Microscopic examination of the cerebrospinal fluid
Determination cytosis
In cerebrospinal fluid of healthy individuals contained a very small number of cells. The clinical significance have mainly leukocytes (lymphocytes). To count of white blood cells do not interfere erythrocytes, They destroy them by adding undiluted cerebrospinal fluid 1/10 parts of acetic acid fuchsin. Magenta colors nucleated cells in red. For painting of leukocytes using the reagent Samson (mixed 30 ml glacial acetic acid, 2 ml of liquefied phenol, 2 ml of an alcoholic solution of fuchsin 1 : 10 and topped 100 ml distilled water). Reagent resistant, good stain cells and within a few hours keeps them from cytolysis.
Apply as a solution, comprising 5 ml 10 % acetic acid 0,1 Mr. metilvioleta. It is less stable, cells stain blue.
Due to the cytolytic properties of cerebrospinal fluid to count the number of cells should be immediately after taking. The liquid is metered into the tube or micropipette drops in proportion 10 parts of cerebrospinal fluid and 1 part colorant solution and left for 10-25 minutes to dye cells. For breeding can be used mixer leukocytes. Cells cerebrospinal fluid very quickly stick to the walls of the tubes, so liquid, box in vitro, before the study must be thoroughly mixed rotational movements between the palms.
To calculate the cell count is used Chamber Fuchs-Rosenthal. Counting produce throughout the grid through 5 min after filling the chamber. Number of cells 1 L is given by:
X=(A*11)/(3.2*10)
wherein X - number of cells in 1 l; A - number of cells, counted on the surface of the screen; 3,2 - Volume of the chamber; 11/10 - Dilution.
Allowed registration of the counts as a fraction, eg 14/3, where 14 - The number of cells counted in the chamber, 3 - Rounding chamber volume. With a large number of cells is sufficient to count them in one half of the grid and the number of received double. With a pronounced pleocytosis (a significant increase in cell number) allowed to count cells 16 Small squares and multiply that number by 16.
In the absence of the Fuchs-Rosenthal chamber can be used Counting chamber Goryaeva with a significantly lower capacity, therefore it is counted cells at least three squares, calculate the arithmetic mean and multiply it on 1,2. Factor 1,2 obtained from the formula
X=(A*11)/(0.9*10)
where 0,9-capacity chamber, 11/10 - Dilution.
When counting the cells in the cerebrospinal fluid of undiluted one of the first drops, arising out of the puncture needle, placed in a Fuchs-Rosenthal and determine the number of cells, as stated above.
Normally, the number of cells (lymphocytes) in 1 l cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles of the brain and cerebellar brain tank is 0-1, and liquid, obtained by lumbar puncture - 2-4.
Children under the age of three months 1 l cerebrospinal fluid is found to 20-23 cells, up to one year - 14-15, up to two years - 11-14, from two to five years - 10-12, from five to seven years, 8-10, seven to ten years - 6-8, more than ten years - 4-5.
When meningitis, tumors of the brain abscess and the number of cells in the cerebrospinal fluid increases.
In the study of hemorrhagic cerebrospinal fluid in some cases it is necessary to establish its true cytosis. For this purpose the Friedman's method: hemorrhagic fluid gain reagent Samson to determine cell count and isotonic sodium chloride solution for counting the number of red 1 l cerebrospinal fluid.
For Example, number of cells in 1 l - 20, the number of red blood cells - 3600. The number of red blood cells and white blood cells recognize the patient from the general analysis, performed before lumbar puncture. For Example, in 1 ml of blood 4 200 000 erythrocyte, 7000 leukocytes. Hence one has to leukocyte 4200000/7000 = 600 erythrocytes.
To obtain the true value of cytosis equate:
on 600 red blood cells - 1 leukocyte;
on 3600 erythrocytes - X leukocytes, Consequently,
X=3600/600=6 leukocytes.
True cerebrospinal fluid cytosis 20-6 = 14 cells 1 l.
