The study of blood coagulation
Methods for studying blood coagulation system include the following groups:
- Indicative (general), giving an idea about the state of the entire coagulation cascade as a whole and its individual stages (registration can be done visually or by individual devices - koagulografa, thromboelastography and others.);
- differentiating deficit of individual factors - corrective coagulation tests, Tests mixing study of blood plasma blood plasma of patients with a known known deficiency of certain factors;
- quantitation of individual components on their functional activity (coagulation tests, studies and other chromogenic substrates) and (or) on immunological markers;
- identification of intravascular activation of blood coagulation and fibrinolysis of functional features or molecular markers such activation - to identify circulating activated coagulation factors, Product platelet degranulation, splitting of the components of blood coagulation or their metabolites, emergence of new antigenic marker activated factors and their complexes, accelerated metabolization labeled components of blood coagulation (reduce the period of their half-life in circulation).
Thus, when assessing the state of the blood coagulation system uses both its own coagulation method (laboratory and instrumental), forming the basis of the diagnostic process, and immunological, Radionuclide and other types of research. In many cases, the components can be defined as a functional activity, and immunologically - the content of the corresponding antigen in the blood. Concurrent use of these techniques allows us to differentiate forms of pathology, related to the lack of synthesis of the respective coagulation factor (in this case the same as it is lowered functional activity, and the amount of antigen), and mold, in which the molecule is synthesized factor, but it is abnormal and functionally defective.
To refer to the number of the first forms of the corresponding factor is added the sign "-" (eg, VIII-, IX- and t. d.), and the second - " " sign (eg, VIII , IX ).
Rough (general) coagulation tests
Determination of clotting time
Determination of clotting time (A preferred method of Lee-White) - Long used bystrovypolnimy (at the bedside) indicative test, allows to identify significant bleeding disorders, associated with a deficit of coagulation factors (besides Factor VII) or with the effect of anticoagulants and fibrinolytic. It is used as a guide for the test and control over heparin, elimination of heparin protamine sulfate. The test is relatively low sensitivity, his figures are broken only at marked decrease in plasma coagulation factors (below 4-5 %), and therefore unsuitable for the detection of mild forms of hemophilia A and B, as well as bleeding disorders when angiohemophilia, Factor XI deficiency, prekallikrein, and high molecular weight kininogen. For these reasons, the test can not be used for preoperative patients: under normal performance test (5-10 Minutes) you may experience profuse postoperative hemorrhage.
Plasma recalcification time
Plasma recalcification time - non-standardized low sensitivity test, less reliable for detecting hypocoagulation, than the whole blood clotting time. It can not be recommended for the diagnosis of disorders of hemostasis.
The activated partial thromboplastin time, plasma
The activated partial thromboplastin time, plasma (APTT, kaolin-kefalinovыy test) - Highly sensitive method, revealing the blood clotting process when you run the internal mechanism. Selectively sensitive to deficiency of plasma clotting factors (because the shortage of platelets and factors 3 Platelet compensated administered externally or Kefalonia eritrofosfatidom).
It is used to monitor heparin therapy, preoperative examination of patients and so on. d. Standard values depend on the samples used kephaline, in most cases up to 37-50 (optimally - from 37-45).
Kaolin time plasma
Kaolin during plasma - test, similar to the previous, but without the addition of plasma kephaline (eritrofosfatida), whereby it is sensitive not only to a deficiency of plasma coagulation factors, but also to the lack of platelet factor 3 Platelet. Estimated activity evaluation of this factor can be performed by comparing the time of the kaolin test plasma with high and low content of platelets (norm - 57-70 with).
We do not recommend the use of phospholipid components, giving in aPTT clotting times equal to 55 s and more, as this greatly reduces the accuracy and reproducibility of the test, including the quantitative determination of factor VIII and IX.
Silicone time plasma
Silicone time plasma - a plasma recalcification time, resulting in a needle silikonirovaniya, microtubes, pipetok, t. it is. with minimal contact activation. The test is sensitive to the hypercoagulable state-of intravascular activation of the contact phase of the start-up (factors XII and XI), however, this violation is revealed more clearly by defining the silicone clotting time of whole blood (on the basis of the Lee-White or tromboelastograficheskoy registration process siliconized cuvette).
