The morphology of the causative agent of malaria tropica in stained blood
Characteristic of this type is the presence of parasites in the peripheral blood, usually, annular trophozoites - the young stages of the parasite - and gametocytes.
The process of schizogony It takes place in the capillaries visceral; the appearance of the mature schizonts in peripheral blood (until morul) It indicates a critical condition of the patient. Annular trophozoites up 1/5 – 1/6 the diameter of a red blood cell, sometimes they are larger. Their cytoplasm has a clear view of a very thin rim, which can be open-, Then at one end is the core, on the other - a small kariosoma (Ring with two cores). There are 2-4, In rare cases 7-9 rings in one erythrocyte. Sometimes annular trophozoite lies on the edge of the erythrocyte.
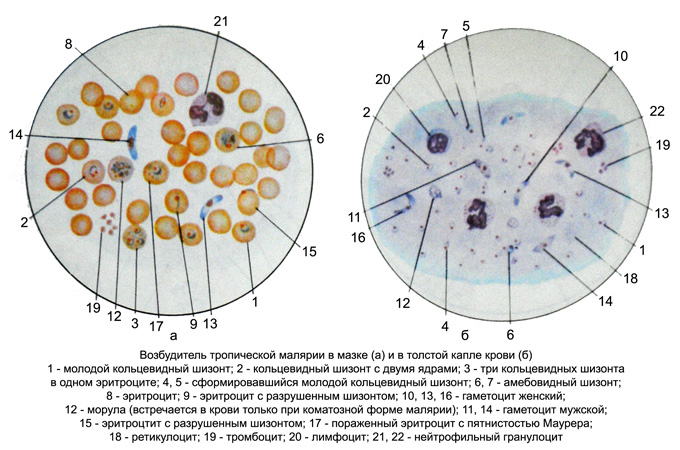
When comatose patient can get into the blood schizonts, their characteristic is early (long before the nuclear fission) accumulation of pigment in a compact pile of dark brown, almost black. Morula 12-24 consists of randomly arranged merozoites.
A few days after the first attack in the blood appear pathogens in the sexual stage (capillaries are formed in the internal organs). These crescent-shaped, with rounded ends, They are in the middle of the core. Women gametocytes larger, They have a compact red nucleus, surrounded by the pigment in the form of grains, blue cytoplasm. In the male gametocytes the core of a large and loose, pinkish hue, cytoplasm light blue, pronounced perinuclear area. Gametocytes lie freely between the cellular elements of the blood, sometimes they are found in the erythrocyte, of which only the rim, noticeable in the form of a pale strip of concave gametocyte.
Infected erythrocytes does not differ from normal. Sometimes they visible Maurer's clefts - Some (5 -10) specks pink-purple.
