White blood cells – Morphology of white blood cells
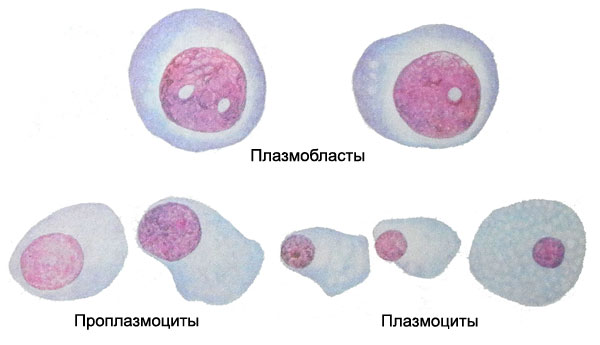
Cells granular series
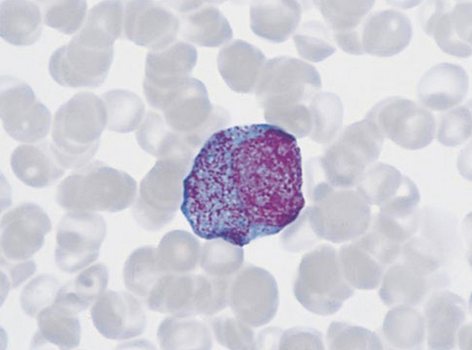
Morphologically distinguishable number of progenitor cells is granular myeloblast.
This cell is often round, less oval, size 15 16 m. The core mieloblastov It has nezhnosetchatuyu chromatin structure, it clearly visible large nucleoli (2-3). The cytoplasm svetlookrašennaâ, basophilic, a perinuclear zone of enlightenment, a small amount of gentle azurophilic inclusions, It gives a positive reaction to the peroxidase.
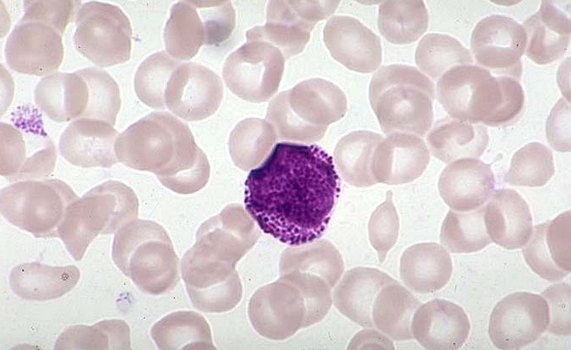
Progranulocyte - Large cell, reaching 25 m or more.
The core and its cytoplasm is gamma transitions aside as myeloblasts, and more mature cells - myelocyte. The core often has a slightly oval, sometimes bean-shaped and located eccentrically. The cytoplasm in some cases surrounds the nucleus narrow belt, in others - a broader. The degree of basophilia of the cytoplasm may be different. The closer to the cell Myelocytes, the more blue substance displaced pink.
Neutrophilic progranulocyte It contains a small grain, the amount of which increases as they mature. Painted in about the grain- mielocite, even in the same cell unequal: red, red-violet, Violet, koričnevatyj, violet-blue, dark blue and red shades.
When a large grain in the cytoplasm basophilic promyelocytes, often covering the core, it can be attributed to the type of basophil, and with a large grain of eosinophilic nature - to eosinophilic. In the initial stages of development of cells eosinophilic granules contain a large amount of basophilic substance, perceiving alkaline (blue) paint, so the majority of the granules are painted in dirty blue. Such cells can be mistakenly taken for basophils- nye. To avoid mistakes, not only the color, but also the size and shape of the granules: in a number of eosinophilic cells are correctly rounded shape and the same size, basophilic cells and their number value ranges from small to large point flake irregular shape, settling and nucleus, and in the cytoplasm of.
Myelocytic. To distinguish two generations of these cells - large motherboards (Immature) and smaller subsidiaries (mature) myelocytes.
Subsidiaries myelocytes formed from the parent as a result of differentiation with simultaneous proliferation. It should be noted, medullocell that is the latest of a number of granulocyte cell, having the ability to proliferate. Under normal conditions, the child in turn metamyelocytes and myelocytes. However, sepsis, purulent inflammation of the large mature segmented neutrophilic granulocytes may develop directly from the parent myelocytes.
Neutrophilic medullocell. The nuclei are different from myelocytes the nuclei of mature white blood cells characterized by the alternation of lighter and darker areas of chromatin. Figure nuclei depends on the degree of maturity of the cells: smaller, subdued, rыhlыy - in nezrelыh myelocytes; sharp, large and thick - for mature. Parent Myelocytes peculiar round shape of the nucleus, as if swollen, and subsidiaries - oval or bean-shaped, chromatin network which is characterized by clearly visible compact dark strands, alternating with intervals of lighter.
