Investigation of acid-forming function of the stomach – Chemical study of stomach contents
Under the study of acid-forming function of the stomach is meant determining total acidity, free and bound hydrochloric acid, acid residue, flow rate for the hydrochloric acid 1 no, acid and alkaline Component secretion, true flow rate of hydrochloric acid, proteolytic activity and content of lactic acid.
Total acidity shall be determined in-synthesized gastric contents, as when standing properties vary. Gastric contents titrated 0,1 n. sodium hydroxide solution in the presence of indicators. To determine the total acidity is used as an indicator phenolphthalein, which in the acidic environment remains colorless, and alkaline (at pH 8.2-10) It turns red.
Free hydrochloric acid is determined in the presence of an indicator dimetilamidoazobenzola: Red color, which appeared in the titration of gastric contents with sodium hydroxide, It goes into brick-yellow (yellowish-pink or salmon color) at pH 2.4-4.0.
In determining the related indicator is hydrochloric acid, sodium alizarinsulfonovokisly, which at pH 4,3-6,2 changes color from yellow to purple. In this case, the neutralization of acid valences, except bound hydrochloric acid.
Determination of the acidity of stomach contents
Reagents: 1 % alcoholic solution of phenolphthalein, 0,5 % alcohol solution dimetilamidoazobenzola (methyl yellow, Dimethyl yellow), 1 % aqueous solution of sodium alizarinsulfonovokislogo (Alizarin red S), 0,1 n. sodium hydroxide. All these solutions are constant at room temperature.
Method Töpfer. The two flasks is poured on 5 ml of filtered gastric contents. At first added 1-2 drops 1 % dimetilamidoazobenzola alcohol solution and 1-2 drops of phenolphthalein alcohol solution. In the second - 1-2 drops of sodium alizarinsulfonovokislogo. Tytruyut 0,1 n. sodium hydroxide with constant stirring. During titration gastric contents change color.
The first portion of the gastric contents note the amount of alkali, required for the initial titration to transfer red to yellowish-pink, which corresponds to the number of free hydrochloric acid and revealed dimetilamidoazobenzolom, and the total amount of alkali, used for titration before moving yellowish-pink color in the rack red, which corresponds to the total acidity and detected phenolphthalein.
The second portion of the gastric contents note the amount of alkali, used for titration of the moment of transition from the initial yellow color to purple (It corresponds to the sum of all substances kisloreagiruyuschih, except bound hydrochloric acid, and revealed alizarinsulfonovokislym sodium).
Total acidity is determined by the number milliliters 0,1 n. sodium hydroxide, izrashodovannogo of titrovanie 100 ml of gastric contents (conventional titration unit). Since taking titration 5 ml of gastric contents, and lead to the payment 100 ml, the amount of the used alkali is multiplied by 20. One conventional titration unit corresponds to the concentration of hydrochloric acid 1 mmol / l.
Method Michaelis. With this method, the total acidity is determined Titrimetric, free and bound hydrochloric acid; final determination of the conditional.
In the absence of gastric contents free hydrochloric acid related hydrochloric acid may be normal or elevated. The absence of not only free, and bound hydrochloric acid shows the appearance of a purple color when added to the gastric contents indicator alizarinsulfonovokislogo sodium.
Since the phenolphthalein color change is not in the neutral, and in an alkaline medium (pH 8,2—10,0), Indicators of total acidity somewhat overstated. Therefore, it is recommended to use as an indicator fenolrota (phenol red), the color of which varies with pH 7,9.
Titration using indicator imprecise, because their color change occurs in a fairly wide range of pH and evaluated subjectively. A display method can control the pH-meter.
Determination of acidity by titrimetry with a control study pH gastric. Using pH-meter set the end of titration. Celebrating volume 0,1 n. edkogo sodium, zatrachennogo of titrovanie 5 ml of the gastric contents to a pH 3,0 in the presence dimetilamiloazobenzola to calculate the amount of free hydrochloric acid to pH 8,2 or in the presence of phenolphthalein to pH 7.9 if fenolrota for determining the total acidity.
In determining the related hydrochloric acid indicator alizarinsulfonovokislym sodium titration end with the advent of violet color corresponds to pH 6,2 (fluctuation range of pH 4,3 to 6,2).
Thus, Control pH-meter eliminates subjective assessment of discoloration titrated in the presence of gastric contents indicators and this increases the accuracy of the study. Calculation of the amount of free and bound hydrochloric acid and total acidity by the above method is carried out based on the number of sodium hydroxide, zatrachennogo of titrovanie.
