Bladder tumors – papilloma, cancer – state and urinalysis
Bladder tumors are about 3 % All tumors. The bulk of bladder tumors comprise epithelial neoplasms, which may be benign (papilloma) and malignant (cancer).
Inverted papilloma
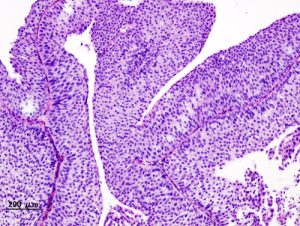
Grossly the tumor is a small or medium-sized education. It may be a single or multiple, located on a thin stalk and reminding fern. Sometimes the legs are short and wide papilloma, while the tumor becomes similar to the sponge.
The basis of the villi is loose connective tissue, well vascularized and infiltrated by lymphocytes, gistiocitami, plasma cells (plazmocitami) and eosinophilic granulocytes. Some authors consider the infiltration of these cells as a manifestation of regressive changes in the tumor, others - as a reaction to the introduction of the virus, others - as the immunological reaction. Connective rod coated with 4-5 layers of papilloma transitional epithelium, cells which are arranged perpendicular to the basal membrane, Polymorphism of weakly expressed. On the surface of the papillae cell papilloma flatter.
Between the cells somewhere visible droplets of mucus, giving positive PAS-reaction. Mucus is on the surface of fibers in the form of fibers and films. The presence of cells in mitosis indicates accelerated tumor growth, not its canceration.
Transitional cell papilloma has a tendency to recur. Recurrent papilloma may be typical or atypical structure. Atipichnaya, or proliferative, inverted papilloma (atypical fibroepitelioma, maligniziruyuschaya papilloma) has shorter, sosochki, sometimes merging with each other. Epithelial cells are polymorphic, violated their arrangement in the form of series. There are cells with large hyperchromatic nuclei. It increases the number of cells in mitosis. Weakens tumor cells similar to the transitional epithelium, and gradually swelling maligniziruetsya.
Urine in the bladder papilloma may be different, in the absence of bleeding, and even normal cystitis. Protein usually occurs in a small amount, it is considered that it falls into the urine through the villi of the tumor. When hematuria protein in the urine increases.
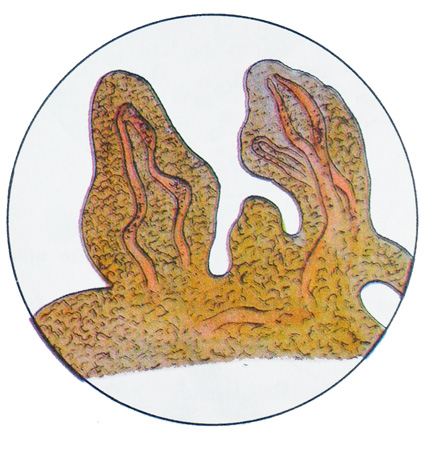
Microscopic examination of sediment observed normal or somewhat increased number of white blood cells, many unmodified erythrocytes, fibrin can be detected and even particle tumor. Macroscopic particles tumor may be brownish or brownish-grayish patches. Under the microscope, they have a papillary structure, at low magnification resemble fern leaves, contains blood capillaries, and a large number of similar cells, arranged in regular rows, and no signs of atypia.

When proliferating transitional cell papilloma cells are a bit messy, different size, some of them with large hyperchromatic nuclei and nucleoli hypertrophied; cytoplasm of cells is being fatty and vacuolar degeneration.
Transitional cell carcinoma
Transitional cell carcinoma is more common, than other types of tumors of the bladder. Grossly it reminds papilloma, but generally it is not on the leg, and on a broad basis; papillae tumor short, Folded, It often resembles cauliflower. On the surface of the tumor is often visible areas of necrosis and ulceration.
Stroma tumor composed of fibrous connective tissue, equipped vessels. Epithelial cells differ pronounced polymorphism and atypia. This cells with large hyperchromatic nuclei and nucleoli hypertrophied, which one nucleus can be many. In the cytoplasm of cells observed fatty degeneration and vacuolization. Epithelial cells of various shapes and sizes, arranged randomly. The tumor has infiltrative growth, germinating even in adjacent organs.