Painting cytoplasm myelocytes It depends on the abundance of basophilic substance. In the youngest myelocytes cytoplasm stained more intensely. Painting maternal cytoplasm and especially child myelocyte bluish-brown tones, uneven: in the center of the cell, near the nucleus, in the region of the Golgi complex is less intense. In the presence of enlightenment in the cytoplasm of myelocytes is easily differentiated even in cases, When grain is bad stained or not stained (in leukemia).
Grain fine myelocytes, of the same type, as in a mature neutrophilic granulocytes, but it is almost always possible to detect and larger grain. In sepsis, and purulent inflammation in myelocytes observed degenerative toxigenic granularity.
Eosinophilic medullocell. By the nature of nuclear structure it differs little from the neutrophil, but it is filled with eosinophilic cytoplasm grit. Painting her mostly yellow-red, but often can be seen with eosinophilic basophilic granularity component, having the blue, the purple-red color (perhaps, maternal medullocell). Such cell with a young dark eosinophilic granularity especially a lot of blood in leukemia.
Basophilic medullocell. The core of its structure also resembles the nucleus neutrophil myelocyte, but it differs in some swelling, because of which the details of the structure less clear. Also basophilic substance in the cytoplasm can be found a little brownish-purple yarn. Granularity is different from the mature grain basophil granulocyte more pronounced variations in color shades of the individual grains (dark- blue, blue and blue-pink), Located in the cytoplasm, and on the core. You can also find oxyphilic pellets, that, apparently, are the result of changes in grain toksikodegenerativnyh.
Neutrophilic metamielotsit circular shape, size of 11-13 microns, a bean-shaped, more compact, than myelocytes, kernel, which is compared with the nucleus stab neutrophils more mature and more friable.
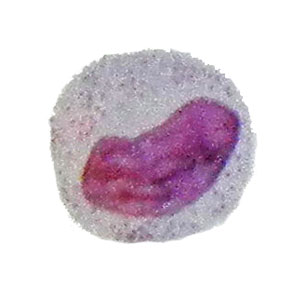
Structureless part of the cytoplasm of the cell as a whole oxyphilic, but sometimes found the remnants of basophilic material and grain pinkish-purple.
Eosinophilic metamielotsit It has a diameter of 10 12 m, round shape, juicy bean kernel with a more compact arrangement of chromatin and abundant, uniform, eosinophilic major grain.
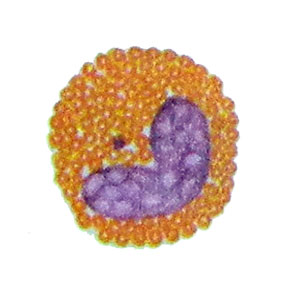
As the ripening stage through stab eosinophilic granulocytes becomes segmented eosinophil granulocyte.
Basophilic metamielotsit not always possible to define precisely because of the blur kernel.
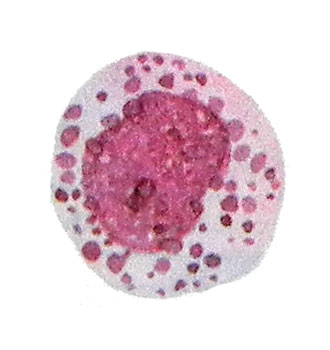
Therefore, cells with basophilic stippling, which can not be attributed with certainty to Metamyelocytes shape and structure of the nucleus, It recommended to be considered mature basophil granulocytes.
Stab neutrophils and segmented respectively have dimensions of 11-12 microns and 8-10, large and giant forms can reach them 20 m, and degenerative, shriveled - 7-8 microns.
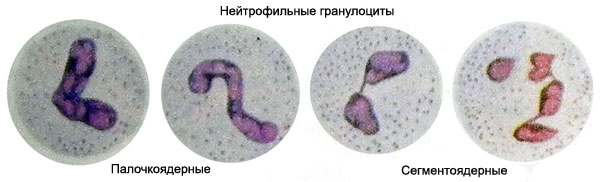
Most of the cells of the cytoplasm, profusely, but not always uniformly filled with fine grit. The cytoplasm is stained by Pappenheim in pink, and grain - in pink and bluish or purple. Neutrophil granularity is specific to these cells, and is different from other types of grain. The kernel has a 2-4 segment, which can be connected by a thin chromatin- howling thread.
Eosinophilic granulocytes stab and segmented circular shape, a diameter of 8-12 mm.
