Cell elementoy thyroid – Morphology
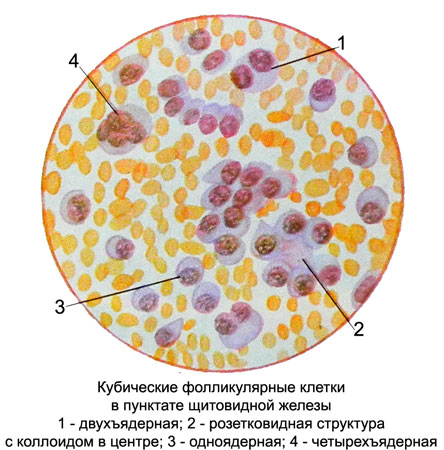
Cubic A-cell reach a diameter of 12 13 m. The nuclei of round or oval, eccentrically located, with tender, evenly distributed network of chromatin and is not always clearly visible nucleoli. There may be two- and quad cells. The cytoplasm of follicular cells homogeneous, basophilic, stained with different intensities. Basophilia cytoplasm and eccentric nuclei give the location of the cells similar to the plasma, However, in contrast to the latter, cubic epithelial cells of the thyroid gland no perinuclear zone of enlightenment and rotate the location of chromatin in the nucleus.
Cylindrical A-cell size to 16-18 microns, more narrowed to the basal end (base) cell. The core of the oval, with delicate chromatin structure, It is located closer to the narrow end of the cell. Sometimes, the kernel fails to distinguish between the nucleolus. The cytoplasm bazofylna, stained with different intensities.
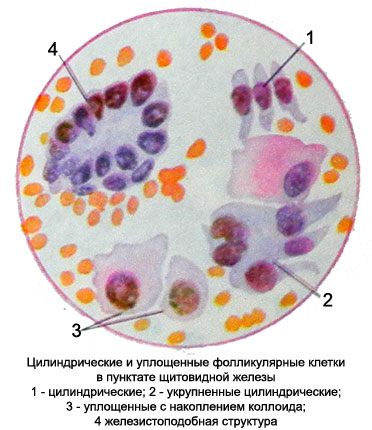
Flattened A-cell irregularly rounded shape, different sizes, but most large. Nuclei are round or oval, located in the center of the cell, or eccentrically. Chromatin cores looks unclear mesh or short sticks. Often some parts of chromatin stained lighter tones and have fuzzy (like greased) or annular structure, resembling a drawing cut down a tree. Such an arrangement and coloring of the chromatin can sometimes be observed in the nuclei of small cubic cells. In the nuclei of flattened cells are often found nucleoli.
Cytoplasm abundant with scalloped, often vague edge, merging with the background of the drug. Painted in bright colors, basophilic, almost always with a pink tinge, indicating the content of the colloid in these cells. The intensity of the pink color of the cytoplasm may be different, sometimes observed in most of the cytoplasm or nucleus only near.
Perinuclear accumulation of colloid can be painted in a more intense pink color, and the cell periphery is then given basophilic scalloped rims. These flattened cells specific for the thyroid gland, and finding them in a punctate with unusual thyroid localization may indicate ectopic or metastasis of thyroid cancer in the study body.
B-cell rather large (from 15 to 25 m), round or spherical, eccentrically located nucleus with average or slightly larger. The cell cytoplasm is abundant large grain, painted in intensive red or pink. The punctate these cells are found in a small amount, are located separately, and when they form a group of proliferation and layers.
C-cellrare. They are similar to the B-cells, but less than their largest (8-14 M). Grit in the cell cytoplasm, fine, Pink colour.
In addition to the cells of the thyroid gland punctate can be detected in other cells, often have a diagnostic value, namely:
blood cells (in different quantities and combinations);
· histiocytes;
Plasma and giant multinucleated cells of the foreign body type;
proliferating epithelial cells;
· phagocyte.
Cells proliferating epithelium meet with goiter and other pathological processes. They slightly increased, have enlarged nuclei (often located eccentrically), which are often found nucleoli, and basophilic cytoplasm. In the study of drugs can be detected spherical clumps lying freely colloid, sometimes placed in the center of zhelezistopodobnyh structures, structurally resembling follicles. Sometimes epithelial cells proliferate so atypical, they are difficult to distinguish from cancer cells.
Phagocytes found in punctate thyroid in different quantity. In the cytoplasm are greenish-black grain hemosiderin, which has a separate clumps or fill the entire cytoplasm. The native preparations, these cells look like macrophages, in stained - no different from the epithelial cells of the thyroid gland.
Epithelial, hemosiderin phagocytic, can be observed in punctate in various pathological processes in the thyroid gland, accompanied by hemorrhage. The large number of such cells and proliferating epithelial cells without signs of atypia characteristic of cystic cavities of the thyroid gland.