Standard values depend on the silicone and determined study the blood of healthy people for each of its separate sample. When choosing silicone is the best, which extends to the greatest degree of clotting time (plasma).
Prothrombin (thromboplastin) time plasma
Prothrombin (thromboplastin) time plasma (Quick time, prothrombin index) characterizes the rate of clotting of blood plasma recalcified startup process to external device, t. it is. adding a human brain thromboplastin (or rabbit).
Active thromboplastin standardized on mixed samples of normal (test) plasma. The most commonly used thromboplastin activity with 12-18 (in classical technique with Kvika- 12-13). The weaker thromboplastin, the greater the error of the method.
Under normal prothrombin time plasma test reveals an isolated or cumulative deficit of prothrombin complex - VII, X, Va II, from which three factors (VII, X joy) K-vitaminozavisimy and their activity decreases under the influence of indirect anticoagulants. In this regard, the prothrombin test is fundamental in controlling the dosage coumarins (neodikumarin, or pelentan, sinkumar et al.) and other drugs in this group (fenilin).
Prothrombin time is normal with a deficit of factors of internal mechanism of activation of prothrombinase - factor XII, XI, IX, VIII (t. it is. for all types of hemophilia and defect Hageman), as well as the deficiency of prekallikrein and high molecular weight kininogen (VM kininogena)
In literature the different designation of prothrombin test results. The most expedient to specify the prothrombin time study and control plasma in seconds (giving the information and the activity of thromboplastin used). Sometimes I use the ratio of these two values, t. it is. index (PV study plasma, from ,)/(MF control plasma, from), (the rate of 0.9-1.1).
Another form of assessment of this indicator, which is the most widely used in laboratories, prothrombin index is a calculation of the percentage by compiling the feedback arithmetic proportions (norm - 90-110%), However, this calculation is wrong, because between the concentration of clotting factors and clotting time has not arithmetic, a logarithmic dependence. Besides, prothrombin test is sensitive only to a decrease in clotting factors below 50 % their normal size. By virtue of this expedient to use determining prothrombin index Percentage by dilution curve (1:2, 1:4, 1:8 and t. d.) mixed sample of normal plasma. Such a curve is built once for thromboplastins different initial activity (from 12 to 18 from) and it is determined by the prothrombin index in the studied patients. The advantage of this technique consists in that, that the results of all studies, including running dynamics on different days, It does not relate to accidental various samples of normal blood plasma, and to average the same standard parameters, resulting in significantly reduced error method. Indices, obtained by proportion and dilution curve of normal plasma, do not correspond to each other. This should be considered when monitoring the effect of indirect anticoagulants, For the index to decline conventional 50 % approximately corresponds to a reduction of the index curve dilution to 25-30% • In this regard, the analysis should always specify, How is the prothrombin ratio, what are the performance standards for the activity of the thromboplastin.
Plasma thrombin time
Plasma thrombin time, t. it is. the clotting time of citrated plasma by adding to it a standard thrombin activity, It is a major test for the evaluation of the final stage of blood clotting. The inclusion of this indicator is important for the correct interpretation of all the other coagulation tests, For violation of the final stage of blood coagulation must inevitably lead to a lengthening of clotting time in all of the above methods.
In most cases, during the test, thrombin used this concentration of thrombin solution, which, when mixed with an equal volume of blood plasma coagulation for giving 12- 18 from, but in recognizing disfibrinogenemy used and weaker concentrations (leading to a reduction of 30-35 with).
Thrombin time - An important diagnostic indicator, violation of its observed as congenital, and when the acquired common (secondary) gipoprotrombinemii, in most disfibrinogenemy, as well as under the influence of heparin, Product fibrinolysis (PDF) and other inhibitors of self-assembly and antithrombins fibrin monomers. By virtue of this thrombin time in the first place and increasingly broken in acute and subacute DIC, that plays an important role for the rapid diagnosis of this pathology.
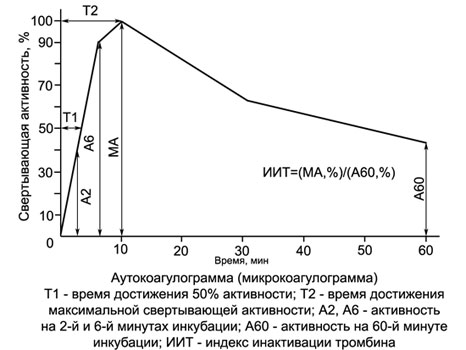
Autokoagulyatsionny test
Autokoagulyatsionny test (Permission) - A highly sensitive two-step, It describes the process of blood clotting when it started the internal mechanism. Like the aPTT, test is not sensitive to a deficiency of factor VII, but at the same time his testimony does not depend on the content of fibrinogen (factors and) in the test serum, how it differs from all the other samples indicative of coagulation.
