Leptospirosis
Description of leptospirosis
Leptospirosis – a rare and contagious bacterial infection, which can lead to very serious consequences. The infection is caused by bacteria of the genus Leptospira. Leptospirosis is most common in warm, tropical conditions and can affect any part of the body. With the rapid and proper treatment, forecast, usually, good. If untreated, complications may develop, that can potentially be fatal.
Causes Leptospirosis
Leptospirosis may occur after contact with fresh water, wet or damp soil or plants, that have been contaminated by the urine of an infected animal.
When there is contact with contaminated material, the bacteria enter the body through open wounds, sores on the skin, or via mucosal. People can also become infected with leptospirosis by drinking water, contaminated with urine of infected animals.
Once the bacterium enters the body, it penetrates into blood and throughout the body, causing infection.
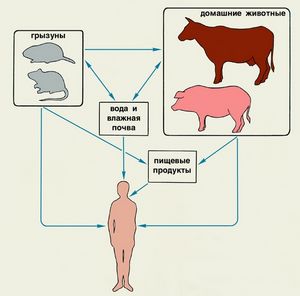
Risk factors for leptospirosis
Anyone can contract leptospirosis, but some people are at increased risk of developing leptospirosis:
- Baidarochniki;
- Paddlers canoe;
- Swimmers (in lakes, Rivers and streams);
- Workers in flood plains;
- Workers in wet agricultural land;
- People, which have pet, especially dogs and livestock;
- People, which run on the ground, including farmers, cattlemen, loggers and working the rice fields;
- People, who work with animals, including veterinarians.
Symptoms of leptospirosis
Symptoms usually appear about 10 days after infection and may include one or more of these disorders:
- The sudden rise in temperature, chills, Pain and Headache;
- Dry cough;
- Nausea, vomiting and diarrhea;
- Conjunctivitis (pink eyes);
- Pain in the joints;
- Sore throat;
- Soreness in the bones;
- Abdominal pain;
- Splenomegaly, liver and lymph glands;
- Muscle stiffness;
- Skin rash.
Diagnosis of leptospirosis
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history, and perform a physical exam.
Diagnostic tests may include:
- Blood test, for determining the presence of antibodies to Leptospira bacteria;
- Isolation of cultures or other laboratory tests.
Treatment of leptospirosis
The doctor will determine the best method of treatment, which may include:
- Antibiotics, including:
- Penicillin;
- Tetracycline;
- Chloramphenicol;
- Erythromycin.
Prevention of leptospirosis
To reduce the likelihood of ill leptospirosis, it is recommended to do the following:
- It is necessary to reduce contact with soil, vegetation and water, that may be contaminated with urine of infected animals, including urine from rodents;
- When working with materials, that can potentially be infected with leptospirosis, you need to wear protective clothing, that covers the skin, including waterproof boots;
- If you are working in an area with a high risk of contracting leptospirosis, it is recommended to consult with your doctor about beginning antibiotic treatment before potential exposure to infection.
