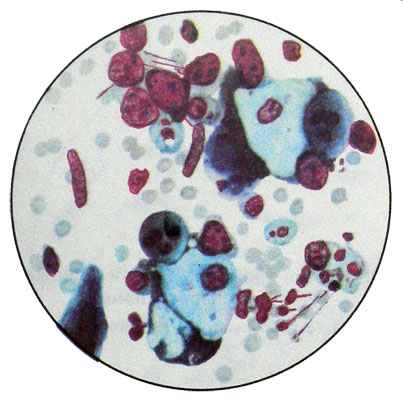
Benign serous tumors account for about 20 % all epithelial ovarian tumors. The cells of these tumors are similar to ciliated cells of the fallopian tubes. Most often it is one-sided- or triple-education of various sizes. Content cyst fluid, clear, colorless or yellowish.
Serous ovarian cystoma (seroznaя cystadenoma, tsilioepitelialnaya setserniruyuschaya ovarian cyst)
The walls are covered with epithelial cysts of four types: prismatic ciliated with round nuclei, larger with granular cytoplasm (secretory) and rod-shaped cores; cells with elongated nucleus and the pear-shaped (slip), located in the upper layer of the epithelium. In large cystoma intracavitary pressure as a result of epithelial cells flatten and lose their cilia, become mono- morphic cylindrical, and in some places completely atrophy. Under the epithelium of two layers of connective tissue located:
- first - a thin layer nezhnovoloknisty, rich cells (among which there are also ksantomnye);
- the second - a dense fibrous.
Sometimes on the inner surface cystoma buds appear or plaques, stroma which consists of coarse fibrous tissue, and the surface is covered with a single-row cylindrical or cubic epithelium.
Occurs serous cystoma most women aged 40 50 years. Based cystoma may develop a malignant tumor. Microscopic studies revealed punctate cystoma erythrocytes and leukocytes, a small number of cells ksantomnyh, sometimes single cells, lining the cyst cavity.
Papillary serous cystoma (papillary serous cystadenoma)
Are benign and borderline formations. Papillary cysts called because of its walls papillary growths in the form of single or multiple outgrowths of the columnar epithelium, filling the entire cavity. It is mostly bilateral multi-chamber formation diameter 100-120 mm, fixed as a result of adhesions to the surrounding tissues.
Free from tumor growths of the chamber filled with the serous fluid of different colors and character (zheltovataya, clear or turbid, viscous, purulent or haemorrhagic). Epithelial, lining the cavity tumors, Single row, but the height of the cells and their shape may vary.
Proliferative papillary cystoma (Frontier)
Proliferative papillary cystoma (Frontier) characterized by epithelial proliferation, forming a multi-row structure. There may be cells in mitosis. Cystoma this type may recur and shatters the peritoneum. However, the colonization of the peritoneum is not seen as a sign of malignancy, because after removal of the tumor growths on the peritoneum may disappear. It occurs in puberty and rarely - in old age. Sometimes there is ascites. According to various authors, malignancy can be observed in 2.5 8 % cases.
Microscopic examination aspirates of kistomy except blood cells and epithelial cells can be detected tiny pieces of papillary excrescences of the cyst wall. The punctate proliferating cystoma found many similar cells, as well as elements of inflammation and accumulation of cells psammous.
Mucinous tumors
Mwcïnoznıx epithelium kïstom morfologïçeskï napomïnaet epithelium channels şeykï matkï shell or slïzïstoy gut tolstıx. This epithelium produces mucopolysaccharides (glikozaminglikany), mukoproteidov and glycoproteins.
Pseudomucinous setserniruyuschaya cystoma – cystadenoma
Pseudomucinous setserniruyuschaya cystoma (cystadenoma) can reach gigantic proportions. Microscopically, the cyst is a multi-chamber. The inner surface of its walls lined with high prismatic single in slime epithelium, cells which are light blue cytoplasm and nucleus hyperchromic, located at the base.