Another advantage of ACT consists in, that investigated diluted blood, which substantially increases the sensitivity of the test to a deficiency of coagulation factors and, Besides, implementation of the ACP does not require the use of kaolin and kephaline, since standardization of the contact activation of phospholipid and it achieved its own red blood cell hemolysate investigated.
SUMMARY ACP is, in that 2 ml of hypotonic solution (0,222 %) Calcium chloride is added 0,1 ml of blood test.
In this hemolysate-calcium mixture is formed and prothrombinase thrombin, Activity is determined by sequentially adding 0,2 ml of this mixture to 0,2 ml test plasma (every 2 min during the first 10 m, and then - after each 10 min for 1 no).
The plasma is the source of fibrinogen investigated, which tested the activity of thrombin generated in the mixture. As shown by numerous studies, it may be replaced by blood plasma of healthy humans or fibrinogen solution. In this case, the patient's blood flow is reduced to 0.1-0,2 ml (It can be taken from the finger!), what transforms autokoagulyatsionny test in mikrokoagulyatsionny (MKT) and it makes it very convenient for pediatric use, including the study of hemostasis in newborns.
Coagulation activity in the ACT and MKT initially increases in healthy people usually reaches a maximum of 10 minutes, incubation of the blood-calcium mix (KKS), When plasma coagulation substrate occurs at 10 ± 1. Then coagulation activity begins to decline KKS, It is indicating that inactivation of thrombin formed therein. With Hemophilia, the action of heparin and other coagulation clotting activity of KKS sharply reduced, and the maximum moves from the 10th minute on a later date. If there is a hypercoagulable earlier and more significant increase in thrombin activity in CCS.
In conducting the test in a single test tube (definition only 10 minutes incubation KKS) it can be used to monitor heparin therapy. The advantage of this test method over activated partial thromboplastin time is, that it leveled the differential impact on different cephalins heparin clotting time.
Based ACP (MKT) It developed a simple and accurate method of differential diagnosis hemophilias.
With references cited in conversion tables indications ACT (MKT) can be expressed as a percentage and graphed - autokoagulogrammy.
To estimate the number of general parameters are widely used blood clotting and instrumental methods of investigation, mainly using various koagulografov and thromboelastography.
Thromboelastography not only gives an idea of the time parameters of the clotting blood or plasma, but also on the structure and mechanical properties of clots formed. In recent years, hardware and methods of registration introduced standardization and phospholipid contact activation of coagulation. Coagulation also created for mass implementation of common coagulation tests - aPTT, prothrombin, thrombin and other automatic recording of the results.
Methods of differentiation of various deficiency of coagulation factors and their quantitative determination
The following table shows data, that tentative study of blood clotting using three basic tests allows for group distinction deficit various plasma coagulation factors. So, slowing only in the prothrombin clotting test (I type violations) under normal readings of all other characteristic of hereditary deficiency of factor VII or to reduce the level of this factor in the early stages of development of obstructive jaundice or in the first 1-2 days of treatment with anticoagulants of indirect action, When the suppression of the synthesis of factor VII is ahead in its development reduction of all other K-vitaminozavisimyh clotting factors.
