Dengue fever
Description of dengue
Dengue fever – flu-like illness, which is caused by a virus. The infection is transmitted to humans through mosquito bites. Infected children and infants, may have no symptoms or only slight, influenza-like malaise. Adult patients may develop more serious, a life-threatening form of the disease.
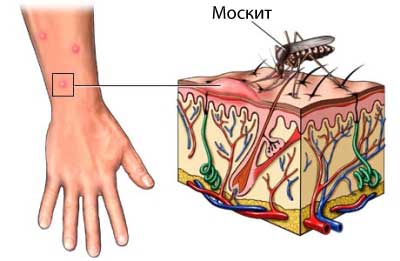
You should contact your doctor immediately, if you suspect, that you have dengue fever.
Causes of dengue
There are four types of dengue viruses, that can cause this disease. Viruses carried by mosquitoes Aedes. When an infected mosquito bites a person, the virus enters the bloodstream. It can then cause illness. The infection is not transmitted from person to person.
Risk factors for dengue fever
Factors, which increases the risk of dengue fever:
- Travel to tropical or subtropical areas, such as:
- Africa;
- India;
- Southeast Asia and China;
- Middle East;
- The Caribbean (including Puerto Rico) and Central and South America;
- Australia;
- Locations in the Central and South Pacific.
Symptoms of dengue fever
These symptoms may be caused by other, less serious diseases. If you experience any of them, consult a doctor.
Symptoms of dengue fever may include:
- Headache;
- Severe pain between the eyes;
- Fever, chills;
- Red throat;
- Nasal congestion;
- Muscle aches;
- Pain in the bones;
- Skin symptoms:
- Erythema;
- Increased sensitivity of skin to touch;
- Skin rash;
- Purple spots on the skin;
- Loss of appetite;
- Nausea;
- Vomiting;
- Enlarged liver and spleen;
- Hepatitis;
- Bad taste in the mouth;
- Minor bleeding from the gums, nosebleeds, blood in urine and stool;
- During recovery:
- Weakness;
- Fatigue;
- Depression.
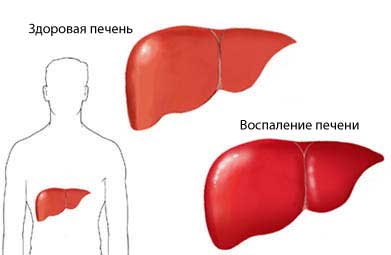
Severe complication is dengue haemorrhagic fever. Its symptoms:
- Dangerously low blood pressure;
- Low pulse;
- Abdominal pain;
- Sweating;
- Pale or blue skin and lips;
- Uncontrolled bleeding (hemorrhage) gums, nose, urinary and / or gastrointestinal tract.
Diagnosis of Dengue
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history, a physical exam. He will also ask about recent travel to tropical areas.
Tests may include the following blood tests:
- Antibody tests – to see, whether the body produces substances, who are struggling with the virus of dengue fever;
- Analysis by polymerase chain reaction reverse transcription (RT-PCR) – for determining the presence and quantity of virus, present in the blood.
Treatment of dengue fever
There are no drugs to treat dengue fever. The treatment is to reduce symptoms and may include:
Bed rest
During recovery you need a rest and postpone work and everyday activities.
Adequate hydration
It is necessary to drink plenty of fluids, to recover liquid, sugar and salt, lost during illness. If you can not drink, fluid may be administered intravenously through a needle in the hand.
Medications to reduce fever and pain
You can use acetaminophen to treat fever and pain. Do not use aspirin, because it can increase the risk of bleeding.
Prevention of dengue fever
To reduce the risk of dengue fever, perform the following steps when traveling in areas of its distribution:
- Try to spend time in places, protected by curtains or air conditioning;
- Wear shirts and pants with long sleeves. Besides, Wear socks and shoes;
- Use repellents. Apply them on your skin and clothes;
- We need to stay indoors or take extra precautions during the increased activity of mosquitoes. Mosquitoes are most active early in the morning and at dusk;
- Mosquitoes breed in standing water. Do not leave for a long time the water in buckets, flower pots or other containers.
