Feature punctates in certain diseases of the lymph nodes
Lymphadenitis
Inflammation of the lymph nodes is mainly due to their barrier function. It can be infectious and noninfectious nature.
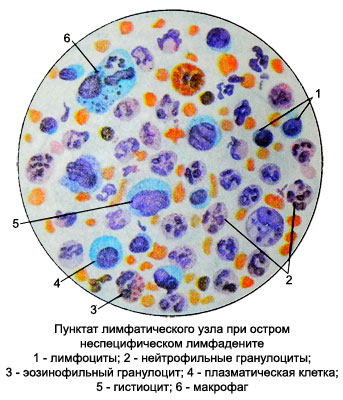
Acute nonspecific lymphadenitis
In acute nonspecific lymphadenitis morphological changes in the lymph node are like three stages of development. First, the node develops reactive hyperplastic process. An increasing number of lymphoid elements mainly due to large lymphocytes, prolymphocytes and lymphoblasts. Several increases macrophage content, plasma and reticular cells.
With the development of inflammation appear neutrophilic granulocytes, gradually their number narastast while reducing the number of lymphocytes. The neutrophils are marked toksogennaya granularity and vacuolization. Further, in the third stage of acute nonspecific lymphadenitis, or abscess occurs with the destruction of neutrophil granulocytes, or reverse the development process.
Macrophages appear early in inflammation lymph node, and their number gradually increases. A significant increase in the number of macrophages is a harbinger of a favorable course of the disease and reverse the development process. Reducing the number of macrophages and even the complete disappearance of their preceding purulent processes in the lymph node. Sometimes in acute lymphadenitis may be found in punctate giant multinucleated cells of foreign bodies.
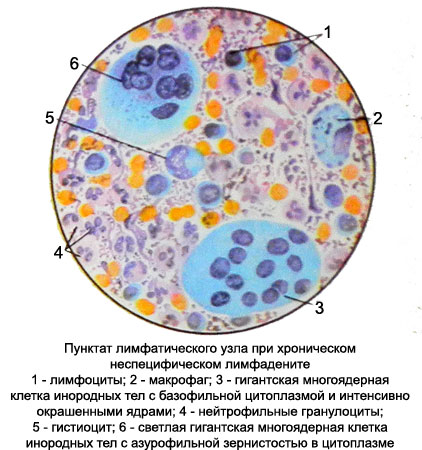
Chronic nonspecific lymphadenitis
In chronic nonspecific lymphadenitis smear dominated by mature lymphocytes, increasing the number of plasma cells, tissue basophils, macrophages, there are giant multinucleated cells and fibroblasts foreign bodies.
Neutrophil granulocytes bit, but as the process of increasing the number.
Specific lymphadenitis
This group of lymph nodes include tuberculosis lymphadenitis, sifilise, aktinomikoze, tularemia, plague, etc..
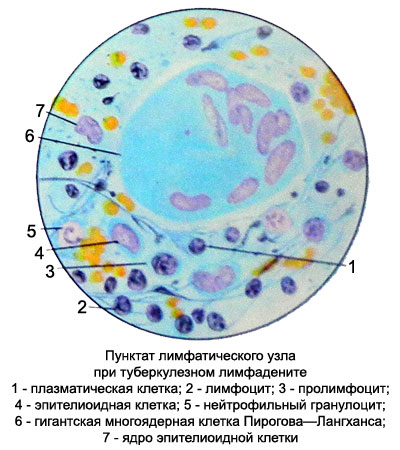
TB lymphadenitis
There are five forms of tuberculous lymph nodes:
- diffuse lymphoid hyperplasia;
- miliary tuberculosis;
- large-TB hyperplasia;
- cheesy (cheesy) tuberculosis;
- indurativnyy tuberculosis.
Diffuse lymphoid hyperplasia. At the beginning of tuberculosis of the lymph nodes of the reaction takes place under customary reactive hyperplastic type. During this period, for punctate lymph node in addition to the large increase in the number of lymphocytes is characterized by increase in the number prolymphocytes, lymphoblasts, reticular, plasma cells, macrophages. Such a punctate cell composition is not specific to any lymph nodes. Bacterioscopic punctate research on Mycobacterium tuberculosis in this form of the disease usually produces negative results.
When miliary tuberculosis of the lymph nodes buhorky (granulomas) located mainly in the lymph node cortex. The punctate can identify epithelioid and giant multinucleated cells Pirogov-Langhans. In the decay of tubercles can be found detritus. However, to receive punctate with elements specific tuberculous granulomas rarely possible. The most common in this form of TB detected punctate lymphoid elements, isolated plasma cells, retikulyarnыe cells and macrophages.
When large-tubercular hyperplasia punctate found in the field of epithelioid cells, among which are occasionally found Langhans cells Pirogova-.