The types of violations of basic coagulation tests deficiency of certain plasma coagulation factors | ||||
Type violations | Scarce factor in the test plasma | Coagulation Tests | ||
APTT, Permission | PV | TV | ||
| I | VII | – | + | – |
| II | XII | + | – | – |
| XI | + | – | – | |
| IX | + | – | – | |
| VIII | + | – | – | |
| Von Willebrand Factor | + | – | – | |
| Plasma prekallikrein | + | – | – | |
| VM kininogena | + | – | – | |
| III | II | + | + | – |
| V | + | + | – | |
| X | + | + | – | |
| VII | – | + | – | |
| IX | + | – | – | |
| I | + | + | + | |
| XIII | – | – | – | |
| IV | Anticoagulants of direct action (Heparin, heparinoids et al.) | + | + | + |
| Antykoahulyantы indirect actions (kumarinы) | + | + | – | |
| Note. (+) - Slowing clotting; (-) - The lack of coagulation disorders. | ||||
Violation of only the internal mechanism of coagulation, t. it is. activated partial thromboplastin time and the ACP (II type), there is deficiency of factor XII, XI, IX, VIII, Villeʙranda (not in all forms), prekallikrein and kininogen VM. Of these defects in hereditary coagulation factor XII deficiency, prekallikrein and kininogen WM is extremely rare and is not accompanied by any bleeding, whereas the factor VIII deficiency (Hemophilia A), IX (Hemophilia B) and von Willebrand factor is very common (is greater than 96 % all hereditary bleeding disorders) and is accompanied by severe bleeding. Between them in the first place and to conduct further differential diagnosis.
Factor XI deficiency relatively rare (about 0.5-1.0 % All hemophilias), proceeds with a very mild bleeding (mostly after injuries and operations) and occupies an intermediate position between the first subgroup of asymptomatic disorders and hemophilia and von Willebrand disease.
Another type of disorders characterized by the elongation as the partial thromboplastin time and the ACP, and prothrombin time. It is characteristic for deficiency of factors V, X or II, either for a complex deficiency of K-factors vitaminozavisimyh (VII, X, IX, II), that is observed in obstructive jaundice and other forms of vitamin K-deficiency, and when receiving indirect anticoagulants.
And finally, as can be seen from this table, possible violation of the testimony of the three tests (IV type), that is observed in hereditary and acquired hypo- and disfibrinogenemiyah (not all), when taking anticoagulants of direct action (geparina, geparinoidov, hirudin et al.), treatment of fibrinolysis activators and defibriniruyuschimi drugs (streptokinase, urokinase et al.), appears in the blood and pathological substances antithrombins, preventing connection (assembly) fibrin-monomerov - paraproteinov, kryohlobulynov, immune complexes, as well as the sophisticated clotting, caused by DIC. Thus thrombin time is often disturbed to a greater extent, and a little bit earlier, than other tests.
When taking into account duration of the disease and the possibility of hereditary origin or secondary links with other diseases and medications or other effects, the presence or absence of bleeding and its type can not correctly identify the genesis of these deep disorders of blood clotting.
Everything differentiating tests are based on the principle of correction, t. it is. for determining, the extent to which revealed a bleeding disorder or eliminated, conversely, not removed samples of blood plasma or blood products obtained artificially clearly known deficiency of a clotting factor.
To this end, specialized laboratories to create a collection of blood plasma faktorodefitsitnyh, getting them from patients with a known set deep (less 1 %) deficiency of each factor and store them in small packages (by 0,5 ml) at a temperature - 30 ° C. If necessary, these samples are thawed and used in diagnostic tests.
Plasma, been accidentally thaw or remain unused, re-freezing is not subject to. The correctional tests should not be used with immune plasma inhibitor of a factor. The diagnostic kits of a number of firms contains freeze-dried samples of blood plasma deficient clotting factors identified (substrate plasma). However, many bleeding disorders rarely seen in clinical practice, concerning use artificially prepared blood components normal deficiency of certain clotting factors, and heterogeneous plasma (chickens, ducklings and others.).
The following table provides information about the content of clotting factors in the blood components, used for correction of coagulation tests, depending on the terms of their storage. Using this table, easy to decipher evidence of any of the three major coagulation tests. The corrective techniques of this kind used tests, standardized by contact and activation of phospholipid, t. it is. kaolin-kefalinovыe or primeneniem gemolizata (in ACT).
