Roundworms - Description, morphology, development cycle
Askarida – description
Askarida (Ascaris lumbricoides) It causes ascariasis. It is a large worm fusiform (female long 0.2-0.4, samets- 0.15-0.25 m). The body is elongated helminth, pointed ends, covered by a thick cuticle white or pink. At the head end are three major cuticular lips with papillae, around the mouth. In appearance distinguish females from males at the rear end of the body: males it is folded in a hook-, females - straight.
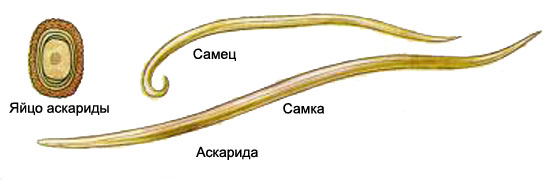
Female, pubescent, highlights the lumen of the intestines to 200 000 fertilized or unfertilized (if the intestines are no male) eggs. Fertilized eggs roundworm slightly oval, provided with a thick multilayer shell, on top of which there is also the outer protein, festonchataya, poorly transparent, coloring pigments of feces in the yellow-brown or brown athletic. Sometimes there are no egg protein shell, smooth transparent and colorless shell. Inside the egg is rounded germ cell dark. The poles of the eggs are free and transparent.
Unfertilized eggs roundworm larger fertilized, oval or irregularly shaped, completely filled with yolk cells. Their protein shell and painted, but it is thinner and sometimes forms outliers projections. In rare cases, the unfertilized eggs have protein coat and then remind the plant cells.
With the patient's feces the eggs to fall into the environment. The warm moist soil with sufficient supply of oxygen to the eggs develop into larvae (for a period of three weeks to a few months).
Invasive roundworm eggs (containing mature larvae) enter the human digestive tract. There shell dissolves, the larvae are released and migrate through the bloodstream and tissues of the host. Through the veins of guts they penetrate into the venous system, and then through the blood capillaries reach the pulmonary alveoli, tearing them and fall into the lumen of the alveoli. Through the bronchi larvae fall into the mouth, and then when ingested in small intestine host, where parasites, developing into adults.
The longevity of helminth – about a year. In most cases, one or more parasitic helminth species, sometimes more. In some cases, the larvae can reach from pulmonary capillaries into the systemic circulation and enter the bloodstream to various organs and tissues, where gradually encapsulated to die.
The clinical picture of ascariasis due to the sensitizing effect of metabolic products and decomposition larvae, and then the adult parasites, the mechanical action of Ascaris on tissues and organs of the patient (larvae during migration causing bleeding in the lungs, and adult roundworm pierce the intestinal wall and go into the peritoneal cavity, vыzыvaya peritonitis). Severe clinical phenomena ascaridosis arise in the localization of Ascaris in the bile ducts, in pancreatic duct, respiratory organs, as well as the development of obstructive ileus. There are cases, When roundworm enters the stomach from the intestines, up the esophagus and penetrate into the larynx, trachea and bronchi, that in most cases leads to death. Sometimes they get into organs of the urogenital system, auditory tube, plaintively-nasal channel, perirenal fat.
Diagnosis ascaridosis phase migration difficult larvae, based on the analysis of clinical manifestations, the results of X-ray inspection (eosinophilic infiltrates in the lungs), microprecipitation positive reaction on live larvae of Ascaris. Sometimes Ascaris larvae can be found in the sputum smear microscopy. The intestinal phase of ascariasis diagnosis is detection of eggs in the feces. The analysis can be negative if only in the intestines of males or immature females. When making the results of fecal need to celebrate, some helminth eggs found: fertilized or unfertilized, since it depends on the treatment and prevention.
Vlasoglav – description
Vlasoglav (Trichocephalus) - Dioecious worms; male length 30-44, female 35-55 mm. Thin front end of the body helminth resembles a thread or hair, the rear end is thickened, it placed the gut, and a female - the queen. Caudal region of the female is slightly bent, the male spirally twisted.
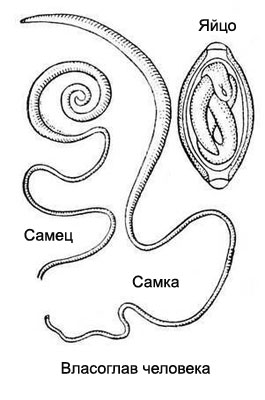
Thin front end whipworm penetrates the intestinal mucosa, and the rear serves lumen.
Whipworm eggs characteristic shape, reminiscent of lemon or keg cork on poles. Surrounded by a thick smooth multi-clad golden or yellow-brown. Traffic poles colorless, clear. Content eggs fines.
Adult whipworms parasitize in the colon, mainly in the cecum, but intense infestation can live in the small intestine.
