Bleeding gums: what is this, causes, symptoms, diagnostics, treatment, prevention
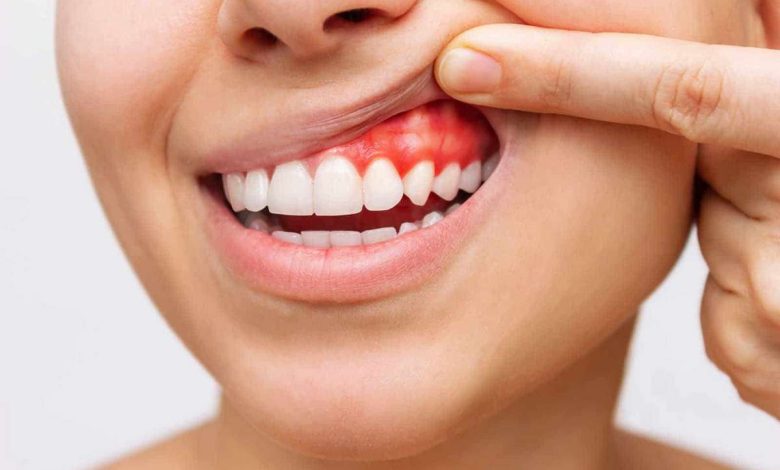
Bleeding gums; Gums – bleeding
Bleeding gums: determination, Diagnosis and Treatment
Bleeding gums is a common oral problem.. It arises, when gum tissue, surrounding teeth, becomes inflamed, causing light bleeding when brushing or flossing. While occasional bleeding is normal, persistent bleeding may be a sign of a more serious underlying condition, such as gum disease.
Causes of bleeding gums
The main cause of bleeding gums is gum disease., also known as periodontal disease. It happens, when plaque and tartar build up on the teeth and irritate the gum tissue, causing inflammation. Other factors, which can contribute to bleeding gums, include:
- Poor oral hygiene
- Hormonal changes
- Some medications
- Vitamin deficiencies, especially vitamins C and K.
- Bruxism (gnashing of teeth)
- Smoking and tobacco use
- Certain diseases, such as diabetes and leukemia
Symptoms of bleeding gums
Bleeding gums are often the first and only symptom of gum disease.. Other symptoms may include:
- Red, swollen and sensitive gums
- Receding gums
- Persistent bad breath
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Changes in the fit of dentures or partial dentures
Diagnosis of bleeding gums
A dentist or periodontist can diagnose bleeding gums, examining the oral cavity, gums and teeth. They can also take x-rays., to determine the degree of damage to bones and tissues, supporting teeth. In some cases, a small tissue sample may be taken for further analysis..
Treatment of bleeding gums
Treatment for bleeding gums depends on the underlying cause. Treatment for gum disease may include:
- Professional cleaning of teeth from plaque and tartar
- Antibiotic therapy to eliminate bacteria, causing infection
- Root scaling and polishing to remove plaque and tartar from under the gum line
- Surgery to remove infected tissue and bone
- Medicines, such as antimicrobial mouthwashes or gels
Home treatment for bleeding gums
In addition to professional treatment, there are several things, which you can make at home, to help manage bleeding gums:
- Brush your teeth regularly and floss, to remove plaque and food particles.
- Use antiseptic mouthwashes, to kill bacteria
- Avoid smoking and tobacco use
- Eat a balanced, nutrient-dense diet, especially vitamin C and K.
- Visit your dentist regularly for checkups and cleanings
Prevention of bleeding gums
To prevent bleeding gums, it is important to maintain good oral hygiene and have regular dental check-ups. Other steps, you can take, include:
- Brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste
- Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles.
- Use an antiseptic mouthwash
- Limit sugary and sour foods and drinks
- Stop smoking and using tobacco
In conclusion, bleeding gums can be a sign of a serious underlying condition, such as gum disease.
If you are experiencing persistent bleeding, it is important to consult a dentist or periodontist for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Maintaining proper oral hygiene and visiting the dentist regularly, you can prevent bleeding gums and keep your gums and teeth healthy.
Used sources and literature
Chow AW. Infections of the oral cavity, neck, and head. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 64.
Hayward CPM. Clinical approach to the patient with bleeding or bruising. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 128.
Teughels W, Laleman I, Quirynen M, Jakubovics N. Biofilm and periodontal microbiology. In: Newman MG, Takei HH, Bell violence PR, Carranza F.A, eds. Newman and Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology. 13th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2019:chap 8.