The content of clotting factors and blood plasma with different retention, used for correction of tests | ||
Blood plasma | Clotting factor | |
internal mechanism | external mechanism | |
VIII IX XI XII precalliricate | VII X X II | |
| Natyvnaya (with a shelf life up to 18 no) | ++++ | ++++ |
| Adsorbed * | +-++ | –+- |
| With a shelf life of more 24 no | -+++ | ++– |
| With a shelf life of 2-4 days (at + 4 ° C) | Not used | ++-+ |
| The filtered ** | Not used | –++ |
| Native chickens or ducklings plasma (aged 3-4 days) | +++- | Not used |
| Note. (+) - Availability factor; (-) - No. | ||
| * Adsorption is carried out either with barium sulfate from plasma oksadatkoy (glass4-plasma). or aluminum hydroxide gel of citrate plasma (To the(OH)3-plasma). | ||
| ** Filtering is performed through two asbestos filter (Seitz filters) - from 20 % (top filter) and 30 % (bottom filter) containing asbestos or by doubling or tripling, respectively, 30 and 20 % filters. | ||
Tests mixing blood plasma of patients with plasma, has certainly known deficiency of a factor
Determine the activated partial thromboplastin time in the test plasma, Normal plasma (control) and plasma clearly known factor VIII deficiency (of patients with hemophilia A), IX (of hemophilia B), XI и XII. Then, a mixture of citrate plasma samples investigated (7/10 the volume) and successively with each of plasmas deficient (3/10 the volume), since deficiency of factor VIII and IX (the most common forms of pathology!).
To the mixture was added kaolin and cephalin, and by 2 min subjected to a recalcification (at a temperature 37 ° C). To the mixture, where the activated partial thromboplastin time is not normalized, It has the same defect in clotting.
So, if the examinee patient activated partial thromboplastin time is normalized by adding blood plasma of patients with a known known deficiency of factor VIII, but corrected blood plasma of patients with deficiency of factor IX, it has Hemophilia A.
Similarly,, but based on the test differentiate prothrombin deficiency prothrombin complex (X, V, VVIVIVIVIVIVIVE .).
Thromboplastin generation test
For the differentiation of violations of the internal mechanism of blood coagulation is most often used classic thromboplastin generation test the replacement of platelet component, preparation of which requires considerable investment of time and blood, Kefalonia disadvantages test thromboplastin generation are its bulkiness, the need to prepare a large number of reagents, significant time on its implementation.
Corrective test, based on the basis of the test autokoagulyatsionnogo.
Rapid diagnosis of problems is quite different answers corrective test, based on the second correction, the same components of the normal blood-based test autokoagulyatsionnogo.
This test is highly reliable, speed and ease of implementation and requires little (no more 0,5 ml) amount of blood test, it can be used in pediatric patients.
In him, as in the thromboplastin generation test, used for correction of the adsorbed plasma and serum old, which re-centrifuged prior to the study. In three vials poured 2 ml 0,222 % calcium chloride solution and two of them were added 0,1 adsorbed ml of normal plasma (1-I vial) and 0,1 ml old normal serum (2-I vial). In the other three tubes made by 0,2 ml normal plasma citratnoj. Then to all tubes with a solution of calcium chloride is added to 0,1 ml citratnoj blood investigated.
Exactly one 4 min incubation, the mixture of its clotting activity was tested on normal plasma.
The sharp decline in the coagulation activity only in the first test tube (normal BaSO4-plasma) certify sick deficit factor IX (Hemophilia B), only in the second test tube (with the old serum) is about the deficiency of factor VIII (Hemophilia A); If correction happens in both test tubes (equally strong), then, obviously, there is a deficiency of factor XI or XII (cm. Table. 14).
Coagulation Tests, differentiating blood coagulation disorders of the inner mechanism (under normal prothrombin and thrombin time) | |||
Scarce factor in the test plasma | The components of normal blood, added to the investigated plasma | ||
DNA adsorbed plasma (without the factor IX) | Old serum (without factor VIII) | Mixture of bound plasma and serum of old | |
| Factor VIII | + | – | + |
| Factor IX | – | + | + |
| Factors XI or XII | + | + | + |
| Note. (+) - Normalization of coagulation; (-) - The lack of normalization of coagulation. | |||
This test is highly sensitive, as the study is being conducted in a divorced 20 at the time the blood factor compensation 3 platelets gemolizatom. Only use reagent is a hypotonic solution of calcium chloride, What makes a public trial.
Equally simple is the method of correction samples, performed on the basis of a test for prothrombin deficiency differentiation factor II, V and VII+, X (in the table).