You can find clusters of goblet cells and restnichatyh. It occurs at a mean age 50 years, but sometimes the disease occurs in young age. When you break the tassels of their content falls into the peritoneal cavity. In cytological preparations punctate cystoma noteworthy slimy nature of the content and the presence of high prismatic epithelial cells.
Papillary mucinous proliferating cystoma
Papillary mucinous proliferating cystoma It refers to the border cystoma (cystadenoma) ovary. It is characterized by marked epithelial proliferation with exophytic growth, t. it is. true to form papillae. There is some cell polymorphism. There are undifferentiated cells, sometimes gigantic sizes. The contents of these cysts is the same, as setserniruyuschey. Possible malignancy.
Microscopic examination against the background of mucus cells are found lying freely in groups and formations papilliform. When malignancy cells appear with severe symptoms, characteristic of malignancies.
Ovarian Cancer
There are primary cancer, arising from ovarian tissue, secondary, develops from benign ovarian tumors, and metastatic.
Some authors deny the possibility of a primary ovarian cancer, because the cancer usually develops from ovarian cystadenoma or tsistadenofibromy. These types of cancer can grow on the type of cystic cavities or papillary formations (papillyarnыy cancer). Microscopic examination of these punctate tumors detected cancer cells with large hyperchromatic nuclei and nucleoli bright. Cytoplasm light blue tones with degenerative changes (vacuolation, fatty degeneration) or signs of secretion.
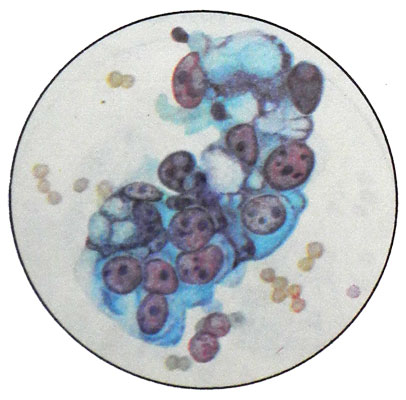
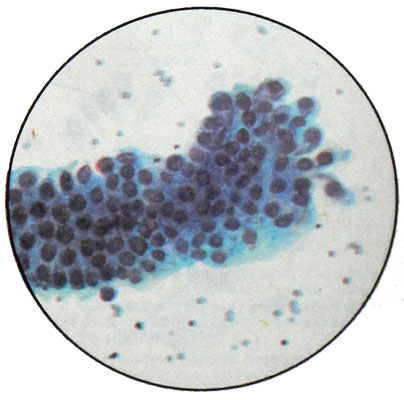
In cancer, developing from cystadenoma, often formed limestone concretions - acervulus. Their formation is due to degenerative processes in the tumor tissue. These corpuscles can be found in benign tumors of the ovary, particularly in proliferating cystadenoma (pseudomucinous proliferating cystoma). Therefore, the identification of ovarian tumors in punctates can not in itself evidence of the nature of the tumor (benign or malignant) ; It should take into account the morphological picture of the whole punctate.
In addition to cancer or cystic papillary structure in the ovary cancer can develop a solid or partially solid structure with pronounced atypia cells, often reaching the point, that affiliation to determine the histological tumor can not be. Such cancers are classified as adenocarcinoma, iron-solid, solid, medullary or fibrous (scirrhoma). Ovarian cancer cells can enter into the uterus. Therefore, they can be aspirated or observed in the secretions from the cervical canal. The appearance of elements of ovarian cancer in the contents of the uterus and through the selection of the cervical canal is rare.
Where, When ovarian cancer is accompanied by the accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity, cytology it can detect cancer of the body elements. Often on the complexes of cancer cells in serous fluid in the metastasis of ovarian cancer found acervulus.
Sex cord stromal tumors
Granulezostromalnokletochnye tumor
Folliculoma
Folliculoma characterized cells, similar to granulosa cells of follicles. Such tumors occur in any age, but more often in the 40- 45 years. The tumor hormonally active. The blood and urine revealed a large amount of estrogen. In girls, there is precocious puberty. In women, menopause occurs hypermenorrhea (menorragija). The childbearing years are possible uterine bleeding, Sometimes amenorrhea, infertility, Abortions. There have endometrial hyperplasia and hypertrophy and other changes. Hormonal disorders may be missing. Clinically, many. The authors attribute the tumor to a potentially malignant tumors, since 15-20% of patients after surgery relapse or metastases. Microscopically, the main component of the tumor cells of the same type are small round or polygonal shape with hyperchromatic nucleus, occupying nearly the entire cell, and a narrow rim of cytoplasm, which may be small inclusions of lipids.
