The study of vascular-platelet hemostasis
Violations at this level of hemostasis can occur with a tendency to hemorrhage or thrombosis, depending on which selected research methods. Besides, All research methods platelet Hemostasis divided into primary and secondary, Tests or second row, which apply only in the case, if using tests revealed any violations. The main (bazïsnım) The following are tests.
Samples for resistance (brittleness) capillaries - cuff, Jar, angiorezistometriya
From these tests, the most accessible and yet sufficiently informative Sample Konchalovsky-Tiller-LEED.
The estimation is made on the number and size of hemorrhage, formed on top of the palmar surface of the forearm (in a circle with a diameter 5 cm) After 5 minutes of compression at a pressure cuff shoulder 12-13,3 kPa (90-100 Mm Hg. Art.). The results are taken into account through 5 min after the removal of the cuff. Number petechiae more 10 points to the increased fragility of microvessels, which it is often associated with thrombocytopenia or platelet function violation angiotroficheskoy. Also takes into account the occurrence of hemorrhage, and right under the collar.
Banochnaya sample is performed in the same area of skin at the negative pressure building up in tiers - from 20 kPa (150 mm Hg. Art.) and lower. In assessing the results counted petechiae, appeared at Banks.
The samples on the duration and magnitude of capillary bleeding
In the classical Duke trial lower roller earlobe after a light warming her pierced to a depth of 3.5-4 mm. The bleeding in this study do not normally exceed 4 m, a drop of blood on filter paper are relatively low and start to decrease rapidly since approximately 1-1.5 minutes after puncture. When expressed thrombocytopenia (less 20 T in 1 l) platelet dysfunction and severe bleeding time increased to 20-40 minutes, blood stains are much larger, and the long-term decrease or diminish the waves, then increase again. Duke sample are not sensitive enough, in 2/3 Patients with thrombocytopathies it gives normal results.
More sensitive tests, in which the bleeding time is investigated on the background of an artificially created venous stasis, for which shoulder is superimposed on the cuff apparatus for measuring blood pressure and for the study supported the pressure, equal 5,3 kPa (40 mm Hg. Art.). Against the background of such stasis in Borchgrevink sample-Vaaler on the palmar surface of the upper third of the forearm lancet applied transverse incision depth 1 mm and a length of 8-10 mm (the rate of bleeding time - up 10 m), and sample Ivey et al. the same applied to the forearm lancet to draw blood from a finger puncture three transverse depth 3 mm (the rate of bleeding time - up 7 m).
Against the background of the same venous stasis performed A study on. FROM. Shitikova, whereby in terminal phalanges applied prick depth 3 mm, then the tip of the finger dipped in a cup 5 ml of isotonic sodium chloride solution and counted bleeding time in transmitted light (If the solution is intensively stained with blood, the follow-up to the finger is moved to a different cup). The amount of blood lost is determined by the increase in the volume of liquid in the cups (the rate of bleeding time - up 4 m, the volume of blood lost - from 0,01 to 0,4 ml).
In the test in T. N. Shushkevich lost blood volume is determined by the color of ammonia (0,04 %) , which are immersed paper with blood stains, by colorimetry on the medical colorimeter.
Indications tests for the duration of bleeding, Abnormal, evidence of abuse expressed platelet-vascular hemostasis, However, under normal results of these samples does not exclude mild expressed thrombocytopathy.
Counting the number of blood platelets
Counting the number of blood platelets (in a counting chamber under Goryaeva phase contrast or tint, or with the help of particle counters) - The most important way to diagnose thrombocytopenia and thrombocytopathy, proceeding with continuous or intermittent decrease in the amount of these cells (anomaly Bernard-Soulier, Meia Hegglina and others.).
Counting the number of platelets also suggests, whether it is possible to carry out their further functional research and in what way it should be done (with preconcentration platelets or without, photometrically or microscopically, and so on. d.).
The study of the size of platelets in the blood smears – trombotsitometriya
The study of the size of platelets in the blood smears (trombotsitometriya) It allows you to make a preliminary judgment on the various populations of cells in the blood of the test and get information on a number of anomalies, as well as the saturation of platelet granules.