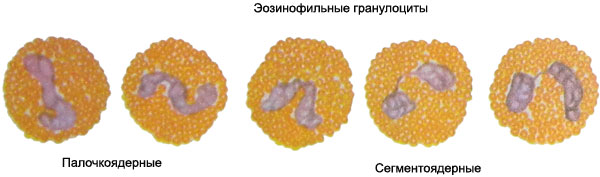
The core of rod-shaped or consists of two segments, connected by a thin, delicate chromatin thread, rarer more segments (three or four). The core occupies a small part of the cell, and the remaining part is filled with characteristic grit. Corn colored acid dyes, particularly well - eosin (Kets resemble caviar).
Basophil granulocyte stab and mature.
Granulosa cells stained metachromatic, It may change its color from violet to blackish blue. Larger and smaller angular and round grains are located in the cytoplasm, and on the core, easily soluble in water. The cytoplasm is painted in bright pink tones (oxyphilic), that is especially evident in areas, where there is no grain. The core of the paddle, sometimes round or oval.
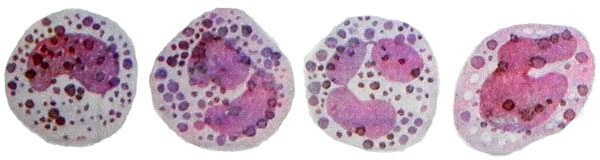
The cells of monocytic series
Mother cell is a monocyte monoblast.
It is derived from a progenitor cell myelopoiesis and like myeloblasts in its development stage colony forming cells in culture. Distinguish monoblast of myeloblasts and lymphoblasts can sometimes be difficult. Same, as these cells, monoblast has nezhnosetchatuyu core structure, containing two or three clearly visible nucleolus. Cytoplasmic covers a large core of relatively narrow belt, basophilic, painted in soft colors. Where, When the kernel has not monoblasta round, and bean, irregular shape, it is easy to determine the nature of the cells.
Promonocit It is a more mature cells of monocytic series. Unlike monoblasta, it may occur in the peripheral blood. The characteristic features of its core: a thick strand of chromatin network, the absence of nucleoli. Basophilic cytoplasm, It contains ase- rofilnuyu grain. Promonotsit is not yet mature functionally cell.
Monocyte. The size of the mature cells within the range of 12-20 microns. In the process of differentiation of monocyte promonotsita in the nucleus appears buhtoobraznoe impression, which is further deepened. The place of depressions nuclear chromatin has a distinct mesh (krupnosetchatuyu) structure, In the future, the nucleus acquires a horseshoe shape, It forms a loop and often annularly closed.
The core of monocyte It can take the most bizarre forms, sometimes it becomes segmented, like segmentoyadernыm neytrofilynыm granulocyte, however, retains the loose, "Sluggish" structure with an irregular arrangement of chromatin. The cytoplasm of monocyte often light blue tones, It contains dust-like granularity azurophil, give it some kind of shade with a clear structure nezhnoyacheistoy.
Macrophages. Found in various pathological processes with careful view of preparations of bone marrow. From the viewpoint of the modern theory of hematopoiesis is associated with the development of myeloid bone marrow.
Macrophages are large, especially high cytoplasmic. The core is relatively small, round or slightly oval, It has a very delicate reticulate-looped structure. It is easily distinguishable centrally or slightly eccentrically located a small nucleolus; sometimes two nucleolus. Wide cytoplasm light- or gray-blue, It has the wrong border. She often as it wraps, covering neighboring cells.
The macrophages can detect a variety of inclusion - fragments of cells, erythrocytes, pigment, fat droplets, sometimes bacteria etc.. P. Depending on the nature of the inclusions can be divided into macrophages eritrofagi, pigmentofagi, lipofagi, bacteriophages and etc. However, the preparations can detect macrophages, absorbing both those and other particles. According to modern views, Macrophages are derived monocyte.
Lipofagi. In any of the sternum punctate can detect single lipofagi, which replace the bone marrow with its depletion. A large number of lipofagov observed in aplastic states. In stained preparations pockets of fat are of the form cavities of various sizes with rounded contours. The core lipofaga often pushed aside in the cell membrane and deformed.
