Nehodzhkinskaya lymphoma
Description of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
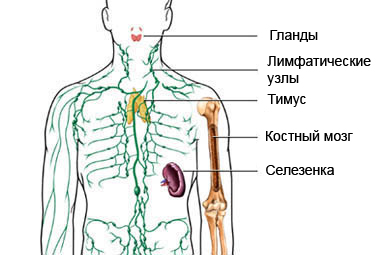
Lymphoma – cancer of the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system regulates the exchange of fluids in the body and helps protect against infections.
Nehodzhkinskaya lymphoma – common name many types of lymphomas. There are several different types of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. These are based on cell type, which develops cancer. Treatment is prescribed according to the type of lymphoma.
In general, different types can be divided into two groups:
- Benign (or slow-growing) lymphoma;
- Aggressive (Malignant) lymphoma.
This type of cancer is different from Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Cancer occurs, when the cell is negative changes, which are transmitted to other cells. They begin to divide and grow as tumors. If the tumor is malignant, This cancer. Cancer cells can invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body.
Reasons for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
Reasons for non-Hodgkin lymphoma is unknown. Maybe, with this form of cancer can be related mutations in the DNA, that occur after birth . Mutations can occur as a result of exposure to radiation or chemicals, cancer-causing. Lymphoma may also occur with age or for no apparent reason.
Risk factors for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
For most people,, who develop non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, the study could not determine the exact risk factors, However, the following factors may increase the likelihood of developing the disease:
- Paul: male;
- Age: 60 – 70 years;
- Constant contact with certain types of chemicals (gerbicidы, pesticides, benzene);
- Infections of the immune system, such as HIV / AIDS and Epstein-Barr virus;
- Predshestvuyushtaya radiatsionnaya therapy or chemotherapy
- Chromosomal translocations (DNA in a chromosome is broken and joined to another);
- Celiac disease – celiac disease (glyutenenteropatiya, intestinal infantilism);
- Obesity.
Symptoms of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
Symptoms include:
- Painless swelling of the neck, armpits, groin, or any other lymph nodes.
- Unexplained fever;
- Profuse sweating;
- Constant fatigue;
- Unexplained weight loss;
- Itching of the skin, especially on the legs and feet;
- Red spots on the skin;
- Chest pain or shortness of breath.
Diagnosis of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
The doctor conducts a physical examination of the lymph nodes. Most patsietntov enlarged or swollen lymph nodes result from infection. If infection is suspected, are issued appropriate medication and after a while re-examination is carried out. If the tumor does not pass, We need to do more tests, the results of which determined, whether the patient is ill with cancer:
- Excisional or incisional biopsy of the lymph nodes or tumors. To select a piece of cloth and examined in the laboratory for cancer cells;
- Punktsionnaya biopsy (PB) – a tissue sample taken from the tumor with a fine needle, and investigated in the laboratory for the presence of cancer cells;
- Aspiration (biopsy) bone marrow – a small amount of bone marrow and bone was removed and examined to determine the extent of lymphoma;
- Spinnaya puncture – a small amount of cerebrospinal fluid is taken for examination. This test is often used to determine the extent of lymphoma;
- Immunogistoximija – antibody used, to distinguish between different types of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma;
- Flow Cytometry – biopsy samples treated with fluorescent antibodies and exposed to the laser beam, to determine the cause of swelling of the lymph nodes and / or to determine the exact type of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma;
- Cytogenetic and / or molecular genetic studies – DNA cell lymphoma is checked for deviations;
- Blood tests, to determine the spread of lymphoma;
- Chest X-ray, to find enlarged lymph nodes;
- CT scan (CT) – made pictures of inside the body, to determine the presence of abdominal lymphomas, heads, clean, chest and neck;
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRT) – used, to make pictures of structures inside the brain and spinal cord;
- Positron emission tomography (PET) – a radioactive substance is injected into a vein, and using a special camera can look for lymphoma throughout the body and / or identify swollen lymph nodes;
- Gallium scan – radioactive solution into a vein, and a special camera can look for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma in bones and other organs. This test is useful when looking for tumors, which can not be detected by PET;
- Bone scan – the organism is administered radioactive solution, and it is directed into the damaged bone lymphoma;
- Ultrasonography – It uses sound waves to study the internal organs.
Treatment of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
Treatment depends on the stage of the cancer and the type of. Treatment includes:
Monitoring the development of
For some forms of slow-growing lymphomas, treatment is not necessary. Treatment should, If the tumor begins to cause symptoms, as:
- Weight loss;
- Fever;
- Night sweat;
- Malfunction bodies due to lymphoma.
Treatment should, if the tumor becomes too large, or enters into a malignant.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves the use of medicines, to kill cancer cells. They may be administered in various forms (tablets, injection, and intravenously through the catheter). The drugs enter the bloodstream, pass through the body, and kill mostly cancer kletki.Chasto chemotherapy drugs kill some healthy cells.
Radiation (Radiation) therapy
Radioactive radiation is directed at the tumor from a source, located outside the body, to kill cancer cells.
Bone marrow transplantation
The patient can be used to transplant their own bone marrow. In this case, bone marrow is removed, treated, and frozen. Involves large doses of chemotherapy and / or radiation therapy, to kill cancer cells. After treatment the bone marrow is injected through a vein.
Bone marrow may also be transplanted from a healthy donor.
Peripheral stem cell transplantation
Stem cells – very immature cells, that produce blood cells. They are selected from circulating blood before chemotherapy or radiation therapy. After the treatment, they are administered back to the circulatory system. Of these developing new healthy cells.
Biological Therapy
Used drugs or substances, produced by the body. They increase or restore the natural defenses against cancer.
One type of biological therapy, interferons, may slow tumor growth. Interferons are produced by the human body. They may also be administered externally.
Sometimes drugs or antibodies, are entered directly into the lymph node, added radioactive substances. This procedure allows further irradiate the tumor with radiation.
Prevention of non-Hodgkin lymphoma
For the prevention of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma does not exist effective methods. To reduce the risk of disease,It is necessary to avoid exposure to chemicals, such as herbicides, pesticides, and benzene. If the patient has celiac disease (gluten intolerance), you must adhere to a gluten-free diet (exclude bread, crackers, biscuits, pastry flour and pasta, pashtetы, sausages). This diet will minimize the stimulation of the immune system using gluten.