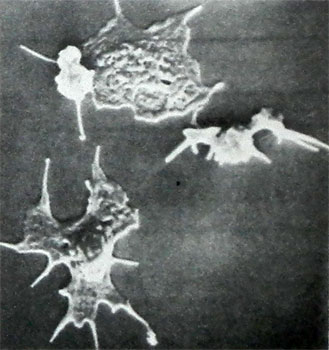
In some thrombocytopathy (Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome) Blood platelets are dominated by very small (to 2 microns in diameter), while others - giant forms (anomaly Bernard-Soulier, Meia Hegglina) - To 8 m or more. In a number of these cells are poor thrombocytopathy granules (cm. below), while others - violated the centralization of granules in platelet spreading on the glass, that constitutes a violation of the reaction and the release of granules they contain substances, necessary for the implementation of hemostasis. All these properties, and the ability of platelets to the spreading and the formation processes, evaluation of the structure of these cells can be studied using conventional and scanning electron microscopy, and by the interference of Nomarski optics.
The retraction of a blood clot regularly violated with severe thrombocytopenia (T in less than 30-40 1 l) and in some forms of qualitative inferiority of platelets, often - with Glanzmann trombotsitoastenii, uremic thrombocytopathy etc..
Research adhesively-aggregation of platelets (AAFT)
Research adhesively-aggregation of platelets (AAFT) - The most important element of laboratory diagnosis of most thrombocytopathy. Currently, a number of easily implementable and publicly available research methods, including visual, microscopic and hardware (aggregometry, microfilters and others.) registration to approximate this function can be assigned the following procedure.
Methods of retention of platelets on the glass (or filters)
Platelet counts were performed in the venous blood before and after passing it on to the standard of velocity through the column with glass beads or the glass fiber pigtail; loss of platelets from the blood are judged on degree of adhesiveness.
More available, though somewhat less accurate, method for determining the number of thrombocytes in the blood before and after contact with it within a certain period with the inner surface of the flask, rotating at a certain speed. A more accurate method for determining the delay platelet Millipore filters (pore diameter - 15-20 microns). In these tests, evaluation can be conducted from the increase in the pressure gradient upstream and downstream of the filter (clogged pores and platelet aggregates leads to an increase in this index).
Methods for studying the aggregation of platelets
Hemolysate-aggregation test based on the ability haemolysate washed erythrocytes, investigated in the breeding 10-2 and 10-6, while stirring to cause aggregation in his own plasma, won a large number of platelets (volume ratio of citrate plasma and hemolysate - 1,0:0,2). Taking into account the time of occurrence of aggregation (the rate at high concentration with hemolysate-11-17, low - 40-54 with) and its severity. The dynamics of the process and its intensity can be estimated as photometric (Medical colorimeter, green filter, stirring) and any design agregografe.
When the graphic registration process using a high dilution haemolysate (10-6) It provides a two-wave agregatogrammu, in which the second wave associated with the release of endogenous platelet aggregation stimulants - ADP, catecholamine, thromboxane, etc.. This second wave is characterized by the reaction of release, it is not observed in the absence of platelet dense granules (storage pool disease) or in violation of reactions release (aspirin-like syndrome and others.).
Hemolysate-aggregation test is available to perform in any laboratory, It requires no special reagents.
Visual micromethod determination of platelet aggregation
Its essence lies in the fact, that obtained under silikonirovaniya venous blood stabilized double capacity 3,8 % sodium citrate (ratio 2,4:0,6 ml), it is centrifuged 6 minutes at 100 v / / min, and the resulting platelet-rich plasma is applied by 0,02 ml on glass slides and treated with the same volume of aggregating agents - ADP, Thrombin, Collagen, noradrenaline or ristomycin. Final concentrations of aggregating agents in the study should be plasma:
- ADF 0,5*10-4 mmol / l;
- noradrenaline - 0,015%;
- thrombin - 0,125 U / ml (the concentration of collagen is selected empirically).
Perhaps the test as lower, and higher concentrations of aggregating agents. Selection of the concentration may vary depending on the activity of unequal production of various preparations and various activity of samples, in connection with which to pre-fit the concentration of each agent on normal plasma.
A mixture of platelet-rich plasma aggregating agent is mixed by rocking the slide, on a dark background with a magnifying glass recorded the time of appearance of units as a "snow storm". In assessing the results counted number of thrombocytes in plasma. So, ADP-time aggregation, increases from 27-37 seconds at 400 T in 1 l platelets to 62-75 seconds at 50 T in 1 l, and thrombin-aggregation - respectively, 40-52 to 79- 106 from.
Graphic registration aggregation
Graphic registration of aggregation under the influence of the same aggregating agents - highly informative method of functional platelet studies. Performed on or agregografah.
