Changes in the cerebrospinal fluid in tumors of the central nervous system
To understand the histogenesis of tumors is important to know the morphology of glial cells in normal.
Along with neurons (nerve cells) in the neural tissue include many, a variety of functional value glia cells. They perform reference, demarcation, trophic, secretory and protective functions. All glial cells divide into two genetically distinct types:
- central gliocytes (macroglia);
- peripheral (microglia).
Among central gliocytes distinguish ependimotsity, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. They develop from the neural tube spongioblastov. Peripheral gliocytes - Derived mesenchymal.
Ependimotsity
Ependimotsity as a thick layer lining the spinal canal and all of the ventricles. During the histogenesis of nerve tissue ependimotsity differentiate the first of neural tube spongioblastov. According to available data, ependimotsity vascular plexus take an active part in the formation of cerebrospinal fluid.
Astrocytes
Astrocytes - Are small cells with multiple processes, operating support function. There are two types of astrocytes: protoplasmic and fibrous.
Protoplasmic astrocytes They found predominantly in the gray matter of the brain and spinal cord. They are characterized by the presence of large, poor chromatin core and a large number of highly branched short processes. The increased number of mitochondria in the cytoplasm of protoplasmic astrocytes korotkoluchistyh evidence of their involvement in metabolic processes. When degeneration of nerve elements in the cytoplasm of protoplasmic astrocytes korotkoluchistyh accumulate various decay products and the inclusion of lipids.
Fibrous astrocytes They are located mainly in the white matter of the brain. They have a 20-40 long slabovetvyaschihsya processes. In the peripheral zone of the cytoplasm of cell bodies and processes going on in the glial fibers, which together form a support unit of the brain. The end of expansion of fibrous astrocytes form a dividing membrane.
Oligodendrocitы
Oligodendrocitы - The largest group of glial cells. They surround the bodies of neurons in the central and peripheral nervous system, included in the membranes of nerve fibers and nerve endings. Form oligodendrocytes may be different. In the gray matter they are small, oval or angular shape and a few bodies short, lightly branched spikes.
Brain Tumors
Brain tumors occur in people of different ages and up 4,2 % all organic diseases of the central nervous system. Most often they occur in the age range 20-50 years.
Based on histogenesis, divided into four groups of tumors:
- Neuroectodermal;
- Shell-vascular;
- Pituitary;
- Metastatic.
Malignant tumors and metastases, and cancers, located near the spaces, which circulates the cerebrospinal fluid, give the most pronounced changes in the cerebrospinal fluid.
Neuroectodermal tumor
Neuroectodermal tumor are the most numerous and diverse group of brain tumors, arising from the ectodermal germ layer. This tumor glial and nerve cells. These include astrocytomas, oligodendroglioma, glioblastoma (multiforme spongioblastoma), medulloblastoma, ependymoma, papilloma (xorioidpapilloma), pinealoma and neuroma.
Shell-vascular tumors
Shell-vascular tumors frequency ranks second among brain tumors. These include meningioma (arakhnoidendotyelioma), histogenetic associated with meninges, and angioretikuloma, evolving from the vessel wall.
Pituitary tumor
Pituitary tumor occur in 7-18 % cases of brain tumors. There are two types of pituitary tumors:
- pituitary adenoma;
- kraniofaringiomu.
Metastatic (secondary) tumor
Metastatic (secondary) tumor - A cancer metastasis, arising in other organs. Tumor cells enter the cerebrospinal fluid as a result of their exclusion from the surface of the tumor during germination in its space, which circulates the cerebrospinal fluid. The morphological features of malignancy of cells, found in cerebrospinal fluid, allow to identify them as belonging to certain tumors of the central nervous system.
Medulloblastoma
Medulloblastoma observed mainly in children, often localized in the cerebellum, and is characterized by rapid growth and propensity to metastasize by multiple spaces, containing the cerebrospinal fluid.
