Tumors of the uterine body – Tsytolohycheskaya description, Diagnosis of tumors
Uterus - A hollow muscular organ, coated on the outside serosa, or perimeter, under which is a powerful muscle layer, or myometrium.
Endometrium (endometrium) lined with epithelium, which is composed of ciliated cells and bezresnitchatyh, releasing secret.
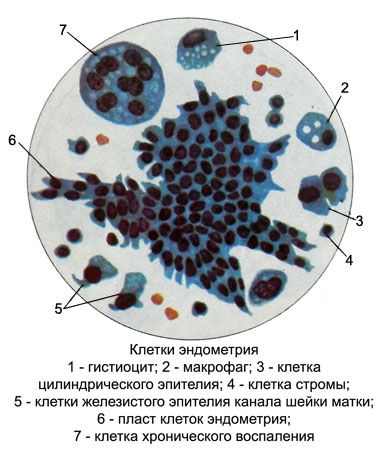
Ciliated cells located among the islands bezresnitchatyh, t. it is. mucous cells. Both types of cells have almost complete similarity with similar cells of the cervical canal.
The loose stroma, situated between the uterine glands, there is a lot of small undifferentiated mesenchymal cells (stromal cells). Ciliated and bezresnitchatye endometrial cells are found in cytological preparations, prepared from secretions from uterus or aspirating fluid. Ciliated cells are less common, mucous than bezresnitchatye. To distinguish cells of columnar epithelium of the cervical canal from cylindrical cells lining of the uterus is almost impossible. For the lining of the uterus characterized by smaller cells. They have a diameter and a generally cylindrically shaped lower.
Apart from endometrial cells in the smears are observed stromal cells of uterine body. This small round cells with narrow rim of cytoplasm around the uniform circular compact nuclei of equal size stromal cells often form groups, so sometimes it is difficult to solve, what type of tissue they are (to connective tissue or epithelium). Yet compared to cells of endometrial stromal cells somewhat greater magnitude, with well distinguishable area of the cytoplasm, form a loose group.
Gistiocitы contents of the uterus occur frequently, especially material, taken from women in the postmenstrual period. These cells are arranged individually or in the form of syncytial formation.
Tumor-like formations of the corpus uteri
K tumor-like formations of the corpus uteri applies endometrial hyperplasia, which develops as a result of violations of the hormonal regulation of the menstrual cycle and manifests proliferation of endometrial glands and stroma. There are glandular and glandular atypical endometrial hyperplasia.
Glandular endometrial hyperplasia (gipertiastichesky proliferative endometrium type)
Glandular endometrial hyperplasia (gipertiastichesky proliferative endometrium type) It occurs most frequently in menopausal or premenopausal, less in its infancy ovarian-menstrual cycle.
The reason for the development of endometrial hyperplasia believe hyperestrogenism or prolonged exposure to estrogens on the endometrium at a low level in their blood. Endometrium thus considerably thicker and may form polyps protrude into the uterus.
There is a development of glandular-cystic hyperplasia, morphological pattern in which the cytological preparations presented an abundance of cells often cubic or columnar epithelium, somewhat larger, cells than normal columnar epithelium of the endometrium in the intermenstrual period, with correspondingly larger hyperchromatic nucleus and basophilic cytoplasm.
Location cell clusters, groups and scraps zhelezistopodobnymi structures. The cells in mitosis there are no.
The degeneration into cancer observed in 0,6 % cases.
Atypical glandular endometrial hyperplasia (psevdozlokachestvennaya glandular hyperplasia, Diffuse adenomatosis, endometrial precancer, cancer in others, 0-stage endometrial cancer)
It refers to precancers, It occurs mainly in women during menopause. At a young age is almost no.
It is characterized by marked proliferation of the endometrium with the formation of foci of adenomatous, consisting of branching glands. In cytological preparations observed abundance of large cells of columnar epithelium with a corresponding increase in "juicy" cores, containing nucleoli. The nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio virtually unchanged. Basophilic cytoplasm.
Against the background of the described cellular elements are large cells bubbles, with several large nucleus and cytoplasm rather broad, and bright cells, containing lipids. The presence of the past is a poor prognostic sign. Mostly found in the product areas of squamous metaplasia in the form of flakes.