When the graphics register determine not only the onset of aggregation, but its intensity (largest deviation curve and area agregatogrammy), the first and second wave of aggregation - when using low concentrations of epinephrine and ADP (It describes the reaction of the second wave of liberation), and pathological disaggregation.
The visual or graphical study platelet aggregation under the influence ristomycin
Very important is the visual or graphic study platelet aggregation under the influence ristomycin. Violates this kind of aggregation (ristomycin final concentration of 0.8-1.0 mg / ml) at one of the most common hemorrhagic diathesis - angiohemophilia (von Willebrand disease), as well as abnormalities of platelets Bernard-Soulier and acquired certain kinds of synthesis inhibition of von Willebrand factor (uremia, immune inhibition, and so it. d.).
The quantitative determination of von Willebrand factor in the blood plasma
The quantitative determination of von Willebrand factor in the blood plasma is carried on ristomycin agglutination formalinized suspension of normal platelets in various dilutions of the test plasma bestrombotsitarnoy.
The method is important both for diagnosis and secondary angiogemofnlii synthesis inhibition of this factor, and for evaluating the severity of endothelial (vasculitis, atherosclerosis and others.) and tendencies to thrombosis, in which the content of von Willebrand factor in the blood often increases significantly.
The level of von Willebrand factor It indicates the ability of the endothelium to synthesize it (reduced when aigiogemofilii) and the extent of the defeat of the endothelium vasculitis, atherosclerosis and other diseases, proceeding with the defeat of the inner lining of blood vessels.
For fixed normal platelets in platelet-rich plasma of healthy individuals are added sequentially 0,2 % EDTA (0,5 ml 5 ml plasma) and by 2 min - fixing solution (20 ml 40 % formalin 1000 ml phosphate buffer 0,2 g EDTA, pH 6,4).
The mixture was kept at 4 ° C for at least 1 no, after which it was subjected to centrifugation, the supernatant was removed, and platelet pellet was washed twice suspending solution (One volume 3,8 % sodium citrate, and five volumes of isotonic sodium chloride solution; pH is adjusted to 7,4). The prepared suspension of normal platelets packed at formalinized 1 ml and stored at -20 ° C. The calibration curve is constructed using dilutions of normal plasma bestrombotsitarnoy, specimens which are mixed formalinized platelets. Further, the mixture is determined ristomycin agglutination. Calibration curve is determined by the amount of von Willebrand factor in the test plasma. Fixed platelets are better preserved when added in a small amount of preservative solution of sodium azide.
Tests, reflecting the spontaneous aggregation of platelets
In a study of patients with venous thromboembolism or increased tendency to thrombosis and ischemia of the core techniques include tests, reflecting the spontaneous aggregation of platelets, t. it is. occurring in whole blood or plasma without addition of aggregating agents.
To identify this phenomenon with the smear of blood draws attention to the ratio of the number of platelets lying separately and their aggregates, 3-5 composed of platelets and more. This phenomenon is best revealed when viewing sludge, by extensive tseitrifu- doping platelet-rich plasma (20Minutes at -30 6000 / min), stabilized by citrate or EDTA citrate solution. However, more stable results provide the following methods for determining the spontaneous aggregation.
Метод Wu-Hoak
Wu-Hoak method based on the, the blood from a vein typed in two test tubes, in a solution containing EDTA, and in the other - a mixture of the same solution with EDTA 4 % formalin solution. After mixing the contents of the vials settles 30 min at room temperature.
During settling aggregates settle, and the individual platelets remain in the supernatant. After standing counts the number of platelets in the supernatant in each of the tubes. Normally, the difference in the amount of platelets in the contents of both vials not exceed 10-15 %, at elevated spontaneous aggregation, it increases.
Method H. AND. Tarasovoj
According to the method of H. AND. Tarasovoj (1984) decrease of platelets from whole blood in the citrated aggregates counted after 3 minutes of agitation on shaker its AVC-1 at a rate 90-100 times 1 m.
The tube containing the 0,5 ml of blood, been subjected to shaking, introduced 1 ml 1 % formalin solution in isotonic sodium chloride solution. The second tube is not subjected to the control shaking, and the blood contained therein through the same test 3 Ming also introduced formalin solution.
Blood in both tubes advocates 30 m, after which the supernatant is counted in the number of platelets. Normally, the difference in platelet counts not exceeding 20 %, at an elevated tendency to aggregation, it increases.
