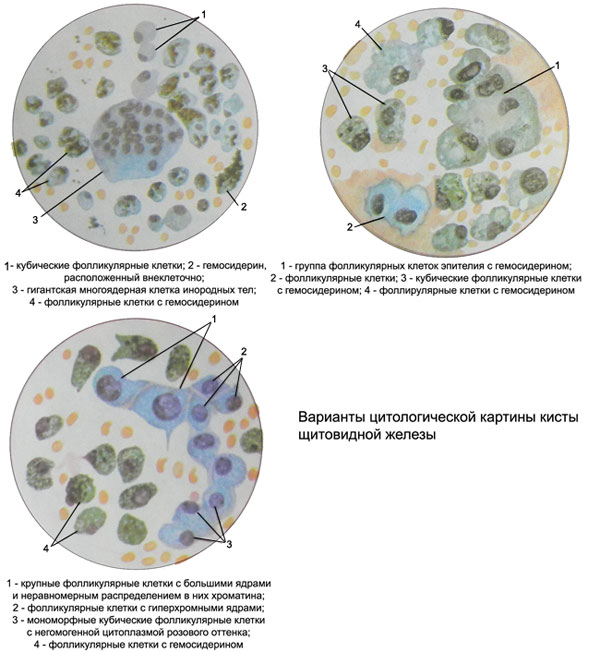
The thyroid gland cyst – characteristic punctate thyroid
It is formed from large follicles, crowded colloid. It occurs adenomatous altered thyroid tissue at any age, but most often seen in children. The diameter varies from cysts 30 to 80 mm. The cavity is filled with mucoid cyst fluid.
When puncture cysts get a few milliliters of a transparent, yellowish or brown, turbid liquid. The brown and murky punctate notes, usually, abundant precipitate. In such a fluid under microscopic examination of native preparations showed a large amount of modified erythrocytes and their fragments, hemosiderin, and sometimes cholesterol crystals. With a large number of cholesterol crystals opalescent liquid surface. Hemosiderin located inside cells, and is blocked, forming large accumulations of extracellular, covering all of the drug and give the impression of contamination.
Because the cells except red blood cells are often detected a large number of phagocytes, foreign body giant cells and flattened follicular cells of the thyroid gland without any inclusions. When inflammation of the cyst are punctate in cells, typical of inflammation, and in the presence of epithelial proliferation can be detect proliferating epithelial cells.