Transitional cell papilloma and carcinoma is considered a single process, which begins with the formation of papillary tumor with a typical arrangement of cells. Then there are cell atypia and polymorphism, but without infiltrative growth (proliferative transitional cell papilloma), and, finally, cancer develops with all the signs of malignancy. Malignancy of cell atypia often begins with a leg tumor.
Other histological forms of bladder cancer are metaplastic. It:
- squamous cell carcinoma of the degree of differentiation;
- less often – adenocarcinoma;
- even rarer - undifferentiated carcinoma.
For bladder cancer is characterized by hematuria, which is observed within 1-2 days, often single, but sometimes repeated after indefinite period. Upon accession to the underlying disease cystitis urination becomes frequent and painful.
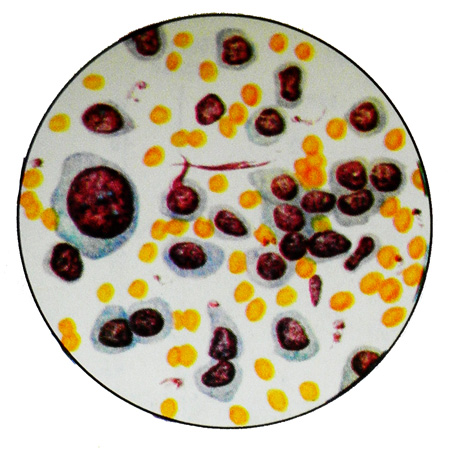
When papillomatoznyh transitional cell carcinoma urine may initially be normal, but later almost constantly observed microhematuria. Protein content, leukocytes, red blood cells and cells of various epithelial transition. Papillae with vessels and epithelium are less common, than with transitional cell papilloma, since they are more open and less dense. Upon detection of a malignant epithelial buds can assume the presence of papillary, t. it is. papillary, TCC. More often than not found the papillae, and individual cells and groups, falling into the urine as a result of desquamation and necrosis of the tumor mass.
Cells TCC polymorphic, various sizes, but most large, mono-, two- and multicore. Kernels large hyperchromic. There are cells in mitosis. The cytoplasm of cells in native preparation yellowish (As in normal epithelial cells) and contains graininess, and formulation, stained by Pappenheim, often takes on a pinkish-brown color.
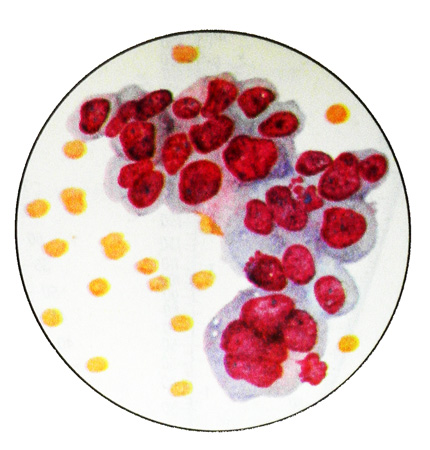

These features make it possible to differentiate the cells of transitional cell carcinoma with squamous cell carcinoma of polymorphonuclear, basophilic cytoplasm which does not contain inclusions. The urine can get necrotic shreds with vessels, but no cancer cells, in these cases to determine their origin with an accuracy not possible. Such necrotic patches may contain crystals gematoidina.
In other histological forms of bladder cancer in urine can enter not only the individual cells, and pieces of tumor tissue. The urine of the same nature, as with transitional cell carcinoma. The draft can be found members, characteristic of squamous cell carcinoma - a highly differentiated, with "pearls" and rods (Stratum), moderately differentiated (polymorphonuclear cell partial keratinization) and poorly differentiated (neorogovevayuschy), as well as adenocarcinoma and undifferentiated cancer. The vessels in the tumor tissue pieces of these are almost never found.
Urine in Kaposi same, as well as in cancer, but macroscopically visible tumor translucent particles, resemble fish meat. Microscopic examination of these particles are found elements miosarkomy.
Elements of malignant tumors found in the urine is relatively rare. For cytological diagnosis of bladder cancer are investigated bladder washings. It uses an isotonic sodium chloride solution or 15 % ethyl alcohol at 1 % novocaine (weak solutions of alcohols enhance exfoliation of tumor cells and have a weak retaining action), or 2 % boric acid solution. We study also punctate bladder tumor, and at papilloma - punctate her legs, where first of all there is the growth of infiltrating transitional cell papilloma.