When a small amount of the recovered gastric contents or its unusual coloration due to impurities of blood, bile, food can try to determine the acidity Microchemical. The study is carried out with diluted gastric contents. The cup is placed 1 ml of gastric juice and 5 ml distilled water. Determine the acidity in the presence of indicators, titrating of microburet or pipette 0,1 n. solution of caustic alkali. The free hydrochloric acid is equal to the amount of alkali, that used for titration of the gastric contents to brick-yellow, umnozhennomu of 100. The total acidity is determined by the number of alkali, spent for titration of gastric contents before the red color (in the presence of phenolphthalein), umenyshennomu of 0,05 (the number of display correction) multiplied by 100 (With a sharp decrease acidity indicator recommended amendment 0,03).
To determine the acidity should be in each 15-minute portion of the basal and stimulated secretion, that allows you to set the type of acid curve, which is important in the diagnosis of diseases of the stomach.
In healthy subjects and in patients with gastritis normatsidnym in histamine-stimulated secretion phase level of free hydrochloric acid is increased by 30 minutes, and reduced by the end of the first hour of the study. When gastritis with secretory deficiency observed retarded acid curve, when the level of free hydrochloric acid is increased only by 60 minutes. In these cases it is necessary to continue sounding, as the maximum acid production can be observed on the 90th or 115th minute (free hydrochloric acid level can be within the normal range) and reduced by the end of the second hour.
When the secretory failure are also possible low acidity curve or false achlorhydria, in which on the background of the state of anatsidnyh free hydrochloric acid occurs only at the end of the second hour of the study and does not reach the normal level. In secretory failure, due to inflammation, also points asthenic type of secretion, t. it is. slow increase in the level of free hydrochloric acid for 45 minutes and reduced it below the norm by the end of the first hour.
In gastric ulcer during the exacerbation of the disease observed elongated acid curve with a slow ramp up to high levels of free hydrochloric acid at the end of the second hour of study.
The presence of duodenal ulcer and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome shows a high acid or speed curve with higher levels of hydrochloric acid than normal. Where, Only when there are functional disorders in the digestive organs, Acid curve is characterized by irregular vibrations.
Determination debit hydrochloric acid
For a more objective evaluation of acid-forming function of the stomach the notion of flow rate of hydrochloric acid, which characterizes its quantity, the separated per unit time (1 no) and expressed in millimoles. To determine the flow rate-hour of hydrochloric acid suggested the following formula:
Dч = V1*IS1*0,001+V2*IS2*0,001+V3*IS3*0,001+V4*IS4*0,001
where Dch --hour production rate of hydrochloric acid, mmol; V - volume portion of gastric contents, ml; E - the concentration of hydrochloric acid of the same portions, microtiter units; 0,001 - Amount of hydrochloric acid in 1 ml of gastric contents at a concentration of it, of equal 1 mmol / l.
Since the value of debit-hour time depends on the secretion of stress, we should strive for more complete extraction of gastric contents.
Depending on, which the acidity of gastric contents used in the calculation, distinguish debit free and bound hydrochloric acid, and total acidity (Acid products), which is determined from the value of total acidity. It is taken to determine flow rate of free hydrochloric acid. Debit-hour basal secretion of hydrochloric acid represent BAO (basal acid output - basal acid products), and at maximum histamine stimulyatsii- MAO (maximal acid output - maximum acid production). Flow portions, received an empty stomach, designated as hungry debit hydrochloric acid. Debit-hour of hydrochloric acid at sub-maximal stimulation of histamine indicate SAO (submaximal acid output - submaximal acid production).
In laboratory practice, to facilitate the determination of flow rate-hour of hydrochloric acid used in the nomogram. IN. Kalinichenko et al.. Thus figures, indicating the volume and acidity of the portion of gastric contents, located on opposite branches of the curve, connecting line. The intersection of line with the central vertical axis are the value of flow rate.
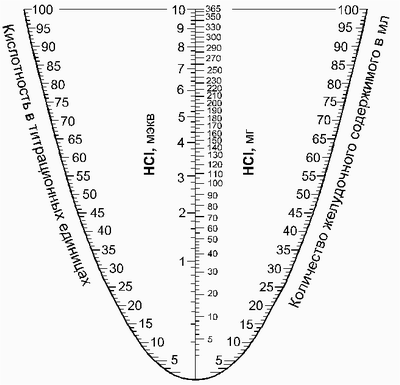
Normal levels of gastric secretion are shown in Table.