Cells of medulloblastoma similar to the lymphocytes, but their larger. In stained preparations are rounded, size of 9-20 microns, with the core, occupying nearly the entire cell. Often in the background gentle nuclear chromatin is determined from one to eight clearly contoured nucleoli. The cytoplasm surrounds the nucleus of a narrow pale blue border.
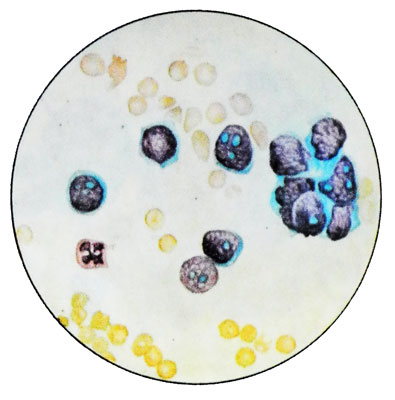
Often you can not see the cytoplasm. Can detect polymorphic medulloblastoma. There may be a dual cells and cells in mitosis, effects of autophagy. Observation after removal medulloblastoma large number of cells in the cerebrospinal fluid may be a sign of metastatic tumor subarachnoid space.
Glioblastoma
Glioblastoma cells in the cerebrospinal fluid found easily due to their pronounced polymorphism. The size of the cells ranges from 12 to 100 m or more. The predominant cells round shape with rounded, clearly contoured nuclei.
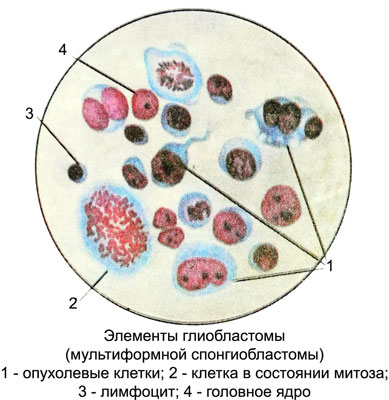
There may be huge or irregularly shaped nuclei. Nuclear chromatin pattern petlistogo, painted Hypochromic. At the core are the nucleoli (from one to eight) various sizes and colors. The cytoplasm of the cells homogeneous, blue or gray-blue. Among described glioblastoma cells very often two- and multicore. Many cells with direct nuclear fission and mitotic figures. There are giant cells with many nuclei of various sizes, containing one or two nucleoli.
Ependymoma
Cells ependymomas, found in cerebrospinal fluid, various sizes - from 12 to 25 m, elongated, They have one or two lengths of process 10 to 50 m. Nuclei are round to oval, clearly contoured, with fine-grained chromatin, It contains one or two small nucleoli. The cytoplasm is painted in gray-blue color. Among the cells of process revealed round or oval.
Oligodendroglioma
Cells oligodendrogliomas in the cerebrospinal fluid monomorphic, size from 15 to 20 m, round or polygonal shape. Kernels large, often round, hyperchromatic, homogeneous with, sometimes large-glybchatym distribution of chromatin. The nucleoli are not always identified. The cytoplasm surrounds the nucleus of a broad border, Pale, grayish-blue, with clear boundaries, sometimes finely vacuolated. Occasionally it can be found in the cytoplasm of small, unevenly distributed grain.
Astrocytoma
Astrocytoma - Most often a benign tumor. Meets undifferentiated astrocytoma, which differs obvious signs of malignancy, morphologically close to glioblastoma and can be located in all parts of the central nervous system.
Astrocytoma cells detected in the cerebrospinal fluid is extremely rare. They have an elongated shape, size from 9 to 14 m, are diametrically extending major length of the processes 6 to 60 m. Kernels extended, Oval, less round, with melkopetlistym or fine-grained pattern of chromatin, Hypo- or normochromic. They contain from one to four small basophilic nucleoli. There are dual cells and direct fission and budding core. The cytoplasm grayish-bluish color, It is in the form of appendages. The native specimens in the cytoplasm of cells can reveal small droplets of fat shiny yellowish.