Rebirth of atypical glandular hyperplasia observed in cancer 2-4 % cases. Located hypertrophied columnar epithelial cells in isolation, groups, as zhelezistopodobnyh and papillary structures. Such cells are of cylindrical shape can be detected in the endometrium in proliferative- tive phase of the menstrual cycle. Endometrial hyperplasia is characterized by the proliferative phase of the menstrual cycle, the lack of cell decidual tissue. In some patients, atypical hyperplasia and endometrial adenomatous polyps in eliminating pathological hormonal influences may regress.
Tumors of the uterine body
Tumors of the uterine body are among the most frequent tumors. They may be of mesenchymal (sarkoma, fiʙroma), muscle (myoma, miosarkoma), epithelial (Polyps, cancer) origin.
Hysterocarcinoma
Hysterocarcinoma ranked second (after breast cancer) among malignant tumors of various organs in women. It develops from the endometrium, It found most often in older age 50 years. For cancer of the uterus is characterized predominantly exophytic growth while infiltrative growth in the thickness of the muscular wall (ekzoendofitny growth). When exophytic tumor growth is usually located on a broad basis, at least - on the leg. Papillary growths give it a resemblance to cauliflower. For purely endophytic tumor grows in the thickness of the uterine wall, and from the endometrium can be ulcer.
From the histological forms of cancer of the corpus uteri distinguish Adenocarcinoma all degrees of differentiation, squamous, svetlokletochnыy cancer, adenoskvamoznuû cancer, nedifferentsirovannыy cancer.
One of the earliest symptoms of endometrial cancer are whites. The main symptom of the disease - bleeding (in 85-87 % patients), especially during menopause. During germination of the tumor in the bladder symptoms of cystitis. The collapse of the tumor and the accession of infection is usually accompanied by fever and the appearance of putrid, malodorous discharge. These symptoms or some, such as bleeding, should cause suspicion of cancer of the uterus. In order to establish the correct diagnosis is usually used cytological methods of investigation, histological study scraping the lining of the uterus and hysterosalpingography.
Material for cytological examination prepared by aspiration syringe Brown. In the laboratory, selected from the aspiration material grayish fabric pieces of the tumor and the uterine mucosa examined under a microscope in the first native preparations (which is important for the diagnosis of squamous cell cancer of the stratum), and then stained.
Adenocarcinoma of the uterine body
Adenocarcinoma, depending on the degree of differentiation of cells may be highly, moderately- and low-grade.
Vysokodiffyeryentsirovannaya adenocarcinoma matki
When high-grade adenocarcinoma of the uterus usually mild cellular polymorphism, marked only increase in cell size. The main features, on which cells can be attributed to cancer, are increasing the size of their nuclei in length and expressed hyperchromia. In the cytoplasm of cancer cells near the apical edge are often vacuoles.
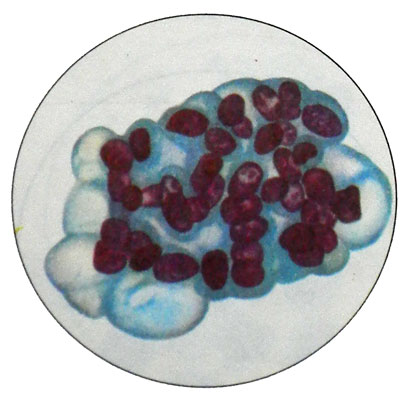
The cores are arranged in rows, even in groups klegok syncytial nature. Characteristic body matkn adenocarcinoma is the presence of glandular structures of cancer cells in the form of sockets.
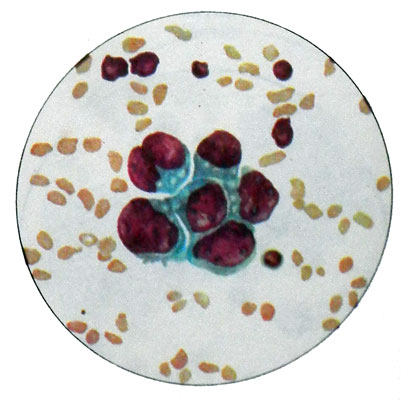
Diagnosing high-grade adenocarcinoma of the uterine cytology preparations presents certain difficulties.
Moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma of the uterus
Moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma of the uterus characterized by a pronounced polymorphism cells. The nuclei of large, comprise one or several nucleoli. Many cells in mitosis. Formation of glandular structures weakly expressed. The formulations can be found areas of squamous epithelium (squamous islands).
Nizkodiffyeryentsirovannaya adenocarcinoma matki
Nizkodiffyeryentsirovannaya adenocarcinoma matki It has a strong cellular polymorphism and more obvious signs of malignancy. It is characterized by the existence of close groups of cells, however, the structure, typical adenocarcinoma, while rarely found.
When adenocarcinoma all degrees of maturity in the product may show areas of squamous (skvamoznoy) metaplazii, consisting of large monomorphic cells with vacuolization of the cytoplasm in the perinuclear area (so-called adenoacanthoma).
Svetlokletochnыy cancer
Clear cell (mezonefroidny) cancer rare. In preparation ballonoobraznye found atypical cells with large nuclei and nucleoli and abundant light foamy cytoplasm. Cells are located separately, as a group, zhelezistopodobnyh and papillae- prominent structures.
Adenoskvamoznaâ cancer
Adenoskvamoznaâ cancer (adenokantoma, mukoépidermoidnaâ cancer, adenokankroid endometrial). Rarely, usually in the elderly. Smears corresponds to similar tumors of the salivary gland.
Squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine body
Squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine body in its morphological features no different from squamous cell carcinoma of other sites. The diagnosis is usually made by the native drugs.
Nedifferentsirovannыy cancer
Microscopic cells predominate in the preparation with pronounced signs of malignancy. Epithelial their nature can only be determined presumably.
Tumors of muscle and connective tissue
Leiomyofibroma – fiʙromioma
Leiomyofibroma (fiʙromioma) - A benign tumor, arises from the cells unutilized- drawing the muscle tissue of the myometrium, the walls of blood vessels, or from undifferentiated mesenchymal cells of the uterine wall. It meets at least 20-25 % Women over the age of 30 years. It may be asymptomatic or manifest violations of the menstrual cycle: erratic bleeding type metrorrhagia.
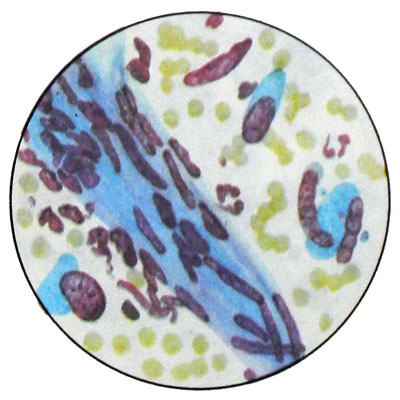
The tumor is in the form of one or multiple nodes rounded shape. It is separated from the surrounding tissue impaction muscle fibers. Microscopically consists of intricately interwoven fiber bundles neischerchennoy muscle.
The nuclei of rod-shaped myocytes, with rounded ends, sometimes arranged in a palisade. With a significant amount of swelling of myocytes referred to fiʙromiome, and atrophy of muscle fibers - to fibroma. When fibroids punctate contains a small number of cells such as fibroblasts with elongated or rod-shaped nuclei and elongated at the poles of the cell cytoplasm.
Diagnosis of fibroids is usually not in doubt. Difficulties arise where, When tumors occur in areas with a large number of polymorphic cells. This pattern can be observed in the growing fibroid and pregnancy.
Uterine Sarcoma
Uterine Sarcoma may develop from leiomyoma. of muscle tissue - LMS, of endometrial stromal cells - endometrial sarcoma.
Leiomyosarcoma
Leiomyosarcoma - A malignant tumor of immature elements neischerchennoy muscle. It is generally located in the bottom and rear surface of the body of the uterus. Most often it grows in a solitary unit; diffuse form of LMS observed approximately 3 % cases.
At the beginning of the disease there are no specific symptoms, in the future, depending on the location of sarcoma may experience heavy bleeding or discharge in the dingy intermenstrual period, to increase the duration of menstruation. This is usually observed in tumor necrosis and decay.
The important diagnostic value give a rapid increase in the tumor or the entire uterus, especially if this sign appears after menopause. In the event of a sarcoma in myoma nodes symptoms scarce. There is a view of a more benign sarcoma, from developing uterine fibroids. Cytological diagnosis of leiomyosarcoma is possible during the germination of the tumor in the endometrium.
