Karцinoid – status and sputum
Carcinoid - the common name of tumors (benign and malignant) APUD-system, to which the cells of various organs and tissues, producing biologically active substances - serotonin, histamine, catecholamines, calcitonin, enterogastrin, enteroglyukagon, insulin, etc.. These tumors are known as pheochromocytoma, paraganglioma, insuloma, gastrinoma, etc.. d. For the whole of this group of tumors proposed the term "apudoma", indicating its functional activity: eg, apudoma, syekryetiruyushaya histamine Ili insulin, and t. d. Finally nomenclature of tumors APUD-system is not developed.
For carcinoid lung or bronchus is characterized by rounded cells, elongated or polygonal form, rounded (oval) nuclei and granular cytoplasm narrow rim, containing fat droplets.
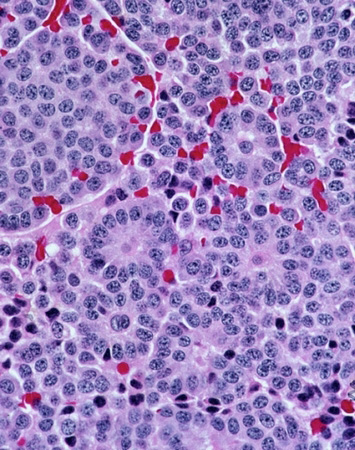
Cells are arranged in groups and clusters of outlets. Tumor cells produce mucus, which is found not only in the cytoplasm, but also in the lumen outlets. A carcinoid tumor is seen as a low-grade, but perhaps its metastasis to regional lymph nodes and distant organs. In the presence of tumor cells in the signs of malignancy prognosis worsens.
For the diagnosis of tumors of the bronchi is currently used cytology scourages bronchi and material, obtained during bronchoscopy. This makes it possible to diagnose and benign tumors of the bronchi. Among them distinguish papilloma, adenoma and tumor mukoepidermoidnuyu.