In case of violations in the application of basic tests, characterizing platelet hemostasis, operate to the extent necessary to conduct additional studies. Of these the most important are the following.
Additional studies to determine platelet hemostasis
Study the number of megakaryocytes in the myelogram and bone marrow trepanate with studying the morphology of these cells
A significant increase in the number of megakaryocytes in the bone marrow sections, usually combined with a more or less marked increase in the number of platelets in the blood, observed at eritremii, hemorrhagic and essential thrombocytosis and other myeloproliferative diseases. Moderate megakariotsitoz, combined with thrombocytopenia, characteristic of thrombocytopenic purpura (idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura).
When aplasia and hypoplasia of the bone marrow of any origin decreased as the content of megakaryocytes in the bone marrow sections, and platelet count in peripheral blood.
Partial amegakariotsitoz observed deficiency trombotsitopoetina (a rare form of congenital thrombocytopenia), the appearance of antibodies in the blood antimegakariotsitarnyh, essential partial aplasia of megakaryocytes (may precede the development of leukemia).
Morphological and cytochemical changes observed in many megakaryocytes thrombocytopathy.
Electron microscopic study of the ultrastructure of platelets
Electron microscopic study of the ultrastructure of platelets is important for the diagnosis of several thrombocytopathy, in which missing or greatly reduced amount of non-protein granules of high optical density (containing ADP, Serotonin, catecholamines, calcium and others.), or protein α-granules, which is typical for a number of thrombocytopathy, united in a group of diseases of the storage pool, the absence of disease or granules.
Also can detect defects in the contractile apparatus (microtubule system) lysosomes and platelet.
When scanning electron microscopy and study of platelets by the interference of Nomarski optics can be detected defects in platelet fixation on foreign surface, their spreading her, sprouting, centralization and granule secretion, which is typical for many kinds thrombocytopathy.
Determination of antiplatelet antibodies by immunoflyuorestsent- tion studies in platelet suspension immunoglobulin, associated with these cells – Dixon method
This complex method allows to differentiate immune thrombocytopenia and non-immune.
However, the most pronounced forms of the disease with a sharp thrombocytopenia it is unacceptable, for the definition of related immunoglobulin requires a sufficiently large (40-50 T in 1 l) platelet count.
Defining life-labeled autologous platelets
Defining life-labeled autologous platelets thrombocytopenia allows to distinguish between a normal life span of platelets in circulation (about 9 Nights) and forms of the disease with a short lifespan of these cells.
The first is most commonly associated with decreased platelet production in the bone marrow, second - with their accelerated death, or with the effect of antiplatelet antibodies (autoimmune thrombocytopenia Platelet lifetime is reduced to a few hours), or intensive diminution of the cells in aggregates and thrombi in disseminated intravascular coagulation or thrombosis massive (thrombocytopenia consumption).
Quantitative determination of the content in the blood plasma before and after the platelet aggregation factors
Quantitative determination of the content in the blood plasma before and after the platelet aggregation number of factors - the membrane phospholipid factor 3, content of α-granules (antigeparinovogo factor 4, b-тромбоглобулина, mitogenic factor platelet) and nonprotein granules high electron optical density (Serotonin, catecholamine, ADF), and acid hydrolases.
These studies give an idea of the content in platelets of appropriate structures and components, their release into the plasma during aggregation, as well as vnutriso- sudistoy platelet activation, accompanied by the release of platelets in blood plasma with increasing concentrations of components in the final dense and α-granules (antigeparinovogo factor 4, b-тромбоглобулина и др.).
Methods of quantitative research of platelet factors are important for the identification of a number of thrombocytopathy (disorders preservation granules and their components, paresis of the reaction the release of these components, increase in the content of blood plasma due to intense inside- vascular adhesion and aggregation of platelets and others.). Several trombotsitopaty characterized decrease platelet content in the membranes factor 3 any breach of its availability to participate in blood clotting.
Study of biochemical characteristics of platelets and their individual structures
Study of biochemical characteristics of platelets and their individual structures - the stroma, granules, mitochondria and t. d. allow to document the connection of different types of pathology and dysfunction of platelets with certain types of enzyme deficiency (COX deficiency, thromboxane etc.), in violation of the structure of membrane lipoproteins, needed to communicate with the aggregating agents, and t. d.
Similar studies are available only well-equipped research laboratories and therefore do not apply general practice.
