Multiple myeloma – Myeloma
There are the most frequently encountered diffuse focal forms of multiple myeloma, diffuse, multiple-focal and rarely occurs visceral form.
Multiple myeloma develops most often between the ages of 45 and 65 years., It occurs with equal frequency in both sexes. In the literature there are reports of a familial disease multiple myeloma, as well as cases of benign paraproteinemia and multiple myeloma in the same family. When cytogenetic analysis of myeloma cells can be detected quantitative (aneuploidija) and structural (deletion, translokaciâ) changes, It is non-specific for multiple myeloma, as they are observed in other hematological malignancies.
The development of the disease can last for years, according to different authors - from 12 years before 20 years or more.
Clinical symptoms of multiple myeloma
Clinical symptoms of the disease is closely linked to changes in various organs and systems, and disorders of protein and mineral metabolism.
The defeat of the bone causes pain, tumors and fractures. Most often affects the flat and short bones (ribs, vertebrae, skull, Grudina), rarely - epiphysis of the long bones. The growth of the tumor tissue is accompanied by destructive changes. Often, a sharp pain fractures occur. Tumors in the form of focal growths of various sizes may extend beyond the bone.
If they puncture sometimes found myeloma cells. As a result of osteolysis myeloma, mobilization of calcium from the bones. However, for a long time their number in the blood of patients is normal, and hypercalcemia is observed in only 20-40 % patients, mainly in the terminal stage of the disease, especially when azotemia.
In strict bedrest patients there is a growing process of osteolysis, leads to a dramatic increase in the amount of calcium in the blood. Reducing the level of calcium in the blood as a result of cytogenetic therapy confirms the pathogenetic link hypercalcemia and myeloma osteolysis.
On radiographs of bone defects found, corresponding in shape and size of the myeloma tumor. The most characteristic is the X-ray of the skull ("Leaky Skull"), where the defects in the round and oval shows alarms as if eaten or forced punch. Similar changes can be observed in metastases of malignant tumors in the bones of the skull, and in cases, when overgrown arachnoid granulation mater give the X-ray centers of enlightenment rounded shape.
Characteristic for multiple myeloma and radiographic changes in the spinal column in a focal or diffuse osteoporosis. The vertebrae in this flattened, wedge-shaped or lenticular, may take the form of a bow, eventually getting kind of fish vertebrae. When the diffuse form of multiple myeloma can be identified radiographically diffuse osteoporosis without bone defects. Roentgen forms of multiple myeloma (in the absence of any changes in the bones) account for about 10 % of all cases of multiple myeloma.
Plasma cell infiltration can be found in almost all the internal organs. Increase liver or spleen observed in 5-13 % patients. However, only half of them increase in these organs and lymph nodes due to the myeloma cell infiltration, wherein the myeloma cells are also contained in peripheral blood (plasma cell leukemia). In other cases, enlarged liver or spleen due to myeloid metaplasia with mielemiey sometimes erythrokaryocytes appearance in the peripheral blood.
In early disease changes in the peripheral blood is not detected. The number of white blood cells and also normal leukogram, although in some cases it may be noted neutropenia with relative lymphocytosis and neutrophilia with a shift to the left to myelocytes and even younger forms. Neutropenia is usually associated with receiving cytotoxic drugs. In most forms of multiple myeloma is often marked by an absolute monocytosis and individual plasma cells are found, except leukemic form, in which the myeloma cells in a large number of outputs in the peripheral blood. Most often, this mielomnokletochny leukemia attributed to chronic diseases, Acute plazmoblastoz very rare. With the development of myeloma patients develop anemia, Pathogenesis is not fully elucidated.
Anemia, usually, normohromnaja. The number of reticulocytes is not elevated. Sometimes in severe anemia in the peripheral blood appear normocytes. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate is increased in most cases of multiple myeloma, except non-secretory myeloma, and myeloma Bence-Jones (disease light chains), flowing with low secretion paraimmunoglobulinov. Platelet count long normal, though sometimes at the beginning of the disease is observed hyperthrombocytosis.
The study of bone marrow in multiple myeloma provides an opportunity for 90-96 % cases detected myeloma cells, which, depending on the stage of the disease and forms (diffuse, diffuse alopecia, alopecia or multiple) or may be positioned in a uniform infiltration, or, it occurs more often, private islands in the mass of myeloid elements. Such islands myeloma cells can be detected in the formulations at low magnification microscope.
Myeloma cells may resemble plazmoblasty, proplazmotsitы and plazmotsitы. Especially characteristic is the presence of two, three- and a large number of myeloma cell nuclei of different sizes.
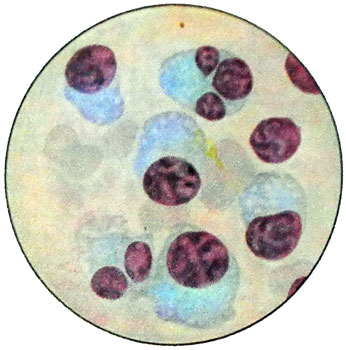
Depending on the predominant cell type distinguish myeloma-plazmoblastomu, mielomu-plazmotsitomu. Education and abnormal secretion of protein cells plasmacytoma now proven. Isolation of tumor cells in blood by secretion occurs golokrinnym, t. it is. the type of single-celled cancer.