Application of this method is limited, since cerebrospinal fluid with a considerable admixture of blood is not suitable for such a study.
Determining the number of erythrocytes in the cerebrospinal fluid It is set to establish the severity of the patient's intracranial hemorrhages.
In the presence of 1 l 2000-5000 erythrocytes cerebrospinal fluid becomes pink, 900-1000 Erythrocytes - only slightly opalescent. The colorless liquid can be detected by the lower red blood cells. The clinical significance is the increase in the dynamics of the level of red blood cells.
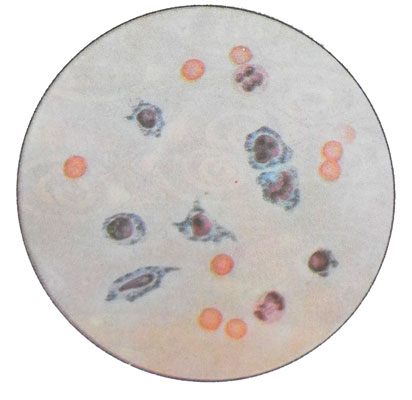
Cell differentiation cerebrospinal fluid held in the counting chamber in the form of native and stained.
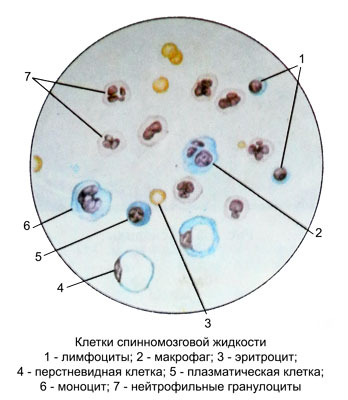
At high magnification (eyepiece 10X or 15X, 40X lens) in the counting chamber paying attention to the amount of cells, form, the location and size of the nuclei, the presence of inclusions in the cytoplasm of. It is easy to differentiate lymphocytes, neutrophilic granulocytes, macrophages. Normally, in the cerebrospinal fluid containing only lymphocytes.
For complete characterization of the cellular composition of cerebrospinal fluid studied stained preparations. Cells were stained fluid worse, than blood cells. There are several ways of coloring: by Rosina, Romp, Papanicolaou, Alekseev, May Gryunvalydu, Pappengeymw.
Determining the nature of the method of fluorescent microscopy pleocytosis
Skim coated glass slide and a drop of cerebrospinal fluid mix it with a fluorochrome dye (a mixture of aqueous salt solutions of acridine orange and rhodamine in the breeding 1:20000). The mixed drug is examined under a fluorescent microscope ML-2 in the blue-violet light in the visible spectrum, using combinations of excitation filters: FS 1-4, FBS 14-4, BS 8-2 and the locking filter LS-1 immersion lens. As neflyuorestsiruyuschego immersion oil used for research dimethyl (orthophthalic acid dimethyl ester).
In the dark background of the field of view and lymphocytes polynuclears easily identified by the green glow of the cytoplasm. Count row 100 cell, given the number of lymphocytes and neutrophils.
Lymphocytes different from the nature of neutrophils nucleus (glybchatoy structure with orange inclusions) and bright green fluorescence.
Neutrophilic granulocytes have a clear structure, their nuclei chromatin diffusely lit, uniform bright- green. Cytoplasmic yellow- green, it scattered brick red granules.
In cases of minor cytosis native cerebrospinal fluid is centrifuged and the precipitate study.
Fluorescent microscopic examination of cerebrospinal fluid makes it easy to conclude that neutrophil, lymphocytic or polymorphonuclear cell nature pleocytosis.
Morphological characteristics of cells of cerebrospinal fluid
Lymphocytes
In cerebrospinal fluid of healthy humans found small and medium lymphocytes (1-2 1 l) size of 4-6 microns. This round-shaped cells with a large nucleus and glybchatym very narrow cytoplasm.
When lymphoid Pleocytosis (tuberculous meningitis, cysticercosis) along with small and medium large lymphocytes appear (8-9 M), occasionally it is possible to detect cells with direct fission.
