Liver tumors
Distinguish Primary liver tumors, emerging from the local tissue, and metastatic, constitute the bulk of liver tumors. Malignancies metastasized to the liver penetrate substantially hematogenous route and from any authority. The most common metastatic gastric cancer, pancreas, esophagus, intestines, breast and t. d. Besides, possible metastasis of melanoma and choriocarcinoma.
Primary liver tumors rare, more often they are epithelial, less connective (sarkoma, hemangioendothelioma et al.) origin.
Epithelial tumors develop from hepatocytes (gepatoma) and of the interlobular bile ducts (kholangioma). Both can be benign or malignant. There are hepatocellular adenoma and carcinoma, and adenoma and cancer of the bile ducts (cholangiocellular). But often have difficulty recognizing certain forms of tumors, especially a histological form of primary liver cancer, as mixed, or gepatoholangiotsellyulyarny, cancer. Besides, in the liver may develop undifferentiated carcinoma and hepatoblastoma.
Benign tumors of the liver very rare. Clinical manifestations of them in most cases, the minimum. Sometimes the tumor accidentally found during laparotomy.
Gepatoma (hepatocellular adenoma)
The tumor is most often found in children. In adults it is rare. The punctate revealed the same type of tumor cells, morphologically similar to normal cells of the liver. Sometimes cells accumulate neutral fat, often glycogen.
Hepatocellular (hepatocellular) cancer
Hepatocellular (hepatocellular) Cancer affects mainly the elderly. The development of cancer on the background of liver cirrhosis is usually observed in men, without signs of cirrhosis - women. In men, it occurs twice as often, than in women.
Depending on the nature of growth are distinguished gnarled form of liver cancer, which is characterized by the presence of multiple sites of different sizes, massive form (tumor affects the whole stake) and diffuse, in which tiny tumor nodules scattered throughout the body.
Microscopically, there are five types of hepatocellular carcinoma:
- Trabecular;
- Tubular;
- Psevdozhelezisty (acinar);
- Clear cell;
- Mixed.
Trabecular hepatocellular carcinoma
When the trabecular type of cells are arranged in the form anastomosing cords. Education bile in swelling occurs.
Tubular hepatocellular carcinoma
Tubular type of hepatocellular carcinoma is characterized by the formation of glandular tubular structures, the lumen of which is filled with bile. True glandular form of primary liver cancer are not found.
Psevdozhelezisty (acinar) hepatocellular carcinoma
For psevdozhelezistogo, or acinar, such as hepatocellular carcinoma peculiar appearance melkodolchatyh structures, with or without bile.
Clear cell hepatocellular carcinoma
Clear cell type of cancer is represented by large polygonal cells, containing fat and glycogen. The cell nuclei and large, round shape. The cytoplasm is abundant, light, zernistaя.
Mixed hepatocellular carcinoma
Mixed tumor represented by a combination of plots, having different histological structure (tubular,trabecular and clear cell type). In cytological preparations tumor cells often retain significant similarity with normal hepatocytes, unlike their larger nuclei, Some polymorphisms and size.
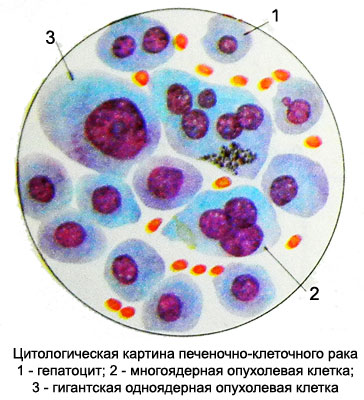
Abundant cytoplasm of cancer cells, homogeneous or contains fine grain. The contours of the cells are not always clearly delineated, possible formation of syncytial structures. When tubular, sometimes, psevdozhelezistom and type of cancer cells can produce bile. In cytological preparations, it is found in the center of zhelezistopodobnyh structures. Did the presence of tumor cells bile pigments. In the field of metastasis (lymph nodes, Lung et al.) also notes choleresis, has diagnostic value.
Bile tumor cells is an indication of the high degree of differentiation. With the accumulation of lipids in their cytoplasm, or glycogen cancer cells can acquire the structure of clear cell elements. A large number of giant multinucleated cells with bizarre hyperchromatic nuclei allows you to regard this as a giant liver cancer- or polymorphonuclear cell. Because of the similarity of cell hepatocellular carcinoma with normal hepatocytes diagnosis is sometimes causes difficulties. However, polymorphism and increase of cancer cells, the presence of large nuclei with a loose structure and large nucleoli, as well as a large number of multi-core cells indicate their atypical. These morphological changes in cancer cells allow them not only to differentiate normal hepatocytes, but with the liver cells when expressed regenerative processes, which are characterized by a significant hypertrophy and the appearance of the two- and triple-form.
Undifferentiated liver cancer
Undifferentiated cancer - primary, characterized by the presence of large cells cytological preparations rounded shape. Kernels take them almost the entire cell, nucleoli are not always visible. Basophilic cytoplasm, as a small rim.
Kholangioma – Adenoma of the bile ducts
The punctate tumor revealed a large number of identical cells or cubic prismatic epithelium with signs of mucus secretion. Arranged in isolation cells, clusters and groups, often in the form of papillary structures.
Cholangiocellular cancer - cancer of the bile ducts
On histological structure is adenocarcinoma. In cytological preparations rounded cells revealed a small and medium sized. The nuclei of large, oval or rod-shaped with a large number of chromatin, It contains nucleoli. The cytoplasm is homogeneous, light, basophilic. The cells do not emit cholangiocellular cancer bile, and mucus. They are located in isolation, clusters and groups, often in the form of structures zhelezistopodobnyh.
Mixed liver cancer – Holangiogepatotsellyulyarny, gepatoholangiotsellyulyarny or liver cancer
It is characterized by the presence of elements in cytological preparations, and hepatocellular cancer cholangiocellular.
Hepatoblastoma
Hepatoblastoma - a primary malignant tumor of the liver, consisting of epithelial cells. It can be mixed epithelial-mesenchymal character. There are usually in children younger than two years, therefore many researchers consider it a congenital neoplasm.
Microscopic examination of tumor punctate epithelial cells there are two options - small monomorphic (embryonic) with nuclei, occupying nearly the entire cell, and large bright cells with large nuclei and abundant cytoplasm rather, full of fat or glycogen. Large cells resemble cells of hepatocellular carcinoma, they are sometimes called "fetal". Light cell bit. The main hepatoblastoma cell mass consists of small cells, that at a value less normal hepatocytes.
The punctate hepatoblastoma cells are located separately, clusters and groups, often in the form of papillary and rozetkopodobnyh structures.
There mitotic figures. Sometimes you can notice signs of bile. When mixed in the formulation found hepatoblastoma cells of epithelial and mesenchymal origin (outstretched, fusiform, Process cells, fibroblasts and others.).
Carcinosarcomas liver
Rarely, It consists of cells or cholangiocellular hepatocellular cancer and sarcomatous cells.