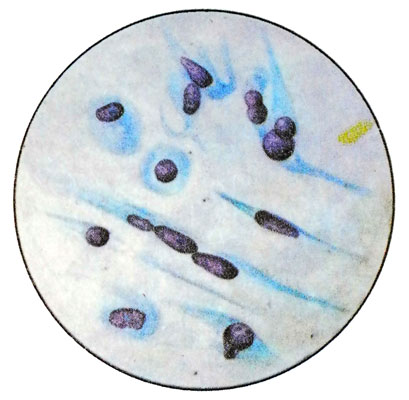
Kraniofaringioma
Kraniofaringioma - A benign tumor, a growing strand of epiphyseal epithelial. Cells craniopharyngioma mainly large (from 10 to 20 m), epithelial character. The contours of the cells is not always clear, Form wrong, sometimes polygonal. Kernels mostly rounded, normohromnaja, homogeneous with, granular or glybcha- fifth pattern of chromatin, contain nucleolus.
The cytoplasm grayish-blue, sometimes vacuolated, often there are bright yellowish lumps of fat. Occasionally found dual cell, granular cell type balls, polyblasts with inclusions of greenish clumps and crystals of cholesterol.
Meningoblastoma
Meningoblastoma - Benign, the most common tumor of the meninges, which tend to slow expansive growth.
Along with meningioma found meningeal sarcoma, characterized by a significant presence of cellular polymorphism and mitotic figures. Cells irregular shape meningioma, average size 25 40 m. Cores of clear, Oval, contains fine chromatin and one or two intensely colored large basophilic nucleolus. The cytoplasm is pale blue, sometimes fine-meshed, often with inclusions of fat droplets or erythrocyte. There are dual-core cells, and often - complex cells, arranged in a bulb.
Angioretikuloma
Cells angioretikulomy - Benign brain tumors of various localization, contains many capillaries, often rounded shape, size from 17 to 20 m. Cores of hypochromic, round or oval, nezhnosetchaty contain chromatin and one or two nucleoli.
Pale cytoplasm, grayish-blue, narrow border surrounds the nucleus, often vacuolated.
Malignant form angioretikulomy - angioretikulosarkoma - Is characterized by a polymorphic cellular composition. The size of the cells reaches 40 m, can reveal multinucleated cells, mitotic figures, the phenomenon of autophagy and granular balls. When angioretikulome in the cerebrospinal fluid is significantly increased protein content, It appears xanthosis.
Cancer
Cancer cells in the cerebrospinal fluid morphologically resemble primary malignant tumor cells, Since cancer is a central nervous system metastases. Most often, in the cerebrospinal fluid can reveal elements of adenocarcinoma. Microscopic examination revealed clusters of tumor cells, arranged in the form of rosettes, ferruginous formations, sometimes fragmented.
Melanoma
Melanoma cells in the cerebrospinal fluid have the same morphological features, as primary tumor cells.
The diffuse sarcomatous lesion of the meninges
At diffuse sarcomatous lesion of the meninges the tumor cells can be detected in cerebrospinal fluid. Their shape and size vary, and depend on the histological structure of the tumor. Characteristically, sarcoma cells relative to the same type, separately located or diffuse clusters, They are very delicate core with hypertrophied nucleoli, basophilic cytoplasm. Found many mitotic figures and granular balls. Sometimes sarcoma cells are very similar to medulloblastoma cells and differentiate them is impossible.
Acute leukemia lymfoblastnыy
At acute lymphoblastic leukemia in the cerebrospinal fluid show lymphoblasts.
Changes in biochemical parameters
In 60-70 % cases in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with tumors of the brain and spinal cord observed increase in the content of total protein, often at a normal number of cells. The most frequently and dramatically (up to 1.0-3.3 g / l) protein levels increased in tumors of the temporal and occipital lobes of the brain.
In patients with malignant tumors of the brain and spinal cord there is a decrease in the content of the cerebrospinal fluid albumin and increase γ- и b-глобулинов, and lipids. Besides, characterized by reduction of β-glycoprotein and α-lipoproteins and increased α-glycoprotein.
Metastases to the brain LDH increased cerebrospinal fluid, and benign tumors of the brain activity of the enzyme is not changed.
