Cervical tumors – Tsytolohycheskaya description, Diagnosis of tumors
In a normal stratified squamous epithelium, covering the vaginal portion of the cervix, in the area of the external opening of the cervical canal passes into the glandular, which consists of a single layer of columnar cells with round or oval nuclei, located at the base of the cells.
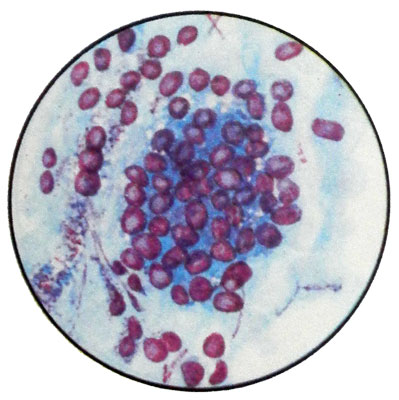
The cells of the glandular epithelium are sometimes villi. Under the influence of various causes (hormonal disorders, congenital anomalies, inflammatory changes, injuries) possible violation of the structure of the epithelium, lining the cervix and its canal, as well as misallocation of it on the vaginal part of the cervix, that can lead to various pathological processes.
Classification of pathological processes in the cervix
Background Processes
Hyperplastic, associated with hormonal disorders: эndotservykoz (proliferating, simple, cicatrizing, polyp (simple, proliferating, epidermiziruyuschy); papilloma (pokrovnıy gland epithelium Should atypia); leukoplakia (simple form); endometriosis.
Inflammatory: true erosion: cervicitis (acute and chronic colpitis different etiologies)
Post-traumatic changes: breaks; ectropion; scarring of the cervix; cervico-vaginal fistula.
Precancerous lesions
Dysplasia, It occurs on the cervix intact, or in the background processes (mild, moderately expressed, expressed)
Leukoplakia with signs of atypia cells
Erythroplakia
Adenomatous
Cervical cancer
The most common changes in the vaginal part of the cervix include erosion (true and false, or endocervicoses).
True erosion of vaginal part of cervix - cytological picture
On the true erosion then say, when the vaginal portion of the cervix is devoid of epithelium and exposed her connective tissue stroma. To diagnose the true erosion of cytologic preparations is quite difficult: in them except the white blood cells and red blood cells are found only squamous cells.
Endocervicoses - cytological picture
Occurrence endocervicosis associated with an imbalance of sex hormones, mainly Hyperestrogenism. Development endocervicosis can promote inflammation.
Endocervicoses morphologically characterized the growth in thickness of the vaginal part of the cervix multiple glands and replacing pavement surface ploskoepitelialnoy single in prismatic epithelium.
There are proliferating (progressive), simple and healing endocervicoses as successive phases of the same process.
Proliferating endocervicoses
Proliferating endocervicoses characterized by the development of new iron from cambial elements of the columnar epithelium of the cervical canal.
Simple endocervicoses
For simple endocervicosis characterized by the absence of new evidence of the formation of the glands.
Healing endocervicoses
When the healing endocervicoses there is a growing of stratified squamous epithelium of cervical cancer in the rejection and death of the columnar epithelium, These glands lining, or reserve cell metaplasia of columnar epithelium in the flat and replace them with the sprouting ottorgsheyusya columnar epithelium glands.
In some cases the squamous epithelium is not growing into cancer, and covers them from above, closing the mouth of the places of their ducts. Setserniruemaya these glands mucus, without going outside, accumulates inside, forming retention cysts. Cysts can be very small, and large, reaching the size of a hazelnut and greatly deformed by this vaginal part of the cervix.
In cytological preparations at endocervicoses except leukocytes and erythrocytes detected planar and cylindrical epithelial cells, and metaplazirovannye cells round or oval with a centrally located nucleus and basophilic, clearly contoured cytoplasm. Cells are located separately, groups and in the form of glandular structures.
When replacing parts of endocervicosis stratified squamous epithelium can be observed pathological actinic - leukoplakia. There are simple leukoplakia (with presence in cytological preparations denuclearized scales) and with signs of malignancy in the parabasal and basal cells. For the differentiation they need to be examined histologically.
One variety is endocervicosis ectropion, characterized by replacement of scars, formed on the spot tears vaginal part of the cervix during labor, glandular tissue. Ectropion is considered the most dangerous background diseases. In cytological preparations prevails columnar epithelium, is a group in the form of glandular structures.
The group also includes background diseases erythroplakia and Cervical polyps.
Erythroplakia cervix - cytological picture
When erythroplakia cervix smears parabasal cells of the upper and lower layers with signs of moderate dysplasia.
Cervical polyps – cytological picture
Cervical polyps It is usually located in the cervical canal, but may be on her vaginal parts, The surface of the polyp is covered with slime cylindrical epithelium.
There are adenomatous and adenomatous polyps, fibrous. Glands and their slime lined cylindrical epithelium. In smears found the individual cells of the epithelium, their group structure and zhelezistopodobnye.