The number of lymphocytes (together with other cells) increases in cerebrospinal fluid in brain tumors, During chronic meningitis. When neurosurgical diseases increase in the number of lymphocytes in the postoperative period occurs after increasing the number of neutrophils and indicates a favorable outcome.
Plasma cells
Plasma cells can be detected in cerebrospinal fluid only when the current long inflammation in the brain and meninges. Morphology plasma cells such as, in blood or bone marrow punctate.
This round-shaped cells with eccentrically located nucleus and intensely colored, basophilic cytoplasm. In some cases the amount may reach their 26%. There are plasma cells in the postoperative period and sluggish course of reparative processes in brain injury.
Gistiocitы
In a normal cerebrospinal fluid are sometimes found in the form of single copies.
The stained preparations histiocytes have a large core and a relatively narrow cytoplasm. The quantity of cells 7 to 10 m, round or irregular shape. The core of bean or incorrect blade form, normohromnaja. Nucleoli are visible in native preparations with phase contrast microscopy.
When tuberculous meningitis in cerebrospinal fluid revealed a large number of histiocytes, spaced apart and clusters, their cytoplasm basophilic, painted more intensively.
According to available data, some types of glial cells can transform into histiocytes. A large number of histiocytes is detected in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients, underwent surgery on the brain or spine (which indicates an active tissue reaction and normal healing wounds), and in individuals, suffering from tuberculous meningitis and cysticercosis in the sluggish current inflammation. When brain tumors with invasion into the subarachnoid space or histiocytes in the ventricular wall can appear in the cerebrospinal fluid in conjunction with the altered cells and macrophages, which is typical for the emergence around the tumor reactive zone.
Macrophages
Macrophages are formed from a single- endothelial cells and multi-arachnoid mater and monocytes. Elements of endothelial arachnoid mater is separated from the syncytium and become rounded cells, possessing amoeboid movement and penetration into the cerebrospinal fluid.
Macrophages actively engulf and digest the cells and other elements, falling into the cerebrospinal fluid in pathological processes, contributing to its purification. The inclusions in the cytoplasm of macrophages differentiated easily in the chamber and in stained.
Macrophages phagocytose erythrocytes, destroyed or unmodified neutrophilic granulocytes, fat droplets, gematoidina crystals, etc.. Often in the cytoplasm of the macrophage vacuoles of various sizes are available, or one large vacuole, which occupies almost the entire cytoplasm, while the core is shifted to the periphery. In such cases, the cell has the form of ring - cricoid macrophage.
Normally macrophages into the spinal fluid absent. Their appearance in the normal cell count indicative of hemorrhage or inflammation in the central nervous system. A large number of macrophages in the cerebrospinal fluid in the postoperative period indicates the active remediation (positive outlook). A small number of macrophages or their absence when expressed Pleocytosis - an unfavorable prognostic sign.
Granular balls – foam cells
Granular balls (foam cells) Macrophages are large with multiple inclusions of fat droplets in the cytoplasm.
This is most often the cells rounded shape, magenta colored in dark brown color. In the treatment of spinal fluid Sudan III granular balls painted in orange-red.
Detected in the cerebrospinal fluid in contact with liquid in it from cysts of different etiologies, the decay of brain tissue (with drops of fat), sometimes in the postoperative period, in certain brain tumors (kraniofaringiome, ependymomas and others.). If the tumor is located near the ventricles, the granular balls often detected in cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles. The source of granular balls are microglia, and oligodendrocytes, the cells of the outer shell of vessels and arachnoid.
