Tumors of the intestines – The cytological diagnosis of diseases of the alimentary canal
Intestinal mucosa is lined with a single layer of prismatic cells (cylindrical) epithelial, containing kistochkovuyu edges. Among the epithelial cells is a large number of goblet cells, mucus.
Rectum in the lower divisions are divided into three zones: columnar, intermediate and skin. In the area of columnar mucosa is lined with multi-layer cubic epithelium, in the interim - stratified squamous neorogovevayuschy, in the skin - a multilayered epithelium orogovevayushim. Go multilayer cubic stratified squamous epithelium is made dramatically in a zigzag line, and the transition to the epithelium of the skin type - gradually, In the intermediate area of the rectum are isolated sebaceous glands. In the area of skin sebaceous glands are attached to hair and sweat glands apocrine type.
According to the International histological classification of tumors of the intestines, the following types of tumors:
Epithelial tumors
Benign
- Adenoma
- Adenomatous
Malignant
Adenocarcinoma
- Mucinous adenokartsnnoma
- Mucinous carcinoma
- Ploskokletochnыy cancer
- Zhelezisto-ploskokletochnыy cancer
- Nedifferentsirovannыy cancer
- Neklassifitsirovannыy cancer
Karцinoid
Non-epithelial tumors
Benign
- Leyomyoma
- Neurinoma
- Lipoma
- Lipomatosis
- Vascular tumors
Malignant
- Leiomyosarcoma
- Other
Hematopoietic and lymphoid tumors
Unclassified tumors
Secondary tumors
Neoplastic lesions
Polyps
Yazvennыy colitis
Endometriosis
Other
Material for cytological diagnosis of malignant tumors of the intestines can be obtained only after removal of their contents. For this purpose the day before the study patient give castor oil, and in the morning do a cleansing enema.
Cytological diagnosis of malignant tumors of the small intestine possible during operations, or tumor punktatsii.
Where, when the tumor is located near the anus, material for cytology take the cotton-gauze and out of the finished product in the form of prints or thin strokes. The material for cytology is also scraping with a spatula from the surface of the tumor, slime, remaining on a sigmoidoscopy at rectoscopy or gloves doctor after rectal digital examination. When infiltrating tumors produce transrectal needle biopsy.
With the high location of the tumor (colon, the descending part of the colon) You need to get flush with the mucosa. To do this, the patient makes an enema siphon warmed isotonic sodium chloride solution (500-1000 Ml). The washings were collected, settle for 1 no, centrifuged and the pellet. From preparing drugs for sediment cytology. For the preparation of medicines are also used scraps of tissue and blood clots.
In preparations, prepared from the wash water of the colon, usually detected goblet cells round or oval with a small mature, eccentrically located nucleus and foamy pale basophilic cytoplasm.
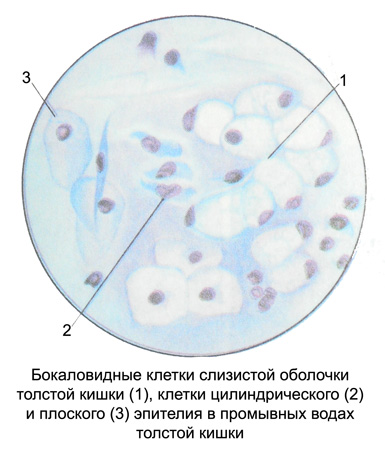
Cylindrical and prismatic epithelial cells are very rare. Usually, found cell surface squamous epithelium, derived from the skin area of the rectum. Among the epithelial cells of the mucous membrane of the intestines is dominated by degenerative forms with the indistinct contours of cytoplasm, sometimes in the form of cells or fragments of naked pyknotic nuclei. Very rarely in the washing waters identified small round cells of the deeper layers of the epithelium.
In addition to the epithelial cells in the washing waters are always observed neutrophilic granulocytes. In inflammatory processes are many and they have the form of clusters. Sometimes there are eosinophilic granulocytes, lymphocytes and histiocytes. The presence of erythrocytes indicates bleeding, which may be due to an injury in the capture of the material. Careful removal of the contents of the intestines food remains are few and do not interfere with microscopic examination.
Benign proliferative processes in the epithelium of the colon (giperplaziya, polyp, adenoma) can often be accompanied by a violation of the differentiation and maturation of cylindrical cells, t. it is. displaziej. Although dysplasia - a reversible process, the progression of her cancer is in a transition. Therefore, cytological diagnosis of dysplasia, conducted during outpatient examination of patients, It helps prevent the development of colon cancer.
There are three degrees of epithelial dysplasia of the colon.
When mild dysplasia architectonic glands colonic mucosa preserved, the mucous membrane is covered with a single-row cylindrical epithelium. Cytology detected a moderate increase in the columnar epithelium cells and their nuclei, hyperchromia cores. The number of goblet cells is reduced, reduced the size of their.
Moderately severe dysplasia It is characterized by a significant structure and cellular atypia, a deformation of the glands of the mucous membrane, reducing the amount of stroma. Columnar epithelial cells of the colonic mucosa increased, several polymorphs. The nuclei are displaced to the apical part of the cell, increased, hyperchromia expressed. There mitotic figures, goblet cells are almost absent.
To severe dysplasia characterized by violation of architectonic glands and cellular polymorphism. In cytological preparations revealed proliferating epithelial layers of different sizes. In the larger cells are large, eccentrically located nucleus, which are viewed nucleoli. Chromatin hyperchromic. The cytoplasm is narrow, nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio shifts vmstoronu core. There mitotic figures; goblet cells substantially lacking.
