Hereditary microspherocytosis – Anemia, associated with an increased krovorazrusheniem
Hereditary microspherocytosis, known as the disease Minkowski-Chauffard - autosomal dominant inherited disease. It is based on the erythrocyte membrane protein defect, whereby violated their permeability, receives an excess amount of sodium, which leads to swelling of erythrocytes, violation of their ability to deform, cleavage in the spleen of their surface, shortening the duration of their lives and the destruction of splenic macrophages.
The disease was found more than 150 years ago, widely across Europe. On average, one person in 50000 He suffers from a hereditary microspherocytosis, disease occurs much less frequently in Japan and Africa.
In most cases signs microspherocytosis Can not find one parent. There may be cases, when in severe disease in the child, it is detected in the father or mother only in the study of blood smear. In 20-25 % Patients with the most careful analysis of signs of disease in parents did not come to light. It is a variation of the disease, related features of circulation in the spleen, any of the mutations in the germ cells of parents, not suffering microspherocytosis, that there is a relatively rare. All of the patients are heterozygous carriers of the disease gene.
The etiology and pathogenesis of hereditary microspherocytosis
As shown by studies of various authors, in different families of patients can be identified microspherocytosis unequal violations erythrocyte membrane protein structures. Probably, in terms of the molecular defect microspherocytosis - is not one disease, and more, with similar clinical picture. These or other changes in the protein structure leading to erythrocyte membranes it hyperpermeability, passive penetrate through it into the erythrocyte sodium ions. Active transport of sodium from the red blood cells significantly increased at microspherocytosis.
Increased permeability results in the erythrocyte membrane penetration of excess sodium and increased accumulation of water. The spherical shape of red blood cells, and structural features of the protein cause impaired ability of red blood cells deformed in narrow areas of blood flow, eg, the transition from mezhsinusnyh spaces spleen sinuses.
The ability of the spleen to destroy red blood cells is associated with the originality of its circulation. Blood enters the body through the splenic artery, thence to the trabecular artery, and then the central artery of the white pulp. Next, the blood enters the red pulp, consisting of a sine - elongated blood vessels and portions, located between sinuses - the so-called splenic ligament. Most of the blood normally passes through the closed circulation path (venous sinuses), a certain part of it enters the space mezhsinusnye, without stopping them. Mezhsinusnye space spleen splenic ligament crossed reticular cells and fibers, where are the macrophages, involved in sequestration of erythrocytes. In these areas the blood flowing slowly. In other areas of the spleen, where the reticular network is almost absent, blood stream much faster. It is here that extends normal blood, that does not fall through the capillaries in the sinuses.
When microspherocytosis certain portion of blood enters the space mezhsinusnye spleen. There's red blood cells are exposed to a number of unfavorable factors. In mezhsinusnyh spaces reduced glucose and reduce the concentration of cholesterol. All these factors even further promote swelling erythrocytes.
When passing through a narrow gap, such can not be deformed erythrocytes. In addition to their swelling matters breach elasticity, leading to a slow down of red blood cells and promote their stagnation in the splenic ligaments. Ultimately, each red blood cell passes through the narrow gap, sometimes losing a portion of the surface.
Red blood cells, lost part of the surface, can not hemolized. The edges of the dangling portion of the erythrocyte membrane connected, and he re-enters the bloodstream. Erythrocyte persist, despite the defect in the shell, probably, physiological adaptation. As it is known, red blood cell can lose the core, denatured protein particles, iron nuggets, without losing part of the envelope.
When microspherocytosis loss of the membrane and the cell surface leads to a gradual reduction in the size of the erythrocyte. For its destruction is necessary, to the erythrocyte mezhsinusnoe again hit the space and re-passed through a narrow slit in the sinus. Several such cycles leads to the destruction of the red blood cell. In most cases, the erythrocytes are another way, mezhsinusnye passing space. Therefore, they gradually die. When the changes of lipids, especially erythrocyte membrane cholesterol, reach a certain level, red blood cells are destroyed by macrophages of the spleen. Thus, spleen - an organ, not only destroys the red blood cells, but gradually reduced their surface, approximating their death.
Clinical manifestations of hereditary microspherocytosis
Like many other forms of hereditary hemolytic anemia, microspherocytosis characterized predominantly intracellular erythrocytolysis. This causes the clinical manifestations of the disease - jaundice, changes in the facial region of the skull, increasing the size of the spleen, greater or lesser degree of anemia, tendency to form stones in the gallbladder, characteristic morphological changes of erythrocytes, retikulotsitov.
All these features alone are not specific and can occur in other forms of hemolytic anemia. They appear at different ages, depending on the severity of the disease. The most severe course microspherocytosis observed in adolescents and adults. Children find it in the family study of probands. Where, when the disease occurs in childhood with severe clinical manifestations, hold skeletal deformities, especially the skull. Patients identified tower square skull, microphthalmia, changes in dentition, sky high, sometimes shortening little fingers. These symptoms occur in other forms of hereditary hemolytic anemia.
Enlargement of the spleen from minor to severe splenomegaly very typical microspherocytosis. In most cases, uncomplicated microspherocytosis liver enlargement is observed. A significant proportion of patients complaining of pain in the right upper quadrant, due to the formation of stones in the gallbladder and bile ducts - one of the most common severe complications microspherocytosis. Education stones due to the high content of bilirubin in the bile. Therefore, the structure of the stones often bilirubin, but sometimes there are mixed, containing cholesterol.
A relatively rare complication are microspherocytosis leg sores.