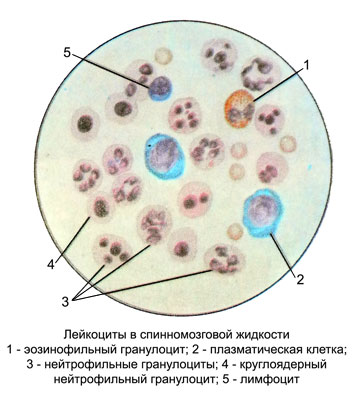
Neutrophilic granulocytes
Neutrophil granulocytes in the cerebrospinal fluid similar to blood neutrophilic granulopitami, their cytoplasm (in the counting chamber and native preparations) often stretched or has a protrusion (pseudopodia). This diversity of cells observed in the first 10-15 minutes after taking the cerebrospinal fluid and indicates the preservation of neutrophilic- the ability of granulocytes to move. Characteristic is a segmented nucleus, the number of segments in which varies from two to five; stab neutrophil granulocytes are rare.
When storing the cerebrospinal fluid neutrophilic granulocytes changed before, than other cells. The nuclei of neutrophil granulocytes can be lysed or segments are rounded, with clear contours, connected by a thin bridge; later they take the form of individual pellets. Microphage, which is stored only one core segment rounded shape, in appearance resembles Loevit cell. There swollen neutrophilic granulocytes with indistinct contours of segments, occupying almost the entire cytoplasm. In stained preparations can observe all stages of the collapse of neutrophilic granulocytes - swelling of the core to the complete destruction of the cell structure, when the contours are not visible cytoplasm, and core segments are shapeless, consisting of soft mesh chromatin. Membership of these cells to neutrophilic granulocytes can be set only by the reaction to peroxidase: the presence of green-yellow or brown granules in the cytoplasm of the destroyed.
Sometimes, in the cerebrospinal fluid found neutrophilic granulocytes with pyknotic nucleus in the form of lumps of irregular shape hyperchromatic.
Neutrophil granulocytes appear in the cerebrospinal fluid with hemorrhages in the subarachnoid space, inflammatory diseases of the nervous system, after neurosurgical operations. The presence of neutrophilic granulocytes in blood in the cerebrospinal fluid indicates inflammation of the meninges.
The predominance of neutrophils unchanged evidence of acute inflammation.
Sudden the appearance of neutrophilic pleocytosis seen in breaking the abscess under the lining of the brain.
When abscess, Located deep in the brain tissue, usually observed expressed mild pleocytosis with a predominance of lymphocytes.
When the attenuation of inflammation in the cerebrospinal fluid appear degenerate forms of neutrophilic granulocytes.
The presence of altered and unaltered neutrophils is characteristic of the ongoing inflammatory process. It should be taken into account, that unmodified neutrophilic granulocytes appear in the cerebrospinal fluid in admixture of fresh blood, in such cases, corrective definition cytosis.
Eosinophilic granulocytes
Eosinophilic granulocytes in native samples of cerebrospinal fluid differentiate with other cells by the presence of a characteristic large shiny grit, filling the cytoplasm. Cells with two-bladed kernel rare, often observed mononuclear form. Morphology in stained eosinophilic granulocytes same, in blood. The cerebrospinal fluid often found destroyed eosinophilic granulocytes.
Contents of eosinophilic granulocytes into the spinal fluid at ranges from cysticercosis 1 to 46%.
The occurrence of meningitis as a complication of arachnoiditis tsistitserkoznogo is accompanied by neutrophilic pleocytosis and a decrease in the number of eosinophilic granulocytes. For abstsedirovaniya echinococcus bubble in the brain characterized by the presence in its content of neutrophil and eosinophil granulocytes, that serves as an auxiliary feature in differentiating it from the abscess. Sometimes a large number of eosinophilic granulocytes can be found in the contents of the cysts tumors of the brain and spinal cord (neuroma, kraniofaringiome, ependymoma, cancer metastases in the brain). The marked increase in the number of eosinophilic granulocytes in the cerebrospinal fluid can be observed after ventricular tsisternoskopii.
After the removal of brain tumors with active wound surgical wound increases the number of eosinophilic granulocytes, that can be regarded as a local allergic reaction to the trauma of the meninges and the absorption of the products of tissue decay.
