Limfogranulematoz (Hodgkin's disease)
Limfogranulematoz - Tumor disease of Leukemia Group. Develop at any age (Men suffer 2.5-3 times more often). The main symptom is a swollen lymph nodes, often in any one area.
At the beginning of the disease are determined by single, moving, not soldered to surrounding tissues lymph nodes, in the future they become dense, soldered together and often form conglomerates. The defeat of the mediastinal lymph nodes are often determined by radiographic methods of investigation, mediastinoscopy with a biopsy or a diagnostic thoracotomy. For detection of lymph nodes, located below the diaphragm, It may be used laparotomy.
During laparotomy performed a biopsy of the lymph nodes available, edge splenectomy and liver biopsy. Histological examination of tissue biopsies to determine the degree of damage of the test and clarify the clinical stage of the disease, it is of paramount importance for the choice of treatment.
As the progression of the process with chlamydia, except lymph nodes, spleen and liver, may be affected practically all organs and tissues: Nervous, bone, lungs, kidneys, gut, endocrine glands, etc..
From Hodgkin extranodal locations is the most common lung disease. According to various researchers, its frequency is from 20 to 45-54 % cases. Often, it is noted and specific pleural. In the pleural fluid revealed lymphoid, reticular cells and Berezovsky-Sternberg.
According to the clinical classification of Hodgkin's disease, depending on the extent of the disease is divided into four steps.
The first stage of Hodgkin's disease
Lymph nodes one area (I) or failure of any organ or tissue (IE).
The second stage of Hodgkin's disease
Lymph nodes of the two or more areas on one side of the diaphragm (II) or the same and localized lesion of any organ or tissue (IIE) on the same side of the diaphragm.
The third stage of Hodgkin's disease
Lymph nodes all areas on both sides of the diaphragm (III), or accompanied by a localized lesion of any organ or tissue (IIIE), or lesion of the spleen (IIIS), or defeat of both (IIIES).
The fourth stage of Hodgkin's disease
Diffuse loss of one or more organs with a lesion or without lymph node involvement.
Localization of lesions in stage IV, histologically proven, denoted by the symbol: L - LIGHT, H - liver, M -kostny brain, O - bone, P - pleura, D - skin, subcutaneous tissue.
Common symptoms of the disease (B):
- Night sweat.
- Body temperature above 38 ° C.
- 3. Weight Loss on 10 % and more for 6 months.
Depending on the presence or absence of one or more common symptoms, t. it is. signs of intoxication, Each stage is divided into two:
- A - in the absence of symptoms;
- D - if present.
Specific changes in the blood picture with chlamydia is not marked. The number of leukocytes may be different. Half of the patients early in the disease observed leukocytosis. Often, especially with involvement of the internal organs, develop leukopenia with relative neutrophilia and shift to the left. Possible and normal white blood cell count.
Neutrophilia is observed regardless of the number of leukocytes and the stage of the disease in 50 % cases. Initially, there may be a stab shift in leukogram, and then appear in the peripheral blood and myelocytes toksogennaya graininess in neutrophilic granulocytes, which increased lipid content, alkaline phosphatase, and a step IV of the process - and peroxidase.
Significant eosinophilia (to 50 % and more) rarely observed (to 3 % cases). In half of the observed decrease in the number of eosinophilic granulocytes, until aneozinofiliya. In the II and III stages of the disease may occur monocytic, which is in the last stage is replaced monocytopenia.
With the progression of the process as a result of toxicity and bone marrow suppression under the influence of cytostatics anemia norm- hyperchromic or character, thrombocytopenia and leykopeniya.
Hodgkin's disease is a characteristic feature increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate (30-40 mm / h, and III and stage IV disease especially - to 70-80 mm / h).
In the study of bone marrow at the beginning of the disease is marked hyperplasia of granular germ hematopoiesis. The number of eosinophilic granulocytes increased, several megakaryocytic cell number unchanged, and the number of red cell number with the growth of intoxication and reduced bone marrow suppression. If it affects the bone marrow punctate tumor in his lymph cells can be detected- granulomas.
Currently, there are different classifications of Hodgkin's disease, trying to link the clinical picture of the disease with morphological changes in the lymph nodes and other organs. Noteworthy morphological classification Lux, Butler and the Hyksos (1966), according to which there are four histological types of Hodgkin's disease.
Lymphohistiocytic version of Hodgkin's disease
Lymphohistiocytic variant is characterized by a predominance of lymphocytes in lymph nodes and histiocytes. When viewing many drugs can be detected isolated small two-bladed Berezovsky-Sternberg cells with a wide light-colored basophilic cytoplasm, as well as single eosinophilic granulocytes and plasma cells.
Nodular sclerosis
When nodular, or nodular, sclerosis lymph node proliferation appear as bands of fibrous tissue. Found Berezovsky-Sternberg cells, their predstadii (Hodgkin's cells) and reticular cells. Berezovsky-Sternberg cells are large sizes, They have a lot of small nuclei or one multiblade core with large nucleoli. Cytoplasmic wide, frothy, light.