Coagulation Tests, differentiating factor II deficiency, V and vII+, +X, performed on the basis of protrombinovogo test (under normal trombinovom time) | ||||
Scarce factor in the test plasma | The components of normal blood, added to the investigated plasma | |||
DNA adsorbed plasma (without factors II, VII, X) | Old plasma (without factor V) | Profiltrovannaja plasma (without the factors VII and X) | Old serum (without the factors (II) and (V)) | |
| Factors VII or X | – | + | – | + |
| Factor V | + | – | + | – |
| Factor II | – | + | + | – |
| Note. (+) - Normalization of coagulation; (-) - The lack of normalization of coagulation. | ||||
In order to separate the factor VII deficiency and X, additional coagulation tests performed with the addition of the studied blood plasma solution snake venom viper - medication lebetoks (selected this concentration of poison, that in the presence of kefalina and calcium chloride causes collapse for 20-25 with; all the ingredients are the number 0,1 ML and mix) (The table below).
With the same purpose the preparation is used Russell viper venom, dwelling in India (preparation stipven).
Coagulation Tests, differentiating factor VII deficiency and X using viper venom (lebetoks) | |||
Scarce factor in the test plasma | Tests | ||
with poison gurzy + kefalin + calcium chloride | with poison gurzy + kefalin + calcium chloride + profiltrovannaja blood plasma (source of factors V and VIII) | Prothrombin | |
| The X Factor | – | – | – |
| Factor VII | – | + | + |
| Note. (+) - Normalization of coagulation; (-) - The lack of normalization of coagulation. | |||
Differential diagnosis is completed, if necessary, by quantifying the scarce factors or specific immune inhibitors, What are special highly standardized methodologies. These construction techniques used dilution curves of mixed samples of normal blood plasma with the correction deficiency of factors, in addition to the test. On these curves is determined by the activity of the investigated factor in plasma of patients with.
Especially It is important to quantify the concentration of factors VIII and IX, and the presence of inhibitors in patients with haemophilia A and B (especially before and during surgery and intensive replacement therapy), as well as in deferred profuzhnykh postpartum bleeding, When it is necessary to differentiate the DVS-sindrom and more rare pathology — the emergence of immune factor VIII inhibitor (still much less - Factor V).
With deep deficiency of factor XIII (a very rare hereditary pathology) all coagulation tests are normal, but dissolve clots in 5M and 7M urea.
It helps to differentiate various deficiency of clotting factors also account the extent and, especially, terms of normalizing readings tests to patients following intravenous administration of blood products, t. it is. Adjusted live by Method A. 3. Barkagan.
This technique is particularly effective when a large difference in life expectancy differentiable factor in circulation. So, duration of half-life factors protrombinovogo complex varies from several hours (Factor VII) up to a few days (factor II). An intermediate position between them occupy factors X (2-2.5 days) and V (12-18).
Therefore, after a massive blast of transfusion of plasma prothrombin index increases in factor VII Deficiency very briefly, at deficiency of factor V is somewhat more long-term (approximately 4-6 times), but with a deficit of factor X and, especially, (II) for a longer period (more than 1-2 days). It is significant in this regard and the impact on the index of protrombin preparation PPSB (concentrate of factor VII, IX, X joy). He also briefly normalizes prothrombin time, factor VII deficiency, and more durable (many times!) deficiency of factor X and II. Since this drug there is no factor V, This deficit they not korrigiruetsja.
A similar difference is revealed in transfusion and substitution therapy internal mechanism of coagulation factors (XII, XI, IX and VIII), that registered an activated partial thromboplastin test.
Of particular interest is dynamics of adjusting the level of factor VIII and testimony in APTT transfusion therapy of hemophilia a and von Willebrand disease. The first of these diseases identified immediate maximum improvement of clotting after transfusion (spray, fast!) antigemofilnoj plasma or Cryoprecipitate, and then quite rapid (for 10-18 h) the steady decline in its, whereas vWF is observed some increase clotting activity within a few hours after transfusion, and then its decline - much more slowly, than when. In this regard, in the treatment of von Willebrand disease more rarely resorted to zamestitelnym transfuzijam, than hemophilia a.
Study on the functional activity of coagulation factors and components kallickrein-kininova and fibrinolytic systems using chromogenic substrates
The methods are based on the study of the activity of proteolytic enzymes and their inhibitors, involved in blood coagulation, fibrinolysis and kinin formation, the intensity and speed of this sensitive specifically cleaving enzymes of peptides, When the degradation which freed coloring agent (β-nitroanilin).
The degree of coloration of the reacting mixture determined by spectrophotometry, and its intensity is judged on the activity of the corresponding enzymes (clotting factor, kallikreina, plasmin and others.), and on the inhibition process is about the activity of enzyme inhibitors.