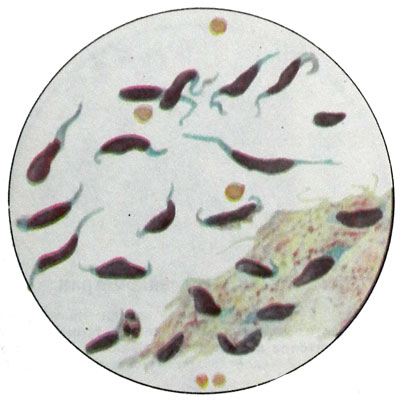
Microscopically, the tumor is composed of spindle-shaped bundles of muscle cells with large rod-shaped or oval nuclei. There are huge multi symplast.
At anaplastic LMS the expressed polymorphism of cells: fine, rounded shape with hyperchromatic nuclei and mitotic figures, fusiform with large rod-shaped cores, elongated with abundant cytoplasm, sometimes large cells of round shape, etc..
Endometrial sarcoma
Endometrial (stromal) sarkoma It may also be limited and diffuse (nodular). The latter is normally located in the uterus as a polyp. Diffuse form of tumor is rare.
Microscopically endometrial sarcoma consists of small spindle-shaped and rounded cells with different amounts of cytoplasm. Perhaps the presence of giant cells with one or more cores and a plurality of mitosis. The cells may be arranged around vessel, Recalling angiogenic tumor.
Cytological diagnosis of uterine sarcoma often presents considerable difficulties because of its similarities with the cells of the myometrium and endometrium in certain inflammatory, hyperplastic and neoplastic processes of a different nature.
Carcinosarcomas
The tumor is localized mainly in the endometrium. Morphologically it includes elements adenocarcinomas and sarcomas. Microscopic examination of specimen revealed cancer cells and atypical stellate mesenchymal cells and elongated: both are randomly shuffled, forming solid clusters and groups of cells in the form of- lezistopodobnyh formations.
Trophoblastic disease
Molar pregnancy
Molar pregnancy - Disease, due to the violation of the ovum (vorsin xoriona), which leads to disruption of metabolism between the organism of mother and fetus and ultimately to his death. Chorionic villi with the increase in volume, mucosal changes, covering their epithelium proliferates, and syncytial cells embedded in the wall of the uterus. Such changes often occur chorion in the first half of pregnancy and are associated with hormonal influences.
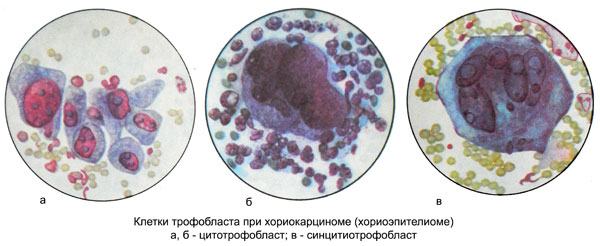
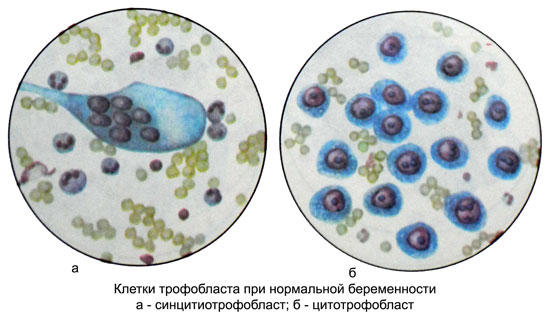
Grossly chorionic villi look like a bunch of grapes. Microscopic examination of the foci of hyperplasia detected large mononuclear cells such as cells of Langhans, received the name of cytotrophoblast cells, and syncytiotrophoblast cells.
Sometimes there is a proliferation of the epithelium with an increase in chorionic cells and their nuclei. This is especially true cytotrophoblast. Nuclei are stained with the intense, appears the figure of their division. In such cases, cytological preparations molar pregnancy is difficult to distinguish from Horio- karcinomy (chorionepithelioma). Such malignant molar pregnancy can grow their naps in the myometrium vessels and then into the myometrium, metastasize to the lung and vagina.