The fertilized females produce by 1000 to 3500 eggs. The whole cycle of formation and maturation of the eggs takes place in the external environment. When injected into the human colon mature egg is released from a larva, which began to develop in a thin, and complete their development in the colon. Lifespan whipworm - five years or more.
In the development of clinical trichuriasis is dominated by mechanical and allergenic effects of parasites.
Diagnosis It is made by detection of eggs in feces, the most efficient allocation method of enrichment of eggs.
Sedge – description
Sedge (Enterobius vermicularis) - Pathogen enterobiasis, small parasite white (female long 5-10, male 3-4 mm), fusiform. Front (head) end of the body is surrounded by a cuticular vesicle - vesicle, Here is located the mouth, provided with three lips. The rear end of the body of the male spirally curved, females awl- prominent spiky. Almost all of the female body cavity fills the uterus, usually heavily stretched lots of eggs.
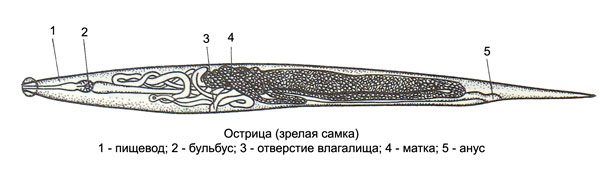
Eggs pinworms oval, Colorless, clear, flattened on one side, on the other hand have a well-defined thin, smooth, double circuit shell. Inside is the larva at different stages of development (usually still immature, neinvazionnaya, golovastikoobraznaya).
Pinworms inhabit the lower parts of the small and large intestine. Mature female as a result of peristaltic movements of the intestines is lowered into their lower sections, active movements moving along the wall of the rectum, crawls out of the anus and lays eggs in the perianal folds. Typically, this occurs at night. Females, got to damp skin, It may be some time crawling over the body of the patient, dry skin accelerates the deposition of eggs and destruction of the females. The male dies after fertilization females.
The longevity of pinworms does not exceed three to four weeks. The perianal folds under oxygen in the eggs mature larvae, that after 4-6 seconds after laying eggs become spindle-shaped and mobility. Such eggs are already invasive. As a result of irritation in females crawl out of the anus itching. Infected people combing the affected area, while invasive eggs fall under the nails, the laundry and other household items and are recorded in the oral cavity, where penetrate the gut, where two - four weeks of larvae produced mature form. This leads to, what, despite the short life cycle of pinworms, enterobiasis can last for years and is one of the most intractable helminthisms. In the human colon can simultaneously parasitize a few thousand pinworms.
In the pathogenesis Enterobiasis pinworm The most important role is played by the mechanical action of parasites and the development of toxic and allergic reactions. Girls and women are sometimes pinworms crawl into the vagina, accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the mucosa and the development of inflammation.
Diagnosis It is made by the detection of eggs in the skin scrapings in the anus. In the study of feces pinworm eggs are rarely found, because usually the female does not lay eggs in the gut.
Trichinella – description
Trichinella (Trichinella spiralis) - Small viviparous nematode length of 1-4 mm (female is slightly larger than the male). The body is elongated parasite, evenly tapering towards the front end. It causes trichinosis.
Adult worms develop in the mucous membrane of the small intestine of humans and animals, consume meat food (dogs, cats, domestic and wild pigs, bald, Wolves, Bears, badgers, etc.. d.). Trichinella circulation occurs between wild and domestic animals by eating them with each other, a person becomes infected by eating insufficiently cooked meat animals.
Everything stage of Trichinella take place in the body of the owner. In the small intestine fertilization, whereupon the male die. Fertilized females pierce the head end wall of the intestine and its lumen give rise to a mass of live larvae (1,5-2 months of life of the parasite - to 2000 larvae). Through the wall of the intestines larvae with the current lymph into the blood and spread throughout the body. Most often they linger in striated (striated) muscles owner. Here, on day 9-10 larvae penetrate the muscle fibers, spiral fold, encapsulated, and then begins calcification of the capsule.
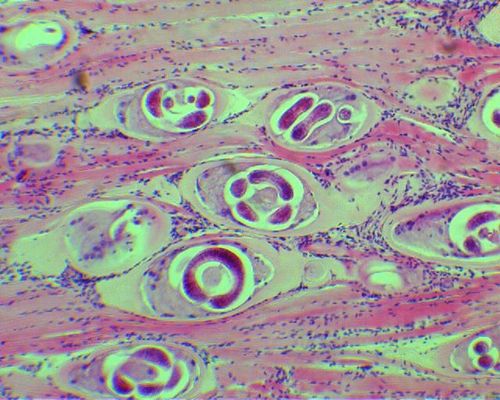
In this state, the larvae can survive for several years. If you get trihinelleznogo meat in the digestive tract of the new host larvae are released from the capsules, penetrate the intestinal mucosa and in two or three days are transformed into adult parasites.