Normal levels of gastric secretory function | ||||
| Indicators | Fasting(maximum values) | Bazalynaya secretion | Sequential reaction to histamine | |
| submaximal | maximum | |||
| Volume, ml | 50 | 50- 100 | 110-140 | 150-200 |
| Total acidity, mmol / l | 40 | 40-60
| 90-100 | 100-200 |
| Free HCl, mmol / l | 20 | 20-40 | 65-85 | 90-100 |
| Related HCl, mmol / l | 10 | 10-15 | 12-15 | 14-16
|
| Debit-hour total acidity, mmol / h | 2 | 1,5-5.4 | 8-14 | 18-26 |
| Flow-hour of free HCl, mmol / h | 1 | 1-4 | 6,5-12 | 16-24 |
| Flow-hour of bound HCl, mmol / h | 0,5 | 0,5-1.5 | 0,6-1.5 | 0,7-1.6 |
| The volume of acid secretion component, ml
| 21 | 21-51 | 68-90 | 90,5-112 |
| True flow-hour HCl, mmol / h
| 2,3
| 3,3-8.2 | 10,5-14.5 | 18,5-26.5 |
| The volume of the alkaline component, ml
| 29 | 29-49 | 30-50 | 50-60 |
| Flow-hour gidrokarbonata, mmol / h | 1,3 | 1,3-2.2 | 1,3-4.0 | 1,8-2.0 |
Note. Debit-hour fasting Secretion calculated in relation to the volume of the respective portions of the gastric juice.
Determination deficit hydrochloric acid
The absence of gastric contents free hydrochloric acid indicates inhibition of acid, which is estimated deficit of hydrochloric acid. Hydrochloric acid deficiency determined by titration of the gastric contents 0,1 n. hydrochloric acid in the presence of an indicator (1 % alcohol solution dimetilamidoazobenzola) until the free hydrochloric acid.
Deficiency of hydrochloric acid points on the content of alkaline components, non-acid. It is considered, the maximum deficit hydrochloric acid, equal 40 titr ed, It indicates the termination of the secretion of hydrochloric acid (Absolute achlorhydria). At a lower value of the deficit hydrochloric acid released by the parietal cells, but due to the binding alkali components in a free form not detected (Relative achlorhydria).
Relative achlorhydria may also occur in the absence of both the free, and bound hydrochloric acid. This is possible in cases, when all the hydrochloric acid is neutralized with sodium bicarbonate.
The presence Absolute achlorhydria It can only be judged after the maximum stimulation of histamine. Such achlorhydria observed mainly at B12-deficiency anemia. At the absolute achlorhydria intragastric pH influenced histamine is not reduced. Because the maximum stimulation of histamine can be used only in exceptional cases, it is desirable to use for the diagnosis of intragastric pH-meter.
A significant deficiency of hydrochloric acid indicates the presence of gastric contents tissue decay products (pus, blood).
Evaluation of basal secretion
The size of the basal secretion of free hydrochloric acid in patients with gastritis anatsidnyh and gipoanatsidnym, stomach cancer is 0-1 mmol / h, in healthy people and those suffering from gastritis normatsidnym - 1-4 mmol / h, a stomach ulcer or duodenal ulcer - 4-5 mmol / h (more 5 mm / h is usually characteristic of duodenal ulcer), Zollinger-Ellison syndrome - 10 20 mmol / h.
Estimation of the maximum secretion
Maximum secretion, vanishing - true achlorhydria observed in atrophic gastritis, stomach cancer (in these cases should be excluded reflux duodenal contents). The amount of MAO 1 to 18 mmol / h indicates a lack of acid production in gastritis or gastric cancer; 18 – 20 mmol / h - at normal production (in healthy people or patients with gastritis normatsidnym); 20-26 - The increased acid production in patients suffering from duodenal ulcer, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.
Evaluation of acid production by the ratio of HLW and MAO
In healthy people, the ratio of HLW:MAO is equal to 1:6.
When braking function and decrease the reactivity of parietal cells, a decrease of basal secretion, Maximum normal acid production, HLW:MAO - 1:10 or 1:12.