Morphological changes in the microspherocytosis characteristic of hemolytic anemia - pallor and jaundice of bodies, hyperplasia in the bone marrow of flat bones and tubular, mainly due to a number of elements of red. In this well-preserved white cells and mega- kariotsitarnogo series.
Laboratory tests at microspherocytosis
The degree of anemia in microspherocytosis may be different. A significant portion of patients with mild anemia expressed: hemoglobin 5,59-6,21 mmol / l (90- 100 g / l). During hemolytic crisis hemoglobin may be reduced to (2,48-3.1 Mmol / l) (40-50 G / l), especially in young children. Hemolytic crises in microspherocytosis often triggered by infection.
Morphological picture of red blood cells in microspherocytosis It is characterized by a tendency to form spherical, decreasing diameter, increasing thickness. When there is no central illumination microspherocytosis, characteristic for normal erythrocytes.
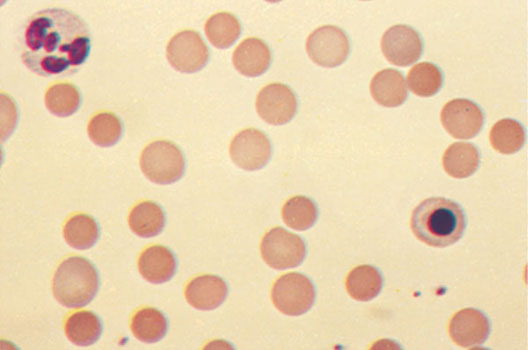
The average diameter of the red blood cells is usually reduced, in the mild form of the disease, it can be normal.
The average volume of red blood cells microspherocytosis when most normal - PL 70-105 (m3). The thickness of the red blood cells, usually, increased - 2.5-3 m (normally 1.9-2.1 microns). Significantly decreases the ratio between the diameter and thickness of erythrocytes (in healthy individuals, it ranges from 3,4 to 3,9). The hemoglobin in red blood cells is normal or slightly elevated. Color index close to unity.
Number microspherocytes It may also be different. Some! they constitute the majority of patients with red blood cells, in these cases usually occur pronounced signs of increased hemolysis. Relatives of the patient microspherocytosis, no complaints, whose disease is detected only with the active examination, most often found small percentage microspherocytes.
Symptom microspherocytosis It is not specific to microspherocytic hemolytic anemia, it often occurs in autoimmune! hemolytic anemia and sometimes with hereditary anemia dizeritropoeticheskoy.
The content of reticulocytes in the microspherocytosis depending on the severity of the disease and the observation period the patient may be different; usually it does not exceed 10 %, However, there are cases, when the number of reticulocytes increased to 50-60 % (After hemolytic crisis). During hemolytic crisis in peripheral blood may appear isolated erythrokaryocytes.
The number of leukocytes in the microspherocytosis most normal, during hemolytic crises observed leukocytosis, sometimes with marked neutrophilic shift. Platelet counts in most cases remains normal.
Lowering the osmotic resistance and increase autogemoliza, correctable glucose, They are not strictly specific to microspherocytosis. They violated in the same or even more in some forms of autoimmune hemolytic anemia and sometimes with hereditary anemia, related enzyme deficiency of red blood cells.
Diagnosis of hereditary microspherocytosis
Substantial assistance in the identification of hereditary microspherocytosis provides application by acid-erythrograms Gitelzon Terskov modification A. AND. Vorobyov. When microspherocytosis acid erythrograms different sharp lengthening of hemolysis, shift of the maximum to the right. The value of the maximum usually not exceeding nebolshaya- 10 %. Money red blood cells from the plasma significantly accelerates hemolysis. This phenomenon is peculiar only microspherocytosis.
Usually, when there is irritation microspherocytosis red growth marrow, thereby changing the ratio leykoeritroidnoe (normal 3:1) - The number of red nuclear elements becomes white or even exceeds it.
The degree of hyperbilirubinemia in patients microspherocytosis It is depending on the severity of the disease and the period of examination of patient. Between hemolytic crisis bilirubin may vary from normal to 50 60 mmol / l. During crises bilirubin level often rises to very high numbers. The degree of hyperbilirubinemia is associated not only with the intensity of the collapse of red blood cells, but with the rate of production of bilirubin in hepatocytes-diglucuronide from free bilirubin. Therefore, under normal liver function and a relatively small increase in bilirubin collapse of red blood cells may be normal.
Naturally, that the bilirubin level and type vary with the complications of hemolytic anemia microspherocytic obstructive jaundice. In these cases, bilirubin increases sometimes up to enormous numbers. Usually, in the urine of patients with bilirubin is not found, however obturapii biliary tract calculi may appear biliru- ʙinurija.
Content urobilin in urine at microspherocytosis, As with other forms of hemolytic anemia, It can be increased. However, some patients reaction to negative urine urobilin, since the amount of it in the urine depends primarily on the functional state of the liver - in normal function it is able to clean the plasma from a significant number of urobilin.
Coombs at microspherocytosis, usually, negative. Available reports of a positive Coombs test at microspherocytic hereditary hemolytic anemia is most commonly associated with errors in diagnosis. However, in rare cases, a combination of hereditary hemolytic microspherocytic and autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Evidence of the presence of this combination is the only detection of hereditary microspherocytosis other family members.
Described isolated cases of severe bone marrow aplasia at microspherocytosis. When hemolytic crisis primarily necessary verification to rule out the diagnosis microspherocytosis connection with autoimmune hemolytic anemia, aplastic crises in which there are significantly more likely. In the literature there are individual descriptions of aplastic crises when microspherocytosis. The work of researchers indicated, that in aplastic crises in patients with sickle cell disease is detected infection by the same virus, parvovirus belonging to the group.