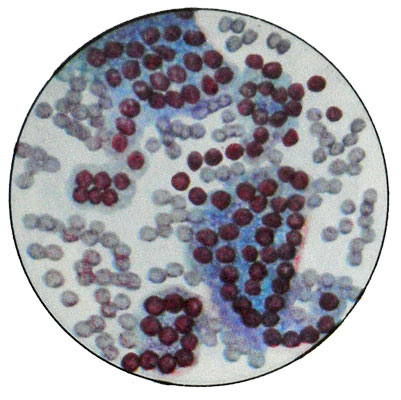
The ovaries can develop malignant folliculoma - (granulezokletochnыy cancer). It differs polymorphism cells, their more severe atypia and a large number of cells in mitosis. Clusters of cells are located, strands of rozetkovid- structures, which is characteristic of granulosa tumors.
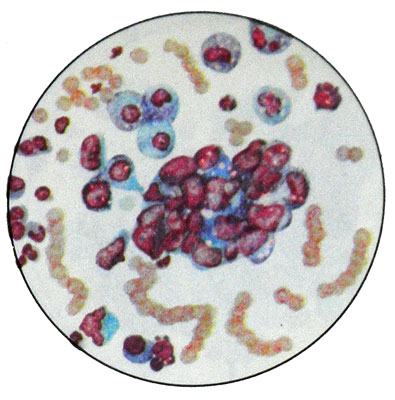
It should be taken into account, that in any morphological picture granulosa tumor may be malignant.
TEKOM (tekakletochnaya tumor)
Unlike granulosa tumor, Tecoma in its histological structure approaches ovarian fibroma. These tumors arise from connective tissue membranes (only) follikula. Normally, the shell of the follicle secrete steroid hormones (mainly estrogens), therefore Tecoma often hormonally active, and clinical picture is similar to its granulosa tumors. Tecoma develops most often in sight- and postmenopausal, but can also occur in childhood and old age. Usually, This tumor-sided.
Grossly the tumor may reach large sizes (to a value of an adult), buhrystaya, fairly firm, the cut diffusely yellow or orange-yellow. Microscopic examination of tumor punctate detect several types of heterogeneous cells:
- when hormonally inactive tumor - elongated cells (fusiform) with elongated, nearly rod-shaped hyperchromatic nucleus and cytoplasm small, elongated at the poles; can meet and naked nuclei;
- when hormone aktivnoyopuholi - larger oval-shaped cells with hyperchromatic nuclei and rather wide rim light foamy cytoplasm, containing a large amount of lipids. Cells of malignant Tecom characterized polymorphism, nuclear atypia, large number of cells in mitosis.
Depending on the nature of TECOM in cytological preparations marked a sheaf arrangement of cells with a predominance of elongated shape or larger clusters of bright cells, lipid-rich. The cells in mitosis bit. Determine the nature of the cytological picture of the TECOM hard. However, with the abundance of cells, expressed their polymorphism, enlargement of the nuclei and nucleoli, set of mitotic figures can assume a malignant character of the process. Sometimes Tecoma meets with dermoid, papillary serous or mucinous cyst and pseudomucinous. In most cases, benign Tecoma, sometimes it is malignant character.
Ovarian fibroma
Ovarian fibroma, usually, accompanied by ascites. Microscopically, it is composed of bundles of spindle-shaped cells, located in different directions, which is particularly well visible under low magnification microscope. The shape of the nuclei can be round, oval, rhabdoid. The nuclei are clearly visible nucleoli. The cells in mitosis normally not detected. Unlike TECOM tumor cells do not contain lipids. In cytological preparations revealed a small number of cells.