When atrophy or damage of parietal cells reduced both basal, and the maximum acid production. Value for HLW:MAO may be increased (if the predominant functional inhibition), and reduced (in severe atrophy of parietal cells).
With increased neurohormonal stimulation of the parietal cells (hyperreactivity condition) an increase of HLW at normal or slightly elevated MAO; HLW:MAO = 1:2 or 1:3.
When hyperplasia of gastric glands with an increase in the number of parietal cells increases as the maximum, Tac and secretion bazalynaya.
Determination of acidic and alkaline components of gastric secretion
In the study of hydrochloric acid production rate is determined not part of the hydrochloric acid, bicarbonate neutralizes stomach. To account for the neutralized part of the hydrochloric acid is determined by the amount of the acidic and alkaline components and the true flow rate of hydrochloric acid.
The acidic component calculated by the formula of Thomson-Wayne
P=V*(0,219+4,88*N+),
where P - the amount of the acid component, ml; V - the volume of gastric juice in the test batch, ml; N+ - The total acidity in this portion, mmol / l; 0,219 and 4.88-constants.
Alkaline component determined by the formula:
NP=V—P,
where NP - amount of alkaline component, ml; V - volume portion of gastric juice, ml; P - amount of acidic component in this portion, ml.
Knowing the amount of the acid component, possible to calculate the true flow rate of hydrochloric acid of the following formula:
Dvh= C * 160 * 0,001
where Dvh - Real-time flow rate of hydrochloric acid, mmol; P - the amount of the acid component, ml; 160 - The value of a constant concentration of hydrochloric acid, allocated gastric parietal cells; 0,001is the number of hydrochloric acid 1 ml of gastric contents at a concentration of it, of equal 1 mmol / l.
In practice, the amount of the acid component and the true flow rate of hydrochloric acid are determined by the following nomogram.
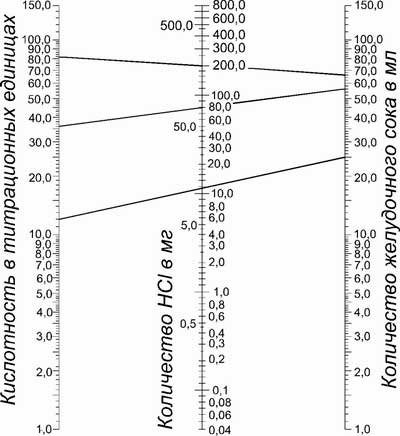
Indicators of the real flow rate of hydrochloric acid include all acidic products, including the amount of hydrochloric acid, bicarbonate which neutralizes gastric juice. The true flow rate of hydrochloric acid above, than MAO.
Alkaline secretion of gastric glands properties depend on the presence of mucus and bicarbonate. The concentration of hydrogen in the alkaline secretions most authors consider a permanent. According to the literature, it is 20-45 mmol / l. Hence, knowing the amount of alkaline component, determine the flow rate of hydrogen-hour by the formula U. AND. Coupon- zone-Ryss:
Dhydraulic=N*P*C*0,001,
where Dhydraulic.- Flow gidrokarbonata, mmol / h; C — concentration of hydrocarbonate, taken as a constant value,- 45 mmol / l; NP - amount of alkaline component, ml.
In patients with duodenal ulcer increases not only sour, and an alkaline component secretion.
Evaluation of secretion and the alkaline component of the true flow rate of hydrochloric acid-hour
The magnitude of the secretion of the alkaline component can judge the severity of the disease and the degree of compensation of the secretory function of gastric hyperacidity states.
If high rates of real output-hour hydrochloric acid levels as high alkaline component, there is a stoppage state giperatsidnyh. In cases, when at a high flow rate of true-hour hydrochloric acid content increased slightly alkaline component, You can talk about subcompensation. Reduced production of an alkali component in giperatsidnom able to indicate decompensation, and the possibility of developing peptic ulcers of the stomach or duodenum.
Thus, elevated levels of alkaline substances in the gastric contents indicates a mild disease, accompanied by high acidity, and, conversely, low levels of alkaline component indicates a more severe disease.
Determination of rate of hydrogen ion secretion
One of the methods of studying gastric secretion is determining the rate of hydrogen ion secretion with maximal histamine test or pentagastrinovogo.
