Nephrotic syndrome – state and urinalysis
Nephrotic syndrome is a clinical and laboratory syndrome, characterized by massive proteinuria and impaired protein-lipid and water-salt metabolism.
Distinguish adipoid nephrosis, that looks for a change in the glomerular filter, and membranous nephropathy, at which the detected changes of the basal membrane of the capillary loops of the glomeruli.
According to statistics,, the disease affects mainly children, especially under 5 years. The average age of sufferers adults 17-35 years, although the described cases of it from individuals 85 and even 95 years.
Nephrotic syndrome is difficult for a variety of kidney disease in approximately 20 % patients.
Most often it occurs against a background of glomerulonephritis and amyloidosis.
The mechanism of nephrotic syndrome It is still not fully elucidated. Great importance is attached to immunological and metabolic disorders. The most recognized is the concept of immunological origin nephrotic syndrome. It relies on the fact of detection of antibodies to the basement membrane glomerular capillaries.
Pathomorphological Nephrotic syndrome is characterized by an increase in, flabbiness of kidneys. Cortical substance on the cut yellowish (large white kidney). Histology revealed degeneration and necrobiosis epithelial tubules of nephrons: tubules extended, çastïçno epithelium atrophied, partially swollen, with granular hyaline droplet degeneration and vacuolation. The basal epithelial cells seen lipid deposits; wide gaps filled tubules of nephrons sluschivshimisya epithelial cells, fine and hyaline droplet protein mass. Many gialinovыh, grained, hyaline droplet and waxy cylinders. The interstitial tissue high lipid content, especially cholesterol, lipofagov, lymphoid elements.
Changes in renal glomeruli cells nephrotic syndrome relate to podocytes and basal membranes. In podocytes disappear tsitopodii (processes), hypertrophic and swollen body, vacuolization of cytoplasm occurs, violated the trabecular structure of the cells. All of these changes contribute to the leakage of protein transepithelial, passing through the basement membrane. In remission normal podocyte structure restored. Changes in the glomerular capillary basement membrane thickening and are loosening their.
Clinically nephrotic syndrome characterized otekami, proteinuria, hypoproteinemia, hypercholesterolemia, gipotenzieй. The majority of patients in serous cavities formed transudate. Nephrotic otekn loose, easily moved, may increase rapidly, when pressing a finger at them is deepening.
The main symptom is a severe nephrotic syndrome proteinuria. Often it reaches 20-50 grams per day.
The mechanism of proteinuria finally clarified. Do not set the reason for increasing the permeability and capillary basement membrane of the glomeruli. Additional factors in the pathogenesis of proteinuria is considered a violation of tubular reabsortsii protein due to surge of the process. Protein urine identical serum. Most urine contains albumin. It increased the number of α1– и b-глобулинов и понижено содержание a2– и c-глобулинов. Proteins by electrophoresis in starch gel (by Smithies) can be obtained from some patients before 11 fractions (Two fractions prealbumin, albumin, transferrin, tseruloplazmyn, Three fractions of haptoglobin, a2-макроглобулин и c-глобулйн, including lgA, IgM, lgD). From the ratio of the individual protein fractions in serum and urine are judged on selectivity (isolation of low molecular weight proteins) or unselective (allocation of high molecular weight proteins) proteinuria. The sign is the presence of non-selectivity of proteinuria in the urine α2-makrohlobulyna, that the majority of patients corresponds to a heavy defeat nephrons and can be an indicator of refractory to steroid therapy. Nonselective proteinuria may be reversible.
If nephrotic syndrome is observed expressed fermenturiya, t. it is. urinary excretion of large amounts of transamidinase, leucine aminopeptidase, acid phosphatase, alanine aminotransferase, AsAT, LDH and aldolase, what, apparently, It reflects the severity of the tubules of nephrons, especially their convoluted departments, and high permeability of the basement membranes. For nephrotic syndrome is characterized by a high content of glycoproteins in α1 and. especially α2-globulin fraction. From lipoproteins in urine in patients with nephrotic syndrome detected two or three fractions, соответствующие a1, b- и c-глобулинам.
Hypoproteinemia - A permanent symptom of nephrotic syndrome. Total protein levels may decline to 30 g / l and more. In this regard, oncotic pressure is reduced to 29,4-39,8 kPa (220-290 Mm Hg. Art.) to 9,8-14,7 kPa (70-100 Mm Hg. Art.), developing hypovolemia and edema. Elevated levels of aldosterone (hyperaldosteronism) It contributes to enhanced sodium reabsorption (and with it the water) and increased potassium excretion. This leads to disruption of electrolyte metabolism and development in advanced cases of alkalosis.
Hypercholesterolemia It can reach large extent (to 25,9 mmol / l and more). However, although it is common, but not a permanent feature of nephrotic syndrome.
Thus, nephrotic syndrome there is a violation of all kinds of exchange: protein, lipid, carbohydrate, mineral, Water.
The most constant symptom of nephrotic syndrome in peripheral blood is sharply elevated ESR (70-80 mm / h), that is associated with dysproteinemia. Can develop hypochromic anemia. Changes in the number of white blood cells is not observed. The platelet count may rise and achieve a number of patients in the 500-600 F 1 l. In the bone marrow, an increase the number of myelokaryocytes.
The urine is often cloudy, what, obviously, due to the admixture of lipids. Along with this there oliguria with high relative density (1,03-1.05). The reaction of the urine alkaline, due to electrolyte imbalance, leading to blood alkalosis and enhanced release of ammonia. High protein content, can reach 50 g / l. Leukocytes and erythrocytes in urine sediment usually slightly.
Red blood cells maloizmenennye Epitheliocytes kidneys are mainly in the stage of fatty degeneration - very often filled with small and larger lipid droplets can reach large sizes! There hyaline, granular epithelial, fat-grained, waxy, hyaline droplets and vacuolated cylinders in large numbers.
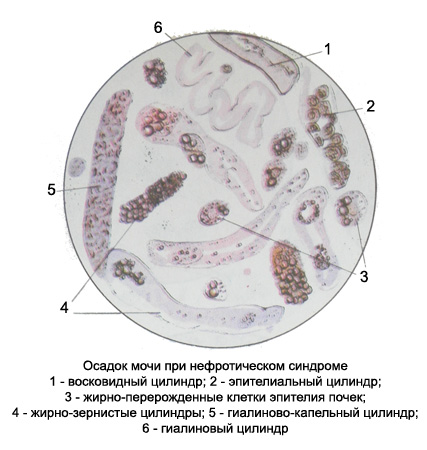
Blood and buropigmentirovannye cylinders for this disease are not typical. In the urinary sediment can be found hyaline balls and hyaline droplet lumps. Crystals can occur cholesterol and fatty acids, lipid droplets.