For cytology necessary information about the place taking material (from the surface of the polyp or site endocervicosis), as the differential diagnosis endocervicosis and adenomatous polyps for cytological preparations causing considerable difficulties.
Cervical dysplasia - cytological picture
According to the wording of the WHO Expert, under dysplasia understand the substitution of the epithelium cells, which observed varying degrees of atypia, loss of polarity or lamination, wherein no change stroma.
There are mild, moderate and pronounced dysplasia of the cervix.
Mild dysplasia of cervical epithelium
Histologically there is a low degree of dysplasia basal cell hyperplasia in the lower third of the thickness of the epithelial layer. At the same time there is a violation of vertical isomorphic cells. There are some ugly cells; mitotic activity increases.
In cytological preparations are found intermediate and superficial cells, often with several enlarged hyperchromatic nuclei and irregular chromatin structure. The cytoplasm can be vacuolar degeneration. There are dual-core cells and mitotic figures.
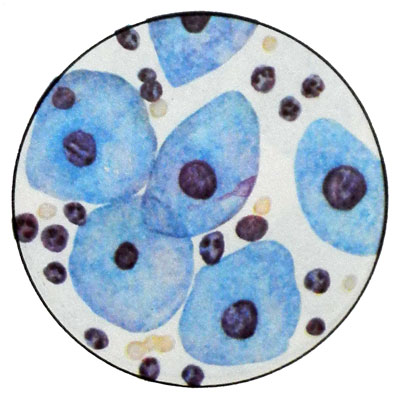
Moderately severe epithelial dysplasia of the cervix
Histologically, in this case the changes apply to the half thickness of the epithelial layer. Observed more pronounced changes in cell morphology and location. The number of cells in mitosis. In cytological preparations are found all layers of cells with a predominance of intermediate cells and parabazaliyh upper and lower layers with moderate polymorphism of nuclei and an increase in, by the presence of nucleoli, coarser grained structure of nuclear chromatin. The cytoplasm of the cell clearly defined, basophilic
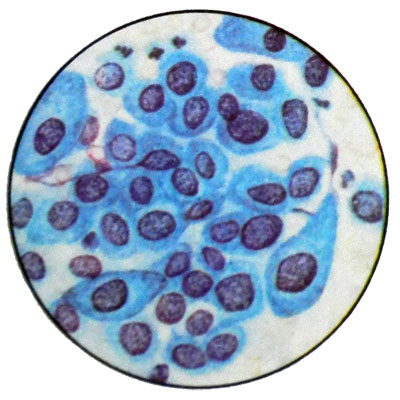
Severe dysplasia of cervical epithelium
With this degree of dysplasia changes in the epithelium are more significant and apply to most of the epithelial layer thickness. Maintain the normal structure of the cells of the surface layers.
In cytological preparations found parabasal cells of the upper and lower layers and intermediate cells, characterized by cellular and nuclear polymorphism. The nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio is more significant changes in the direction of the nucleus. Kernels hyperchromic, chromatin structure in these places is uneven and grainy.
Contours nukleolemmy (nuclear envelope) rough, nucleoli are often absent. Perhaps the presence of cells and multi-core. Sometimes there are giant cells with one or two large nuclei.
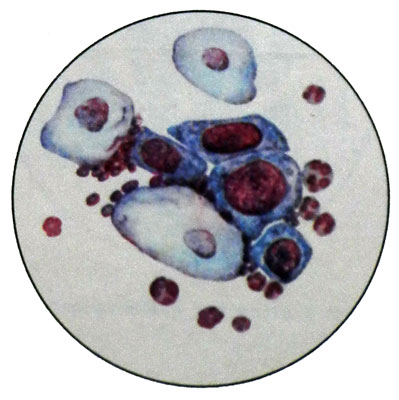
Material for cytological examination is taken by light scraping around the external opening of the cervical canal across the surface of the vaginal portion of the cervix.
Intraepithelial cervical cancer - cytological picture
Intraepithelial cervical cancer (Carcinoma and Citu) develop at any age,, but more often in 30-40 years. Depending on the source, there are three varieties of intraepithelial cancer:
- Cancer of the stratified squamous epithelium;
- Cancer of the reserve cells;
- Cancer of the columnar epithelium.
In the case of Carcinoma and Citu of stratified squamous epithelium, that is the most common, the process is localized in the vaginal portion of the cervix, and a macroscopically looks erosion or laceration of the cervix, like recently given birth women.
Microscopically, at the junction of columnar epithelium in the stratified squamous epithelium found unique changes in the cervix, expressed in violation of the layers of the epithelium, Thesis- complexing it, the appearance of different size and shape of cells with large hyperchromatic nuclei and clearly visible nucleoli. Sometimes in the cytoplasm of such cells and collects keratohyalin they begin Stratum.
Intraepithelial cancer diagnosis can be put only in the event, when all epithelial layer consists of tumor cells, and the basement membrane is not broken.
Cases have also been described, when changes develop in the deep layers of the squamous epithelium with the defeat of the basement membrane, and surface layers may remain unchanged. Usually, intraepithelial carcinoma clearly demarcated from the adjacent epithelium, but in some cases there is a gradual transition into a dysplasia, that, in turn, returns to normal epithelium.