Research carried out as follows. The patient swallows an empty stomach gavage, end of which must be located in the lower compartment of the stomach (his position is controlled fluoroscopically), to maximize suck gastric juice. A portion of the secretion aspirated during fasting 5 min and discarded. Gastric juice hour basal secretion of the patient receives their own by regularly sucking his syringe. Through 30 minutes from the start of the collection of gastric juice administered intramuscularly I mL 1 % solution dimedrol.
Upon receipt hour basal secretion subcutaneously 0,1 % solution of histamine dihydrochloride based 0,025 mg / kg body weight. After 10 m starting to gather over 1 h maximum dose of gastric secretion. Measure the volume of the two portions of the received time, gain on 20 ml each portion into cups, immersed electrode pH-probe and determine the pH. Further, using data volume and time portions of the secretion pH, nomogram for determining the rate of secretion of hydrogen ions (N ).
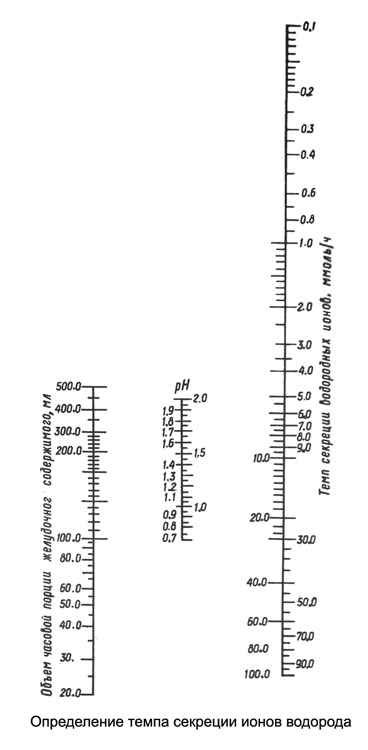
Almost at pH = 3,15 tempo secretion H+=0. When intragastric pH from 0,7 to 2,0 the rate of secretion of H+ determined from a nomogram, connecting line indicators of volume and pH of gastric juice. Crossing the line with the scale of the rate of secretion of H+ It indicates the corresponding amount in millimoles per hour. At pH values of 2,0 to 3,15 determining the rate of secretion of H+ carried out in the same manner, but the pH value is reduced by a 1,0, and the result is reduced in 10 time (comma transferred to the left by one character).
The normal pace of secretion of hydrogen ions in a portion of basal secretion ranges from 0 to 5 mmol / h, maximal stimulation of histamine - from 5 to 20 mmol / h, when using pentagastrin - from 9 to 22 mmol / h.
The above method of determining the acidity of gastric juice are inaccurate, as the study of the acidity of gastric juice aspirated, wherein the acid component is neutralized with an alkaline, knowingly gives low results. Errors in the determination of product hydrochloric acid may be due to incomplete recovery of gastric juice. Exclude these inaccuracies allows intragastric pH-meter.
Intragastric pH-metry performed by pH-probe. It is advisable to use a dual-channel pH-probe, enabling them to measure the pH directly from the stomach wall, t. it is. to determine the acidity of the primary in the bottom of the stomach, where the secret is acidic, and in the pyloric, where his glands secrete alkaline secret, which is normally capable of neutralizing acid. Simultaneous recording of the pH value in these parts of the stomach allows you to explore kislotovydelitelnuyu function and alkalizing ability of gastric juice.
Probe, used for pH-meter, It has a thickness 5 mm, length of about 1,5 mm, covered with a soft, smooth, plastic cover. At the end of the probe has a metallic olive, in which the electrodes are mounted (antimony and calomel). Enter the pH-probe on an empty stomach, about 0,7 m, wherein one electrode is placed in the stomach, and the other - in the pyloric cave. It is desirable to introduce the probe under X-ray control. It is connected to a special pH-meter - atsidomehanografu Linara or remodeled lab pH-meters, which are mounted, two measuring range for the body of the stomach and the pyloric cave. Normally an empty stomach in the stomach pH 5,0 6,0, in the pyloric cave - 7,0, indicating physiological dormancy gastric secretion.
According to some reports, Possible fluctuations in the pH values of the basal secretion of gastric body: 0,8- 1,5 - Hyperacidity (sour or irritated stomach); 1,6- 2,0 - Normatsidnost; 2,1-5.9 - Gipoacidnostь; 6,0 and above - achlorhydria.
Establishing a low pH does not give complete information about the strength of acid-forming function of the stomach. To differentiate lowest basal secretion (hyperacidity, normatsidnost) not used stimulants, superpressory and gastric secretion. In these cases, a test atropinovy.