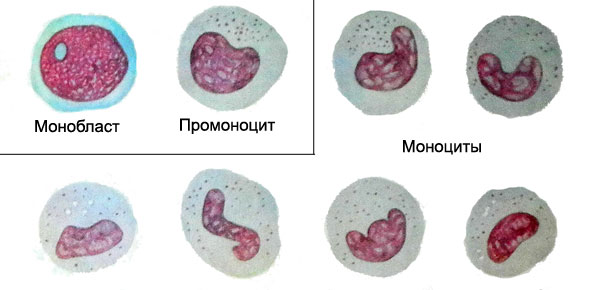
Cells lymphocytic series
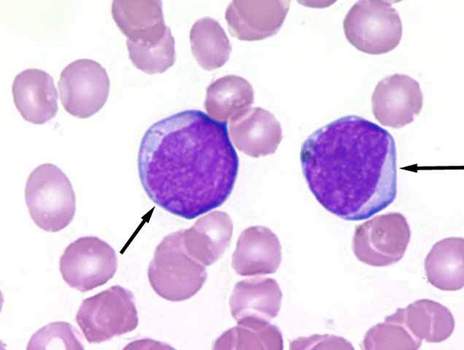
Lymphoblasts - The parent, morphologically recognizable elements of lymphatic cell number - often originates from progenitor T cells and less of progenitor B cells, that, in turn, cells derived from- predecessor lymphocytopoiesis.
The diameter of the lymphoblasts 12-15 M, and occasionally a few larger. The kernel round or slightly oval, chromatin it is distributed and loosely places, especially around the nucleoli, irregularly. Specific for the presence of lymphoblasts is one large nucleolus, rarely there may be two or three. The cytoplasm bazofylna, but less, than undifferentiated Blasta, clearly expressed perinuclear area (enlightenment around the nucleus). Notwithstanding the signs, lymphoblast often difficult to distinguish from myeloblasts. Clarify the nature of the cells is possible using cytochemical methods.
Prolymphocytes. To distinguish it from the cell lymphoblasts allows coarser structure of the nucleus, where only occasionally can find their remains or nucleoli. Prolimfotsit - it is an intermediate stage between lymphoblasts and mature lymphocytes, wherein the last uniform distribution of chromatin and several large size. Painting basophilic cytoplasm prolymphocytes more intense, than mature lymphocytes.
Lymphocyte. The kernel round, sometimes with a bean-shaped impression (riderovskaya form) or cleavage, different density. Chromatin structure hrubohlыbchataya.
The peculiar alternation of dark and light areas of the core due to the distribution of it bazi- and oksihromatina. Some nuclei are nucleoli, which are easier to detect when special painting techniques. The cytoplasm often light blue, basophilic, a zone near the nucleus of enlightenment. Most cell cytoplasm has a narrow rim of lymphocytes are also found with the broader cytoplasm and shirokotsitoplazmennye.
The diameter of the lymphocyte 7-9 M, shirokotsitoplazmenny can reach 15 m. The blood cells are commonly found small and medium sized. Occasionally observed large lymphoid cells lymphocytes or large size to 14-15 microns or more round shape have a core, where you can find nucleoli.
Gruboglybchaty chromatin is located on the edge of the outer nuclear membrane. Increasing the number of such cells in the blood often indicates increased cell proliferation of lymphoid tissue.
In the cytoplasm of lymphocytes can be detected some graininess azurophil, that some researchers see as a sign of aging cells.
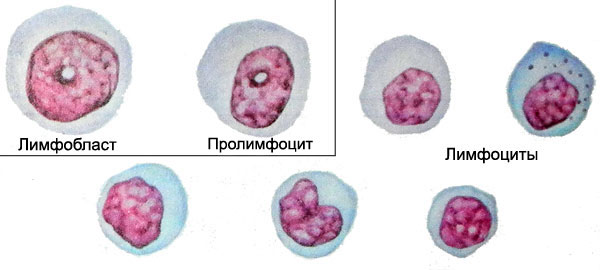
The plasma cells in the bone marrow
The plasma cells in the bone marrow develop from precursor cells B-lymphocyte younger predstadiyu - plazmoblast.
In the bone marrow it is found only rarely. Its dimensions reach 16-25 microns in diameter, a centrally located nucleus, or more eccentric, It occupies most of the cells, It has a delicate structure and contains nucleoli. Noteworthy intense blue color of the cytoplasm, by which determine the status of the cell to the plasma series. However, there have plazmoblasta characteristic perinuclear area of enlightenment. Plaemoblast develop into mature plasma cell, passing stage proplazmotsita.
Proplazmocit characterized by an eccentrically located nucleus, which is not always possible to find nucleoli: chromatin network still has some loose structure, and often has a characteristic rotate location. For cytoplasm proplazmotsita not always a characteristic feature of this cell number. Coating it can be intensely blue, and with a grayish tinge, perinuclear zone enlightenment sometimes missing.
The presence of such cells in the bone marrow, spleen and lymph nodes provides a basis for the allocation of two morphological variants of plasma cells:
- pyknotic nucleus with distinct rotate structure, located, usually, eccentrically, and intensely stained basophilic cytoplasm with enlightenment around the nucleus (perinuclear), sometimes containing vacuoles;
- with the same characteristics, but slightly larger, with blue-gray cytoplasm, perinuclear area where enlightenment less distinct or absent.