Syndrome protein pathology in multiple myeloma proyavlyayetsya gipyerparaprotyeinyemiyei, which develops due hyperglobulinemia.
The level of albumin decreases, and accordingly reduced the albumin-globulin ratio up to 0.6 to 0,2. Increased blood viscosity, observed spontaneous agglutination of red blood cells in the form of rouleaux, sedimentary positive protein reactions, delay hemolysis phenomenon when Wasserman.
Characteristics globulin at mielomnoй Illness
The most important and specific criteria of multiple myeloma - the emergence paraimmunoglobulinov G, A, D, E less (plazmokletochnыh with leukemia) types.
There are the following options for biochemical myeloma:
- G-MM;
- A myeloma-;
- D-myeloma;
- E-myeloma;
- Disease light chains (mikromolekuljarnaja mieloma Benz-Dƶonsa);
- Necekretiruyushtaya myeloma;
- Diklonovaya myeloma.
Rarely (0,5 % cases) vstrechaetsya M-myeloma.
In serum electrophoregram PIg arranged as a narrow, intensely colored cavity between γ- и beta, реже c- и a2-globulinovыmi frakciяmi.
The compact narrow band on electrophoregram paraproteinovuyu called M-gradient.
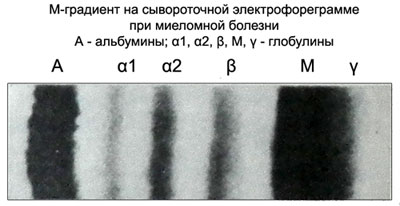
On proteinogram M-gradient has the form of a peak.
Hypergammaglobulinemia reactive nature (rheumatoid arthritis, cirrhosis of the liver, tumor) Unlike M-gradient in multiple myeloma has the form of a broad band. When illness Bence-Jones M-gradient on serum proteinogram missing. PIg only detected in the urine.
Mikromolekulyarny Bence-Jones protein electrophoregram urine presented on a narrow strip between the γ- и a2-globulinami. This figure is absolutely pathognomonic for paraproteinemic Leukemia and is diagnosed in 95 %.
Electrophoresis of serum and urine reveals myeloma in 99 % cases, Cromme nesekretiruyushtey mielomы.
As the tumor increases the number paraproteins, but under the influence of cytostatic therapy is reduced, that is an indicator of the effectiveness of the applied treatment.
The manifestations of multiple myeloma
Paraproteinemic nephrosis - The most common manifestation of multiple myeloma. Constant, persistent proteinuria may be the only symptom of multiple myeloma, its severity varies widely. Even with the significant indicators of proteinuria (to 60 % squirrel) in patients with no edema, hypoproteinemia, hypercholesterolemia and hypertension.
At the heart of renal failure in multiple myeloma is ascending nephrosclerosis (nephrotic kidney scarring), which is caused by the reabsorption of Bence-Jones protein. Additional factors are the loss in the tubules of nephrons Bence-Jones protein with the development of pockets of intrarenal nefrogidroza, and calcification of the kidneys, amiloidoz stromal, plasma cell infiltration and ascending urinary tract infection.
In the pathological process involved the basal membrane and glomerular mesangium.
The urinary sediment in multiple myeloma in the background of proteinuria and hyaline found (less often) granular and epithelial cylinders. Occasionally there may be microhematuria. The reaction of the urine alkaline, in urine appear phosphates. When fractures, pneumonia, stress in patients with multiple myeloma can develop acute renal failure up to anuria. In 15 % patients have paraamiloidoz (cloth paraproteinoz).
For multiple myeloma is characterized by a decrease in the number of normal immunoglobulin. The mechanism of this process is not yet known. Hypogammaglobulinemia often accompanied by a decrease in the formation of antibodies, which affects the sensitivity of patients to infections.
Sometimes (2-5 % cases) in patients with multiple myeloma when cooled below the serum 37 ° C paraproteins precipitate. It - cryoglobulins, proteins, possessing property or gelifikatsii precipitation during cooling serum. They appear in subacute bacterial endocarditis, periarteritis nodosa, chronic kidney disease.
Sometimes, when cooling is enhanced blood viscosity without the formation of visible precipitate. Thus, Laboratory diagnosis of multiple myeloma is based on the detection of bone marrow plasma cells, paraimmunoglobulinov detection in serum and urine, or one of these media. Only in the presence of cells and can think about the diagnosis of plasmacytoma. Additionally, the diagnosis of the disease is an X-ray examination, but the lack of osteodestruktivnyh change does not exclude the diagnosis of multiple myeloma, as well as the positive radiological findings without cytology and can not serve as a basis for the diagnosis of multiple myeloma. Mielomnuyu bolezny (M-mielomu) often necessary to differentiate the disease Waldenstrom.