Mixed-cell variant of Hodgkin's disease
Mixed-cell variant is characterized by diversity of cellular composition of lymph node. Also lymphocytes, found in preparations of eosinophilic and neutrophilic granulocytes, plasmacytes, reticular cells, Hodgkin cells and typical Sternberg cell Berezovskogo-.
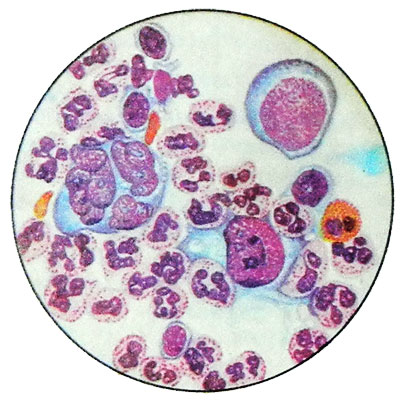
Lymphogranulomatosis with lymphoid depletion
For the option of lymphoid depletion characteristic coarse fiber or a massive expansion of the connective tissue (fibrotic option), the presence of areas of necrosis and a small number of cells of Hodgkin, atypical cells Berezovskogo- Sternberg, a predominance of reticular cells and Berezovsky-Sternberg with moderate sclerosis (reticular option).
Many believe morphology histological variants of the successive stages of development of lymphoid predominance Hodgkin's disease at the beginning of the process until the end of lymphoid depletion of the disease, when the number of lymphocytes decreased significantly.
One of the methods of diagnosis of Hodgkin's disease is a histological and cytological study of drugs. The diagnosis can be considered valid only if it detects a cell preparations Berezovskogo- Sternberg. These cells are multi-specific elements lymphogranuloma. They rounded shape, size from 40 to 80 m, round, bean-shaped nuclei or palmate, is a central or eccentric. In the nuclei of most visible 1-2 very large nucleolus, less fine 5-8. Classic Berezovsky-Sternberg cells dual, wherein the core of the same shape and size, They are like mirror images of each other.
In more mature cells Berezovsky-Sternberg usually have multiple cores. Basophilic cytoplasm, painted in pale bluish or dark blue tone.
Predstadii, or young Berezovsky-Sternberg cells, mononuclear, Smaller. The nuclei of round, centrally located and have two or three large nucleolus light blue, cytoplasm is more intensely colored, basophilic.
When cytochemical study in Berezovsky-Sternberg cells are found glycogen, A nonspecific naftilatsetatesteraza, kislaya phosphatase, RNA-ase and DNA-ase, sukcinatdegidrogeiaza, OVER and OVER-diaphorase, glucose-6-fosfatdegidrogenaza, cytochrome oxidase.
The presence in a punctate lymph node eosinophilic and neutrophilic granulocytes, plasma and reticular cells, lymphocytes, Berezovsky-Sternberg cells, the ratio of which may vary, It creates a mixed picture and allows you to safely put the cytologic diagnosis of Hodgkin's disease. The absence of pathognomonic for Hodgkin's disease cells Berezovsky-Sternberg exclude the diagnosis of the disease, since a similar pattern can be observed in inflammatory and other pathological processes.
Establishing a morphological variant of Hodgkin's disease to determine the approximate forecast. So, when lymphohistiocytic version (the beginning of the pathological process) We can assume a steady flow of disease. In nodular sclerosis possible long duration of the process in the lymph nodes and organs, located above the diaphragm, metastasis to bone. Intoxication symptoms develop later. Mixed-cell variant - the most frequent (in 60 % patients), with an average life expectancy of 3-5 years, It is characterized by more severe than in previous versions. When lymphoid depletion the disease may be rapid and malignant.
The criteria of malignancy include the growth of these indicators, as the ESR, the amount of fibrinogen in the blood, a2-globulin, haptoglobin and ceruloplasmin. Active during the process noted in the cases, If all of these laboratory findings, or at least some of them exceed certain critical values (ESR above 30 mm / h, Fibrinogen ≥ 5 g / l, a2-hlobulynы ≥ 10 g / l, gaptoglobin ≥ 1,5 g / l, tseruloplazmyn ≥ 0,4 Power. ekstiaktsii).
Subject to availability (B) or lack of (A) common symptoms and the presence of (to) or lack of (and) indicators of biological activity there are three groups of patients:
- Aa - with local symptoms (common symptoms are absent, laboratory parameters are normal);
- Bb - a generalization of the process (common symptoms are);
- Ab - with an increase in laboratory values, preceded by the appearance of symptoms of intoxication.
After treatment in patients at Ab indicators of biological activity normalized, in the absence of treatment, these patients go to a group Bb, in which full normalization of laboratory tests after treatment does not occur.