Hydatidiform mole and choriocarcinoma referred to trophoblastic tumors. Benign molar pregnancy is transformed into a choriocarcinoma in 5 % cases, and malignant - in 50 %.
Xoriokarцinoma – Horionэpitelioma
Xoriokarцinoma (horionэpitelioma) - Tumor, growing epithelial cells and chorionic localizes in the body of the uterus, sometimes the fallopian tubes, and even more rarely - in the ovaries.
It is believed, what choriocarcinoma develops from trophoblastic elements and precedes normal or pathological (molar pregnancy) pregnancy.
There are cases of choriocarcinoma and during pregnancy. Most often it occurs in multiparous women. Choriocarcinoma may also develop after the abortion and childbirth, when there are small particles ovum, giving rise to polyps plantsentarnym. This is evidenced by the fact the development of choriocarcinoma in the uterus at the site of implantation of the ovum (placental site).
Chorionic elements may spread to the blood throughout the body and implanted in various organs and tissues. In such cases ectopic choriocarcinoma may develop in distant organs from the uterus (light, brain and spinal cord, liver and others.).
In most cases, choriocarcinoma occurs in the implementation of the ovum. It has a kind of node, reminiscent of a blood clot. In the future, possible exophytic, endophytic tumor growth or mixed.
Microscopically it consists of two types of tumor cells, occurring both in molar pregnancy, and in normal pregnancy. It cytotrophoblast cells and syncytiotrophoblast. Tumor necrosis riddled and bleeding. Tumor cells have the ability to penetrate the vascular wall, from which it receives power. Horionepitelioma own vessels are not allowed. Trophoblast cells have anticoagulant properties, than, apparently, It is due to the difficulty of stopping the bleeding from the tumor focus.
The main clinical symptoms of uterine choriocarcinoma – permanent or observed with short breaks spotting, JavaScript, along with them, or at intervals between them whiter. The decay and infection of the tumor whites become a fetid smell and dirty look.
When choriocarcinoma, located within the wall of the uterus and has no direct connection with the cavity of the uterus, spotting are not always, but during germination tumor perimetry can intraperitoneal bleeding. With the simultaneous development of choriocarcinoma and pregnancy bleeding may not occur until delivery.
A distinctive feature of choriocarcinoma is an increased formation in the body of patients with gonadotropin, which is excreted in the urine. If during normal pregnancy 1 l urine contained by 5000 to 30000 ED hormone, then the number of its horiokartsinome increases 100 time. Described, However, cases of choriocarcinoma with a low content of gonadotropin in the urine.
The material, delivered to the laboratory for cytology, It draws attention to the abundance of gray-whitish patches of fabric, among which are sometimes found, and necrotic.
Microscopic examination of blood cells among the detritus somewhere found two types of cells with distinct signs of malignancy: Langhans-type (cytotrophoblast cells) and syncytial formation (syncytiotrophoblast cells).
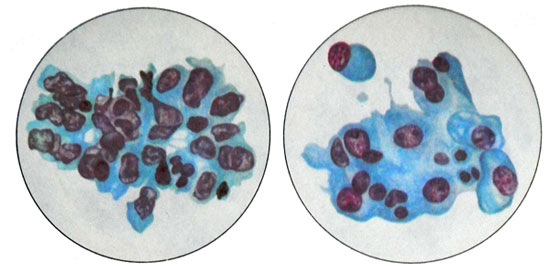
Langhans cells are polygonal or round, well-defined, with light, quite abundant, sometimes vacuolated cytoplasm, or "empty" due to the high content of glycogen. The cell nuclei large Langhans, polymorphic, light-colored, several hypochromic, with a clearly discernible chromatin network. Dimensions of cells and their nuclei vary greatly. (Option A in the figure below)
There may be up to a diameter cores 22 m. Often there are atypical mitosis. Cells are arranged in groups, small layers or strands. Sometimes bands or layers of Langhans cells may in any area as it move into cells syncytiotrophoblast, having a form of giant multinucleated syncytia razlichinoy shapes and sizes. (Option B in the figure below)
The cytoplasm of the cells homogeneous syncytiotrophoblast, often vacuolated. The nuclei of different sizes, round, oval or irregularly shaped, rich in chromatin. In areas of necrosis can be found crystals gematoidina. (Option B in the figure below)