Intraepithelial carcinoma cells of columnar epithelium It develops extremely rare and poorly understood. In this form of intraepithelial cancer in cytological preparations are found round or oval cells of medium size with large hyperchromatic nuclei, occupying nearly the entire cell. In the nuclei contains 1-2 nucleoli. The cytoplasm has a narrow rim of basophilic. Cells are located mainly in the form of small groups and formations zhelezistopodobnyh. In the area of the cancer is found abundant intraepithelial infiltration of lymphoid cells and histiocytes.
Currently, most researchers consider carcinoma in citu cancer, which after a while can become invasive during pregnancy and lactation in the cervix may occur resembling intraepithelial carcinoma epithelial changes, which will eventually disappear.
Cervical cancer - cytological picture
Cervical cancer It can occur at any age, most often in parous women 40-50 years. Clinically, the disease may initially be asymptomatic, Then there are whites, recurring acyclic spotting from the vagina, pain.
By the nature of growth are distinguished exophytic, endophytic and mixed cancer.
Exophytic cervical cancer
Эkzofitnыy cancer It grows into the lumen of the vagina, its appearance resembles a cauliflower. As a result of the collapse of the tumor on the vaginal part of the cervix is formed a deep ulcer crater.
Endophytic cervical cancer
The most frequently observed эndofitnыy cancer. It is characterized by the growth of deep tissue and ulceration.
Mixed cervical cancer
At mixed form tumors combines both types of growth. Sprouting cervix, Cancer can spread to the parameters, vaginal wall, uterine body, and then to the bladder wall, rectum. Metastases observed in the regional lymph nodes (pelvic).
Squamous (epidermal) cervical cancer
Approximately 90-95 % of all cancers of the cervix squamous, or epidermal carcinoma. Material for the study with the lesions is applied on glass slides and stained after drying at Pappenheim (Romanovsky, Leishman et al.).
At highly differentiated squamous (stratum) Cancer (5% of all cases of cervical cancer) in preparations against a background of white blood cells and normal epithelial cells of the vagina are observed polymorphic tumor cells flat epithelial stratum with hyperchromatic large nuclei, which are located separately, groups, and part of a "cancer pearls" and rod-shaped structures.
This cancer is diagnosed primarily in native preparations.
Squamous moderately differentiated (partially stratum) cancer characterized by a great variety of forms of epithelial cells (round, Oval, Lozenges, bulavovydnыe, a racket, irregular shape, ribbon-like, and so on.), different values of the cells, preferred cores hyperchromia, steatosis and partial cytoplasmic keratinization, phenomena including early keratinization immature parabasal cell type.
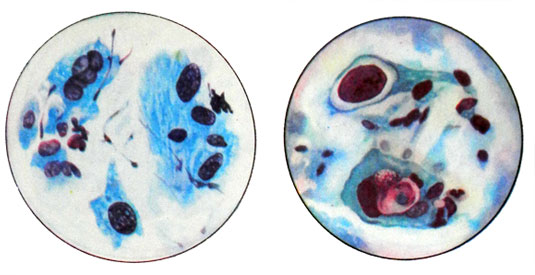
This cancer is diagnosed in native, and in stained.
Low-grade squamous (neorogovevayuschy) cancer. Often in preparations of cervical cancer occur round or oval squamous cells of considerable size with large, intensely colored hyperchromatic nuclei. Bare nuclei can be detected with one large or two or three nucleoli. Signs of keratinization in tumor cells expressed barely. The cells in mitosis are rare. Cytological picture is more informative in stained.
In small cell neorogovevayuschy poorly differentiated cancer cytological preparations are present in atypical epithelial cells of small size round, elongated and spindle-shaped with a relatively large nuclei. Spindle cells are characterized by rod-shaped cores. Can meet and large bright cells. As with neorogovevayuschy moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma cytological picture is more informative in stained.
Cervix adenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma cervical cancer is rare and cytological picture is not different from those in the body of the uterus.
Classification of the degree of change in the vaginal epithelium
When preventive examinations of women to determine the degree of change in the vaginal epithelium smears for early detection of cervical cancer have been proposed various classifications. The most recognized of these is classification by Papanicolaou, according to which the cytological picture of vaginal smears can distinguish five groups surveyed.
The first group - undoubtedly negative (with respect to cancer), smears unmodified cells of vaginal mucosa.
The second group - negative, smear - single cells with minor changes in the nucleus or cytoplasm. Their presence may indicate inflammatory and regenerative processes (slabaya dysplasia). You must control study.
The third group - doubtful, smears detected cells, which can not be attributed with certainty to any normal, or tumor. Having to repeatedly re-investigation, and for the stability of the cytological picture - and histological examination (moderate dysplasia).
The fourth group - suspicious for malignancy, smears, individual cells with signs of malignancy (severe dysplasia). Need histological control.
The fifth group - a positive for malignancy (cancer), smears are a lot of tumor cells. Need histological control.