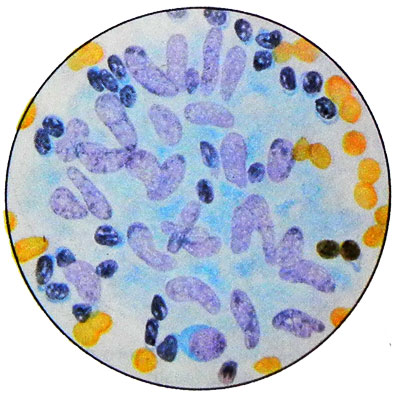
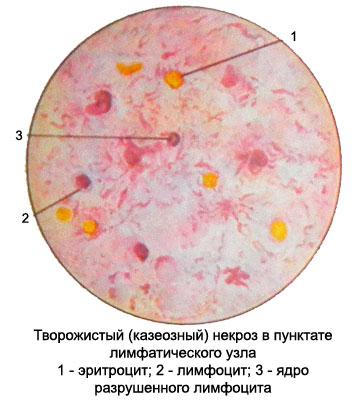
If this form of tuberculosis lymphadenitis does occur curdled (cheesy) degeneration of epithelioid elements, in punctate along with preserved epite- lioidnymi cells found detritus. In such cases it is difficult to solve, which of the latter two forms of TB lymphadenitis occurs.
Every form of tuberculosis of the lymph nodes can result in a complete rebirth clotty, t. it is. development tvorozhystoho (caseous) TB. The punctate of lymph node revealed such detritus, against which there may be single-preserved lymphocytes, reticular cells.
Occasionally can get changed giant multinucleated cells Pirogov-Langhans. When painting curd Ziehl-Nelsenu found a lot of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
When you join secondary infection curd hotspots softening with neutrophilic granulocytes and microorganisms. Sometimes fistulas are formed and excreted pus and curd. In the absence of the drug, prepared from the separated mass sinus, cells tuberculous granulomas judge the nature of the pathological process can not be. About tuberculous lymphadenitis indicates chronic process, and preparations - the predominance of lymphocytes of neutrophilic granulocytes. Purulent lymphadenitis of other etiologies usually occurs acutely.
In all forms of tuberculosis lymphadenitis possible recovery with the development of scar connective tissue - indurativnyy tuberculosis of the lymph nodes. The punctate revealed a small amount of lymphocytes, among which are found the typical fibroblasts.
Actinomycotic lymphadenitis
Lymph nodes Lumpy, usually, proceeds chronically. The material for the study is the pus, escaping from the fistula, and in the absence of fistulas - punctate of lymph node area softened. Because of purulent or bloody-purulent masses collected grayish-yellowish grains and study them under the microscope, in native and in Gram-stained preparation.
As with any other localization process, when lymph node actinomycosis in punctate on a background of purulent masses are found Druze actinomycetes and foam cells. In Gram-stained preparations revealed gram dichotomously dividing strands of mycelium actinomycetes.
Syphilitic lymphadenitis
Syphilitic lymphadenitis most usually observed in primary and secondary period of syphilis, but can occur in the Tertiary period. Normally increased inguinal lymph nodes. They are of small size, tight, painless, not soldered to the underlying tissues. The puncture sites performed for diagnostic purposes, while the main is the detection of pale Trenaunay. They are identified in punctate in 80 % of cases in the early stages of the disease, when Wasserman gives another negative.
Microscopic examination revealed signs of punctate reactive hyperplastic process, having syphilis protracted, but not rolling in festering and necrosis, except in the case of education in the lymph node gummas.
Tularemia lymphadenitis
A characteristic cytologic picture in punctates lymph nodes in the bubonic form of tularemia is not. Also lymphocytes and neutrophils identified reticular epithelioid and giant multinucleated cells Pirogov-Langhans. A feature of lymphadenitis when tularemia is early abscess, wherein in the formulations are almost exclusively neutrophilic granulocytes at different stages of decomposition. The diagnosis is placed with the clinical picture and specific reactions.
Plagued lymphadenitis
The puncture of a lymph node is performed to identify the plague sticks.
Lymphadenitis disease cat scratch
Lymphadenitis disease cat scratch - a relatively rare disease, characterized by inflammation of regional lymph nodes as a result of a cat scratch or bite. The causative agent of the disease is a virus from a specific group of psittacosis. The incubation period lasts until after the bite 20 days, after which the body temperature rises (to 39 ° C or higher). On the site of the bite for a few hours there is a reddening, and after 1-2 weeks there papule, sometimes with suppuration, that can stay for a month.
In some cases, significant changes to the scratch or bite does not occur. Since scratches often occur on the hands, lymphadenitis is usually develops in the elbow and axillary regional lymph nodes, which increase, become painful, and the skin over them giperemiruetsya. When suppuration of lymph nodes appears floating. In the blood revealed leukocytosis, increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate, sometimes increase the number of eosinophilic granulocytes.
At the initial stage of lymphadenitis in punctate lymph node revealed many large reticular cells, are sometimes detected in the lymph node for long periods, even after the decay process. The structure of the lymph node in this stage of the disease resembles changes, observed in the lymph nodes in infectious mononucleosis. The punctate of lymph node detected fluctuating pus.
Lymphadenitis in systemic lupus erythematosus
In punctates of lymph nodes revealed a large number of reticular cells with more or less wide rim of cytoplasm, many macrophages and plasma cells. If punctate of lymph node mixed with serum of patients, and then appropriately treated, it is possible to detect the LE-cells.