The pathogenesis of trichinosis is sensitizing effect of metabolic products and decomposition of Trichinella, autoimmune processes, which is manifested by fever, increase the number of eosinophilic granulocytes, eruptions, systemic vasculitis with hemorrhage in the intestines, skin, the fundus, swelling of the face and various parts of the body. Characterized by pain in muscles.
Diagnosing the presence of Trichinella made on the basis of clinical manifestations and outcomes research. If you suspect trichinosis in humans resort to muscle biopsy (biceps femoris tendon and calf near). Biopsies placed in a piece of 3 % formalin solution, and then slide in 50 % glycerol solution splits it into the finest fibers. Ravel compress two slides and examined under a microscope at low magnification and field of vision in the dark. A positive result is observed not earlier than on the eighth day of the disease, When Trichinella found in muscles in the form of spirals and covered by a thin capsule, At an earlier date the larvae do not yet have the capsules, therefore it is difficult to identify, and at long capsule invasion is much thicker (to 10 m) and find it easier to.
More effective the study of muscle fibers in a special microscope, the compressor trichinelloscope. Compressor is a two broad thick glass, held together by the type of press with two screws. The fibers are arranged therein with a thin layer and good translucent when examined under a low magnification microscope.
Rather informative method is digestion muscles: shredded muscle pour 15-20- times with artificial gastric fluid and placed in an incubator at a temperature 37 At 12 ° C 16 no. The precipitate is then examined under a microscope. The larvae are found in the free state among the masses of the digested remains of muscle fibers.
Securities are serological methods of diagnosis of Trichinella. The most effective response microprecipitation on live larvae, the reaction of indirect hemagglutination, agglutination with adsorbed antigen and to a lesser extent - interfacial precipitin test. The disadvantage of all these reactions is, that they become positive only in the second or third week after infection.
Ankylostoma – Kryvoholovka dvenadtsatyperstnaya – Some – description
Ankylostoma, krivogolovka or duodenum (Ancylostoma duodenale), and Some, or krivogolovka US (American killer) - Small worms up to 10 20 mm, pinkish yellow. They are similar in structure and cause ancylostomiasis (hookworm and necatoriasis). Their head end of the oral capsule has four teeth have hookworms and two cutting blades in American hookworm. Males are distinguished by the presence on the tail end of the extension of the cuticle kolokolovidnogo, and in hookworm it bigger and wider, while the American hookworm - less and has. The tail end of the female body has a conical shape and is provided with a sharp Brad have hookworm, And no American hookworm brad. American hookworm and hookworm eggs are indistinguishable: Oval, Colorless, clear, with blunt rounded ends and thin shell.
Ancylostoma belong to the group geohelminthes. Parasites in the upper part of the small intestine. Here the fertilized female lays more than a day 10 000 eggs, that stand out with the feces out and get into the soil. Under favorable conditions, (humidity, temperature, oxygen supply) through 24 h from the egg comes out the larva, which undergoes several stages of development and is transformed into an invasive filariform. In humans, the larvae get into the alimentary canal, which turn into adult parasites. Pathogenic effects of Ancylostoma is mechanically damaged intestinal mucosa with the formation of long-bleeding wounds, as well as metabolic products sensitization with the development of allergy.
Life expectancy of American hookworm 10-15, hookworm - 4-5 years.
Diagnosis made on the basis of clinical and epidemiological data and the results of laboratory research. Crucial discovery of eggs in the feces of Ancylostoma. The best results are obtained Pap Kato and Miura and method of cultivation of larvae.
Strongiloid – Ugritsa E. – description
Strongiloid, or intestinal ugritsa (Strongyloides stercoralis) - Fine threadlike nematode length of 1-3 mm. Infests the small intestine, where the female lays about 50 eggs per day. Eggs ugritsy oval, clear, covered with a thin shell, similar to the eggs of Ancylostoma.
Eggs are the larva of 0.2-0.5 mm. Getting with feces on the ground, they are in unfavorable conditions turn into invasive. A person infected by ingestion of larvae or their active implementation through the skin. In either case larvae enter the blood vessels, migrate through the large and small circle of blood circulation, entered the lungs, penetrate into the alveoli, then the bronchi, re-swallowed in the gut and develop to sexual maturity. This is the direct path of development. It is also possible indirect way of development, when under favorable environmental conditions the larvae turn into free-living adult parasites. Their generations succeed one another until, until environmental conditions become unfavorable.
Sometimes, some of the larvae are released with feces, and lingers in the intestines and turning into invasive (without departing from the outside environment). These larvae penetrate the intestinal wall and capillaries undergo the whole cycle of development first (type autoynvazyy).