The process of dysplasia can spread to other (neighbors) cell, which leads to mucosal thickening, change the pattern of intestinal crypts. In the area of dysplasia can occupy the entire intestinal crypt or localized only in its upper sections. Epithelial dysplasia state can cover the polyp or adenoma. Besides, may occur against a background of dysplasia of single or multiple polyps or adenomas. Proliferative polyps or sigmoid colon are the most common in people over the age of 40 years.
When dysplasia colon goblet cells observed increase their proliferation, they increase, It accumulates in the cytoplasm of a large number of secret, which gives them a bright appearance. The nuclei of these cells pushed to the periphery of the secret, flattened, hyperchromatic.
Dysplasia of goblet cells can be observed in the proliferative processes of inflammatory genesis, and when the primary adenoma. In the transition of dysplasia of goblet cells in the malignant process occurs signet ring cell carcinoma.
Adenocarcinoma
From various malignancies most common gut adenocarcinoma, arising from the glandular epithelium. Often formed quickly ulcerate flat knot. Introduced ulcer becomes irregular in shape with raised edges or overhanging.
Depending on the degree of malignancy of adenocarcinoma of the colon can be highly, moderately- and low-grade.
When high-grade adenocarcinoma cytology detected glandular like structures oval or round shape, consisting of malignant changes of cylindrical or cubic cells, arranged in one or more rows.
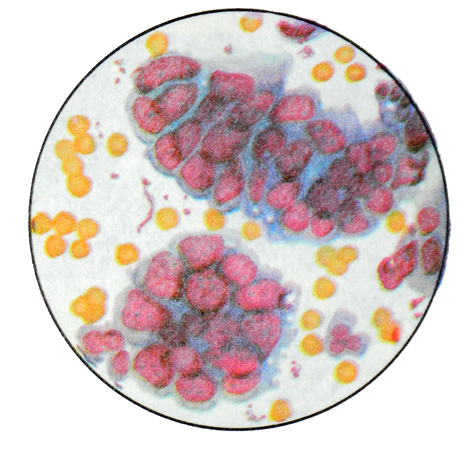
Cores of elongated or irregular shape, hyperchromatic, at different levels. There is also the location of the malignant changes rozetkopodobnoe cells, which form the core outline of the circle, and the cytoplasm rays converge toward the center.
To moderately- and low- differentiated adenocarcinoma characterized complexes and malignantly transformed cells symplast, which are randomly polymorphic kernel.
Colon cancer
Colon cancer can occur in the form of glandular villous polyps and growths. Frequently cancer localized in the sigmoid colon, rarely in a straight line.
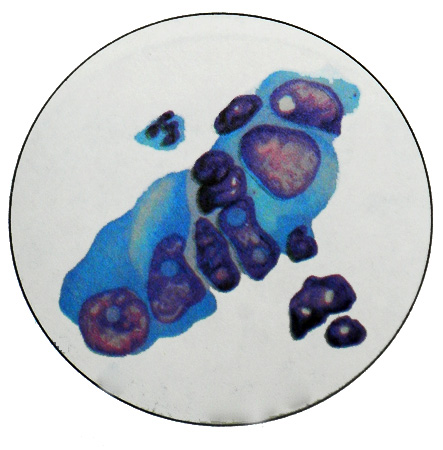
Cancer, developing from a polyp, It grows in the intestine in the form of a mushroom tumor, sitting on a thick stalk or broad base. He is also quick to ulcerate. With the growth of the tumor can be formed around the circumference of the circular constriction and obstruction (kolytsevidnыy cancer). Also exophytic form of tumor growth occurs and diffuse infiltrative. In these cases the thickening of the bowel wall, edematous mucosa first, unevenly raised, she later ulcerate and form an ulcer crater.
When a polyp malignancy cytology detected fragments tore tissue, which consists of glandular structures, lined by columnar epithelium, disposed in one, at least - in two- three rows. The nuclei of these cells are in the center, oval, hyperchromatic, with lots of mitosis. In some places there is atypical and disorderly arrangement of cells, having enlarged nuclei (one or more) hypertrophied nucleoli.
From adenocarcinoma this form of cancer characterized by less pronounced polymorphism.
Along with adenocarcinoma found its varieties - blennogenic, sometimes solid cancer.
Solid cancer
When cytology meet sharply polymorphic atypical cells with centrally located bright large nuclei, Have nucleoli. Most cells are found in a state of degeneration. Cells are arranged solid fields. In this form of tumor glandular structures are not formed.
For slime cancer characterized by the presence of mucus, which may be located intra-, and extracellularly, Although formed only inside the cell, It displaces the nucleus to the periphery of the cells and gives signet ring shape. In the glandular tumor cells can be so much mucus, complexes that individual cells are suspended therein. Often among the mucus cells identified, presented bare nuclei of large size with large nucleoli. Mostly unable to detect traces of pale basophilic cytoplasm.
Extensive fragments of tumor tissue are often detected in the mucus from the swab or gloves doctor transrectal digital examination.
Other types of colon cancer
Sometimes when there is a tumor in the lower portion of the rectum cytology can detect elements of squamous cell carcinoma of varying degrees of differentiation. Detection in native preparations bulbs of malignant transformed cells, rods and single atypical cells indicates the presence of well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma. Identify sharply polymorphic squamous cells, arranged separately or in small groups, with large and very large, often hyperchromatic nuclei and signs characteristic of keratinization squamous cell carcinoma with moderate differentiation.
When undifferentiated squamous cell carcinoma found concentrations of various sizes moderately polymorphic tumor cells, having enlarged oval or round nuclei, some of them are revealed nucleoli. The cytoplasm of these cells is basophilic.
Occasionally found dimorphic malignant tumor - glandular squamous cell cancer of the lower portion of the rectum.
Other tumors of the rectum are rare, cytologically they are similar to the same tumors at other sites.