The modified cells and shadow cells
Thanks cytolytic properties of cerebrospinal fluid cells, contained in it for a long time, retain only the contours of the cytoplasm and nuclei of residues. To determine their morphological affiliation is not possible. In most cases these changes are subject to neutrophilic granulocytes, sometimes it is the cells of malignant tumors. Easy to undergo cytolysis arachnoid cells and ependymal ventricles.
Tissue basophils are found in the spinal fluid after neurosurgery.
Cells arachnoid mater in the cerebrospinal fluid
Cells arachnoid mater (arahnoэndoteliya) - A single layer of epithelium cells, they can be differentiated as a counting chamber cell count, and in stained, prepared from sludge cerebrospinal fluid. This relatively large irregularly shaped cells or rounded with a relatively small circular or oval nucleus, a centrally located.
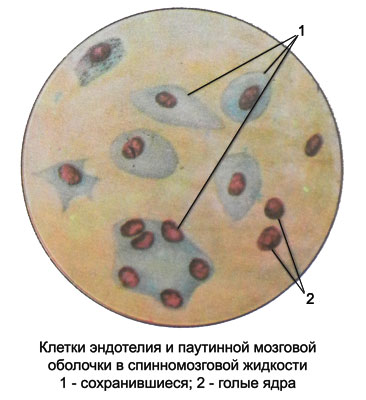
The cell nuclei are stained Hypochromic, and the cytoplasm - pale- or grayish-blue color, thus it is often uneven contours and contains inclusions of particles phagocytosed (fat droplets, cellular elements, vacuole). The cytoplasm of the cells of the arachnoid mater often destroyed, in such cases are detected characteristic of the nucleus and cytoplasm fragments. Chromatin has melkopetlistuyu cores or grain structure, sometimes much one blue nucleolus. The size of the nuclei of 5 to 19 m.
The presence in the cerebrospinal fluid of unit cells of the arachnoid is not yet evidence of pathology, as these cells line the subarachnoid space and, exfoliating, fall into the cerebrospinal fluid. Increasing the number of cells observed in the arachnoid arachnoiditis, brain cysticercosis. The contents of the arachnoid cysts are found in separate locations arachnoid cells and their symplast as groups of nuclei of different sizes and color intensity, surrounded by a pale cytoplasm without clear boundaries between cells.
The cells of the choroid plexus
From the choroid plexus of the ventricles into the spinal fluid can enter polygonal, rounded, sometimes large cylindrical (15-19 M) cell. Small (4-5 M) Located in the center of the nucleus, or eccentrically, hyperchromatic, eosinophilic cytoplasm, intensely colored. In the cytoplasm of the cells of the choroid plexus has graininess, sometimes in the form of inclusions and clumps, size 1-3 microns, round or irregular shape, greenish or bluish color. Some cells may be detected or captured by the red blood cells vacuolar.
The cells of the choroid plexus is most often found in fluid from the ventricles of the brain.
Cells ependymal ventricular cerebrospinal fluid in the brain
Cells ependymal ventricular cerebrospinal fluid in the brain, obtained by lumbar puncture, It is easily destroyed in the cooking process and staining. In stained smears they have the kind of education, consisting of oval nuclei with delicate structure. In some cells preserved cytoplasm surrounds the nucleus in the form of a narrow border.
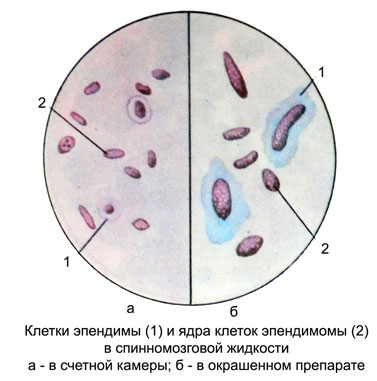
The fluid from the ventricles of the brain are the most common ependymal cells with preserved structure, morphologically resemble the cells of the arachnoid mater, but the core of their painted paler and have more tender, homogeneous distribution of chromatin. The poles of the oval ependymal cells often pointed, The cytoplasm has a grayish hue. There are separately located and large clusters of cells, which can not be determined by the boundaries of the individual cells.