Pathogenesis strongyloidosis due to mechanical damage of the vascular wall and the lung tissue larvae, followed by the development of the inflammatory process, sensitization of the waste products and the collapse of the larvae to the development of allergic reactions (strongyloidosis characteristic for increasing the number of eosinophilic granulocytes). Mechanical damage to the intestinal mucosa parasites along with their allergenic action results in the disruption of the function of the digestive system.
Diagnosis of strongyloidiasis based on the detection rhabditiform larvae in the faeces or the contents of the duodenum. In the early phase of the disease accounted for a large number of eosinophilic granulocytes (It holds the chronic course) and examined sputum to detect larvae.
Trihostrongilidy – description
Trihostrongilidy (Trichostrongylidae) - Small dioecious helminths (to 6 mm) six species. Parasitic in the small intestine and in small cattle. In humans, it is rare.
Eggs Oval, with a thin, transparent, colorless and slightly tapered shell with one pole. From eggs, allocated to the external environment with the faeces of animals, rapidly developing larvae. A person infected by ingestion of water and plant food. The pathogenesis of the disease has not been studied.
Diagnosis is placed upon detection of eggs in the feces.
Filaria – description
Filaria (Filariidae) - Pathogens filariases, common in tropical and subtropical climates,- White threadlike nematode length of 30-100 mm, to the ends of their body thins, at the head end has a mouth opening. Females are viviparous. The development takes place with a change of filarial owners: definitive host is a human, and intermediate - arthropods (Mosquitoes, slepni, midges, mokrecy). Adult filarial parasites in closed systems and cavities of the human body.
Larvae (mikrofiljarii) circulating in the circulatory system, or concentrated in the surface layers of the skin. Some noted filarial larvae in the circulation pattern (microfilariae): and some hours of the day they are in deep, in others - in peripheral vessels. Blood-sucking insects by the bite of a sick person with his blood ingest microfilaria. In the body of the insect, they undergo a series of stages, and after two or three weeks is able to infect human transporter. When the bite of larvae enter the skin, embedded in its thickness, penetrate into the blood vessels and entered into internal organs, where they grow, develop and after one- Two years into an adult parasite. By this time, developing and clinical manifestations.
The basic rights are filariasis:
- Wuchereriasis, characterized by allergic reactions, in the later stages - lymphadenitis, and then the emergence of elephantiasis of the lower extremities;
- Loaoz, manifested by fever and allergic reactions, further symptoms of the subcutaneous tissue - edema, burning, zudom, men sometimes development of hydrocele, may cause abscesses in the muscles and lymph nodes;
- Dipetalonematoz, or acanthocheilonemiasis, in the pathogenesis of which plays a major role in sensitizing action-patients have dizziness, fever, hives, itching and others.;
- Blinding filarial disease, at which a skin ulceration (mainly in the area of the blades, chest and thighs), slowly healing with scar formation, there may lymphadenitis, orkhita, Hydrocele, elephantiasis of the lower extremities and scrotum, abscesses and arthritis, as well as the destruction of the body with the development of cataracts, Glaucoma, atrophy of the optic nerve and blindness!
Diagnosis wuchereriasis made on the basis of clinical data and identify microfilariae in a drop of fresh blood (native drug). For the differentiation of certain types of pathogens studied stained preparations. At low concentrations of larvae in the blood, as well as the negative result of the study it is recommended to use the method of enrichment. Blood samples taken at periodic strain after 18 no (pronounced nocturnal peak concentration in the peripheral blood of larvae), subperiodichnom- at any time of day. Applied also immunological reactions, However, using them only put a group diagnosis.
Diagnosis Loiasis based on clinical manifestations and helminth larvae detected in the blood during the daytime. Used serological methods: complement reaction svyazыvaniya, vnutrikozhnaya allergicheskaya sample.
For the diagnosis of onchocerciasis important is the presence of characteristic nodes under the skin, defeat eyeballs with identifying them microfilariae. We study also thin sections of the epidermis, smears of blood and lymph, painted on Romanovsky, serological tests are carried out.
Diagnosis acanthocheilonemiasis based on the detection of microfilariae in the blood.
Buckle – description
Buckle (Dracunculus medinensis) - Pathogen dracunculiasis, occurring in Asia, Africa, South America. It has long (0,3-1.2 M) filamentary body, parasite in the subcutaneous tissue and intramuscular connective tissue.
If the clinical picture of dracunculiasis characterized by rash, puffy face, redness of the mucous membranes, asthma, synovitis, the appearance of abscesses, phlegmons, gangrene, Sepsis. The subcutaneous tissue can be palpable hardening, which subsequently ulcerate detection head helminth. Most prominently contoured worms under the skin in the form of a roll. A person infected with guinea worm when swallowed with water Cyclops - intermediate hosts, infected mikrofilya- Riyami.
The diagnosis of dracunculiasis made on the basis of characteristic clinical symptoms and the results of serological tests, in particular skin test antigen from guinea worm. Calcification of the parasite can be detected by X-ray examination.