So, eg, effect of heparin and Antithrombin III can be evaluated to mitigate the chromogenic substrates splitting Factor Xa or trombinom, and activity of α2-antiplazmina — to reduce the action of plasmin corresponding chromogenic substrate. Chromogenic substrates or have digital signage (eg, s-2222), or referred to an abbreviated prefix hromozinami, denoting the enzyme, to which the sensitive substrate (eg, Chromozym Pl - Plasmine Substrate, Chromozym th - a substrate thrombin, Chromozym PK-substrate prekallikreina/kallickreina and t. d.).
Chromogenic substrates empower research of the hemostasis system, but are not available for many laboratories. Some research, made using them, do not have advantages over conventional koaguljacionnymi tests and give them matching results; in other cases, their use simplifies and speeds up study, It makes it more accurate; in third - these techniques have an independent meaning and can not be replaced coagulation tests (eg, definition prekallikrein).
Immunological identification of components of the hemostatic system
Immunological identification of components of the hemostatic system executes methods:
- Immunoprecipitation;
- Immunojelektroforeza;
- Radioimmunologicheskimi and others with relevant Antisera
When this content is measured in plasma Antigen of a coagulation factor (or its fragments), not functional activity, which can be dramatically reduced with normal antigen in plasma. This situation is typical for all cases, where in the body are abnormal (functionally defective) factors, preserving its antigenicity, but deprived of the ability to participate in gemostaze.
This allows you to distinguish between the complete cessation of synthesis of relevant factors and the formation of abnormal forms.
However, some components of the hemostatic system can only be determined immunologically.
This group includes such important research, as the definition of the following components::
- b-тромбоглобулина;
- α2-macroglobulin;
- proteins C and S;
- factor VIII Antigen:(C) and (VIII):RCOF;
- Product fibrinolysis (PDF);
- neoantigenov complexes of Thrombin-Antithrombin III and plasmin-doesn t;
- a number of other tests.
Therefore, immunological study significantly complement the functional evaluation of the different components of the system of hemostasis.
Diagnostic tests, based on the use as reagents preparations of snake poisons
Long established, that poisons so many snakes contain highly active proteolytic enzymes, cause clotting and affect different parts of the coagulation cascade. Consequently, Snake venoms and koagulazy of them are widely used for recognition of Hemostatic disorders, quantitative determination of coagulation factors, identification and quantitative determination of soluble fibrin-monomeric complexes (RFMK) and a number of other studies.
Samples with serpent-poisons are often much easier and make more rapid diagnosis of Hemostatic disorders.
This table contains data about the mechanism of action of poisons on svertawatuyu blood and diagnostic features of each of them.
Gemokoagulirujushhie properties of snake poisons and their use in diagnostic practices | |||
The name of the serpent * and preparations of their poisons | The mechanism of action on svertawatuyu | Differences from the properties of natural coagulation factors | Possible diagnostic use |
| Levantine Viper Vipera lebetina); lebetoks (Viper Russell; stipven) | Activator X factor (in the presence of calcium, factor V and fosfolipida **) | Unlike tissue thromboplastin contains no fosfolipida and does not compensate its deficits. Does not need to implement a clotting factor VII | Determining factors and platelets and its liberation when aggregation; distinction deficit factors VII and X; quantification of factor X |
| Eva mnogocheshujchataja (Echis multisgumatos) and EFA sand (Echis keel); ekarin, ehitoks | Activator Factor II, obrazuet atipichnыy thrombin-Em | Unlike α-thrombin, Thrombin-Em is not blocked by heparin and antithrombin III, It activates factor XIII (clots lysed in urea), koaguliruet entire Fibrinogen and pool all soluble fibrin-monomer complexes | The identification of coagulation, including hidden, in the treatment of heparin; quantification of Fibrinogen, and only for the purpose of diagnosis RFMK thrombinemia and DIC- syndrome |
| CopperHead Vulgaris (Halus halus Aghistrodon), as well as many rattlesnakes tropical America and Asia; ancistron-H1, reptilaza, botropklotaza, krotalaza, ancrod, etc. | Roll Fibrinogen, otshhepljaja only peptides and to form fibrin monomers are incomplete (des-a-fibrin) | Not cleaves peptides at, does not activate factor XIII and platelets, lid does not cause clots, heparin does not block, quickly analyzes clots | Disfibrinogenemij recognition; evaluation of the role of heparin in violation of the final liquidation phase (in comparison with trombinovym time) |
| * All of these snakes live in Central Asia (in parentheses are the other species with a similar mechanism of action and branded drugs from them; Viper Russell lives in India, Viper Daboja in Australia. | |||
| ** Equivalent kefalina and trombozitarnogo factor 3. | |||
These opportunities have expanded even more if you use several poisons and the simplest common coagulation tests. So, eg, simultaneous application of coagulation assays poison gurzy and EFA allows you to easily differentiate deficiency factor VII, X-V II (in the table below), and with an additional correction filtered normal plasma (source of factors V and II) — X and V factors deficiency.
