Natal (Congenital) teeth: what is this, causes, symptoms, diagnostics, treatment, prevention
Natal teeth; Fetal teeth; Congenital teeth; Predeciduous teeth; Precocious teeth
Natal teeth are teeth, already present at birth. They are different from neonatal teeth, that grow during the first 30 days after birth. These teeth can sometimes cause difficulty in breastfeeding., and can also be a source of concern for new parents.
What are natal teeth?
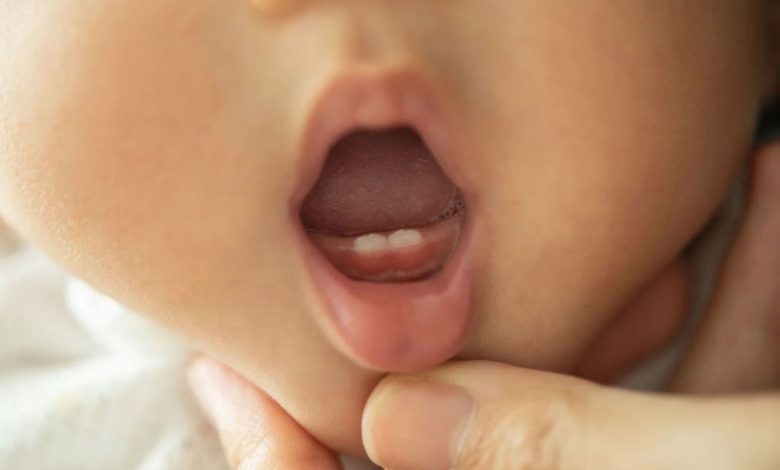
Natal teeth are the primary teeth (or baby teeth), that are present in the mouth of the newborn at the time of birth. Natal teeth can be fully formed and functional, and can only be partially developed. Congenital teeth are usually found in the front of the mouth, although they can be located anywhere in the mouth. Natal teeth are relatively rare, occurring in about one in 2,000 to 3,000 newborns.
Causes of natal teeth
The exact cause of the appearance of congenital teeth is not entirely clear., but several theories have been proposed. Some researchers believe, that congenital teeth can be hereditary, since it was reported, that the disease is inherited. Other theories suggest, that congenital teeth may be caused by an overproduction of dental tissue or an abnormal development of the teeth. In some cases, birth teeth may be the result of hormonal imbalances during pregnancy or may be associated with certain genetic disorders..
Symptoms of natal teeth
The most obvious sign of congenital teeth is the presence of one or more teeth in a newborn's mouth at the time of birth.. These teeth may be fully formed and functional., and can only be partially developed. In some cases, natal teeth may be loose and unstable, what can cause discomfort and difficulty with breastfeeding.
When to contact a healthcare professional
If you notice one or more teeth in your newborn's mouth, you should see a doctor as soon as possible. Natal teeth can sometimes make breastfeeding difficult, and can also be a source of concern for parents. Your healthcare provider can examine your child and determine, whether the congenital teeth cause any problems or need to be removed.
Questions, that your doctor may ask
Your doctor may ask you a few questions, to determine, does your child have congenital teeth and are they causing any problems. Some of the questions, that your doctor may ask, include:
- How many teeth does your child have?
- Where are the teeth located in the mouth?
- Teeth fully formed or only partially?
- Teeth loose or resistant?
- Your baby is having difficulty breastfeeding?
Diagnosis of natal teeth
The diagnosis of congenital teeth is usually based on a physical examination of the child's mouth.. The doctor may also take x-rays., to evaluate tooth development and determine, do they cause any problems. In some cases, your doctor may also do a series of tests., to rule out any underlying disease, which may contribute to the development of congenital teeth.
Treatment of natal teeth
The treatment of congenital teeth will depend on several factors., including the number of existing teeth, their location in the mouth and that, do they cause any problems. In some cases, congenital teeth may not require treatment and may be left in place.. In other cases, extraction of congenital teeth may be required., if they cause difficulty in breastfeeding or if they are unstable and present a risk of choking or injury.
If it is necessary to remove congenital teeth, this can usually be done under local anesthesia.. The procedure is relatively simple and involves the extraction of congenital teeth with a pair of dental forceps.. In some cases, the doctor may decide to remove the birth teeth a few weeks after birth., to allow the gum tissue to mature and reduce the risk of bleeding or other complications.
Home treatment of natal teeth
If your child has congenital teeth, that do not need to be removed, there are several steps, things you can do at home, to ensure his health and comfort:
- Encourage your baby to suckle properly, as this will help keep the birth teeth stable and prevent any problems with breastfeeding.
- Do not expose your child to any source of oral infection, such as contaminated pacifiers or toys.
- Clean your child's mouth regularly, using a damp cloth, to gently wipe away food or milk residues.
- Check, that your child is eating well, to support healthy oral development.
Prevention of natal teeth
Unfortunately, there is no known way to prevent birth teeth. Nonetheless, you can reduce your child's risk of developing oral health problems, by following a few simple steps:
- Check, that your child is eating well, to support healthy oral development.
- Do not expose your child to any source of oral infection, such as contaminated pacifiers or toys.
- Clean your child's mouth regularly, using a damp cloth, to gently wipe away food or milk residues.
- Schedule regular dental checkups for your child as they grow and encourage good oral hygiene habits from an early age.
Conclusion
Natal teeth are a rare medical condition. Although congenital teeth do not always require treatment, it is important to seek medical attention, if you notice one or more teeth in your newborn's mouth at the time of birth. With proper care and attention, you can control your child's birth teeth and maintain overall oral health.. If you have any questions or concerns about congenital teeth, be sure to talk to your doctor.
Used sources and literature
Ball JW, Dains I, Flynn YES, Solomon BS, Stewart RW. Ears, nose, and throat. In: Ball JW, Dains I, Flynn YES, Solomon BS, Stewart RW, eds. Seidel’s Guide to Physical Examination. 10th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2023:chap 13.
Dhar V. Development and developmental anomalies of the teeth. In: Kliegman RM, , St. Geme JW, Bloom NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 333.