Germ cell tumors
Dysgerminoma ovary
Disgerminoma - A rare malignant tumor, which develops from the undifferentiated germ cells of the ovary. It occurs mainly in girls and women aged 30 years. Often it occurs on the background of signs of infantilism or improper sexual development (psevdogermafroditizm, Syndrome Ternera). It grows quickly, attaining a diameter 200 mm and more.
Dysgerminoma microscopically resembles ovarian seminoma. Cells dysgerminoma depending on the content of glycogen look different. When a small amount of glycogen, they have a narrow bezel granular cytoplasm. The accumulation of glycogen leads to an increase in cell volume due to increase in the cytoplasm (it gets a little frothy appearance) and its enlightenment. With a large number of glycogen cells acquire resemblance to the plant because of a clear path and as if floating in the void nucleus. The core of a major, with delicate chromatin network and one - three nucleoli, it is usually in the center of the cell.
Degenerative changes in the cells expressed in the nuclei and giperhromatoz goloyadernosti. Often, the microparticles fall punctate tumor. Microscopic examination found adjacent to each other cells, that arrangement reminiscent of cobblestones. The stroma dysgerminoma observed infiltration of lymphoid elements. Sometimes there are giant multinucleated cells, similar to cells Pirogov-Langhans.
Ovarian teratoma
The origin of the tumor is due to abnormal differentiation of germ cells, so it is referred to as germ cell tumors. Developing teratoma often at a young age. There are cystic and solid teratoma.
Mixed cyst (dermoid) It refers to the mature, and solid, as consisting of a wide variety of, often immature tissue structures and wearing a malignant character - immature.
Mature teratoma (dermoid, mixed cyst, Mixed cyst) It occurs at any age, but most often in people 20-40 years. Tumor-sided, It grows slowly. Microscopic examination of the epidermis often found with its appendages, bone elements, gut epithelium, retina, flat epithelial cells at different stages of keratinization, cylindrical epithelial cells, cartilage cells, etc.. Besides, can be observed cholesterol crystals and fat droplets and when festering cysts - elements of pus. Occasionally such a cyst is degenerating into squamous cell carcinoma.
Teratomas, contains flattened cells of the thyroid gland, often rich in colloid, called ovary Struma. The tumor is sometimes accompanied by hyperthyroidism.
Immature teratoma observed in young, characterized by the rapid growth. Microscopic structures characterized by considerable polymorphism, among whom distinguish epithelial and mezenhimopodobnye.
Epithelial structures represented by low and high prismatic epithelial cells, folding in tubular formation, in papillary excrescences. Shape flattened cells, cubic, cylindrical, they often have a vacuolated cytoplasm and one core.
Mezenhimopodobnye structure - This Process, closely related cells. Can meet and bright cell rounded shape. Both have large hypochromic nuclei with one - three nucleoli and more.
Ovarian choriocarcinoma – Horionepitelioma ovary
There are horiokartsnnomu, develop against teratoblastomy, and horiokartsnnomu, in which there are no traces of any structures teratomatous. Proof of the existence of true hornokartsinom is the ability of their cells secrete gonadotropin horionicheskny, which is connected with the action of the development of mastitis in men, suffering from choriocarcinoma or testicular mediastinum. Grossly horiokartsnnomu ovarian difficult to distinguish from normal structure teratoblastomy. A sign, allowing suspected its presence, They are small and large hemorrhages and necrosis ochagn.
Choriocarcinoma and teratoblastoma with horionepitelialnymi structures characterized by rapid growth and the ability to metastasize. They are observed predominantly in the age range 20-40 years. The response to gonadotropins, usually, positive.
In a typical structure of ovarian choriocarcinoma (as uterus) It consists of elements sintsitsiotrofoblasta, having the form of a giant multinuclear syncytium various shapes and sizes, and cytotrophoblast - Langhans cells.
Atipichnaya form horiokartsinomы It consists only of cells called the Langhans tsitotrofoblastomoy.
Choriocarcinoma gonads can arise only from a germ cell. It can be sources of trophoblast fetal calf, psevdomorula directly itself gamete.