Coagulation tests using various poisons, differentiating deficit factors protrombinovogo complex | |||
Scarce factor in the test plasma | Tests | ||
with poison gurzy + kefalinom | with poison EFA | Prothrombin | |
| VII | + | + | – |
| X + V | – | + | – |
| II | – | – | – |
| Note. (+) - Normalization of coagulation; (-)-lack of normalization of clotting. | |||
Definition of basic physiological anticoagulants
The most important is the defining activity of the basic physiological anticoagulant — antitrombina III, reduction which may be genetic (primary thrombophilia) or secondary, due to intensive consumption (DIC, massive thrombosis) or accelerated metabolism (heparin treatment, L-asparaginazoj, synthetic contraception) and the siege of immune complexes, paraproteinami, with fibronectin, acute phase proteins.
In any case, the reduced activity antitrombina III below 60-65 % supports intravascular clotting, makes less pronounced anticoagulant heparin. However, very often between the level of sensitivity and decrease of antitrombina III to geparino no consistent pattern of conformity.
Usually a weakening of antikoaguljantnogo action of heparin substantially prevails over the degree of reduction activity antitrombina III. Proved, that deficit at different forms of antitrombina III his affinity to heparin can vary in different degrees. Besides, various factions of heparin, the ratio which medicines very choppy, also have different affinity to antitrombino III. Therefore, practically, it is important to investigate both the actual activity of antithrombin III, and its ability to turn under the influence of fast-acting anticoagulant heparin.
Anticoagulant activity antitrombina III
Anticoagulant activity antitrombina III is determined by the ability of analyzing blood plasma (divorced Copley is a method of Vintershtejna or defibrination of the thermal denaturaciei at a temperature 56 ° С — Loligera methods, Abildgaarda, etc.) inactivate within a certain period of time the input externally Thrombin. The residual activity of Thrombin in such a plasma can be measured by its coagulation activity (on fibrinogene, Barium sulfate adsorbed plasma) either by splitting hromogennogo substrate, sensitive to trombinu or factor Xa (as Antithrombin III and inactivate factor).
Heparin-kofaktornaja activity
Heparin-kofaktornaja activity contained in the blood plasma Antithrombin III a longer period was determined using the test tolerance to geparino plasma, which may be deemed to be indicative, because it gives a very wide range of normal indicators and not sufficiently repeatable.
Much more accurate and maintains a izvodimy tests, which explores the effects of various concentrations of heparin for Thrombin time investigated plasma, containing a small amount of platelets. Comparison with elongation of Thrombin time control normal blood plasma, to which are added the same heparin samples.
So, in the Thrombin-geparinovom test to the investigated plasma added such amounts of heparin, that control extend Thrombin time with 15 up to 32-35 with (small concentration) and up to 95-110 with (the high concentration of heparin). These figures are calculated indexes of activity antitrombinov plasma (AARP) and reserve antikoaguljantnogo plasma (ARP).
Similar techniques are also commonly used to assess both the human Thrombin inactivation of coagulation tests, and the chromogenic substrates.
Immunological identification of Antigen antitrombina III
Immunological identification of Antigen antitrombina III allows to differentiate different types of thrombophilia:
- insufficient synthesis of antitrombina III (level antigenic marker lowered adequately reduce activity);
- with a saved synthesis of abnormal and functionally sub-standard forms (antigenic marker level is much higher, than the activity).
Proteins C and S, Thrombomodulin and α2-macroglobulin are defined immunojenzimaticheskimi methods.