Atropinovy test
After the introduction of the stomach pH -zonda and radiological control of the correctness of its position in the patient register for 1 h fundal and antral basal pH (4-6 Definitions intervals 10 15 m).
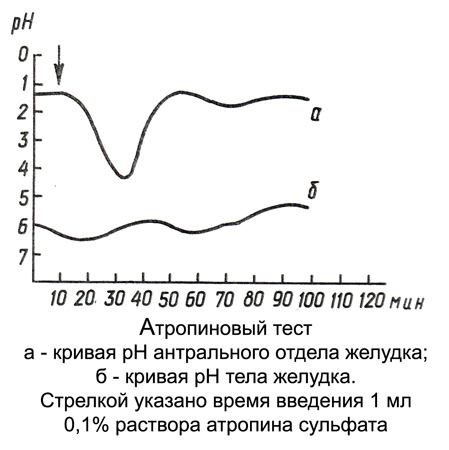
In identifying low basal pH (less 2,0) administered subcutaneously 1 ml 0,1 % atropine sulfate and continued over the next hour in the same manner registration pH (Serial pH). Atropinovogo test results are evaluated not only by the extent and duration of pH increase, but also by the difference of averages of basal and sequential pH (short-term changes in pH, observed in duodenal reflux, not taken into account). Where, when intragastric pH at the last measurement rises, additionally conducted two measurements (with intervals of 10-15 min) to exclude duodenal reflux.
By increasing the degree of pH reaction are following atropinovy test:
- pH above 2,0 - Strong;
- from 1,0 to 2,0 - Average;
- from 0,5 to 1,0 - Weak;
- less 0,5 - Small;
- no change - negative.
If the difference averages basal and consistent pH is 0,6, atropinovy test is weakly positive, 0,02 - Negative. At a pH greater than the difference 0,6 - Positive.
Evaluation atropinovogo test is possible not only for the average values of basal and consistent time pH measurement, but also by the peak value of pH in the stomach fundus following administration of atropine. This method of determining the intragastric pH is more informative, however duodeno-gastric reflux may be side effects.
As alkalizing ability gastric secretion in the pyloric cave distinguish:
- acid production stoppage, when the pH exceeds the antrum and body of the stomach pH is close to neutral;
- decompensated acid production with little difference between pH antrum (neutralizing region) and the body of the stomach (acid-forming region);
- partially offset by the difference of acid pH between antrum and corpus 1.0-1.5.
Thus, atropinovy test can distinguish among patients with low intragastric pH fasting group atropinorezistentnyh persons, in which the fractional probing revealed a large flow rate of hydrochloric acid due to its high secretion. In patients sensitive to atropine amount of hydrochloric acid secretion less high. Atropinovy test increases the information content of intragastric pH-meter, It provides diagnostic and prognostic test for duodenal ulcer and other types of gastric hyperchlorhydria. It is used to select a surgical method for the treatment of peptic ulcer.
To judge the degree of compensation can be sour stomach based on the intragastric pH-meter with a load of sodium bicarbonate - an alkali test.
Determination of lactic acid
Addition of hydrochloric acid in gastric contents may be other acid, of which the greatest clinical interest is milk. It is a result of metabolic disorders in cancer, affecting the stomach, or stagnant processes in the stomach, in the absence of free hydrochloric acid and the presence of lactic acid fermentation rods.
Qualitative screening tests based on lactic acid appears at its interaction with ferric chloride yellow-green color due to the formation of iron lactate.
Determination of the activity of pepsin
Determination of the activity of pepsin is based on indirect methods of studying the digestive ability of gastric contents. Several methods, which differ from each other using different substrates for digestion and contact time with the enzyme. In order to determine the total proteolytic activity can take native gastric juices or the gastric juice with a buffer, providing optimum action of pepsin.
The most common method for determining the activity of pepsin is Method Tugolukova. It can help you to determine the gastric juice pepsin, uropepsinogen and blood pepsinogen, allowing you to compare the data obtained. The content of pepsin in gastric contents are judged by the amount of digested protein dry plasma.
In Definition This flow-hours (time voltage) the pepsin content in milliliters in this portion is multiplied by the volume of a portion of the gastric contents, then figures, obtained for 1 no, add up.
Second standardized method for determining the activity of pepsin - Anson method modification Chernikov. It is based on the study of the digestive ability of pepsin in gastric juice in the presence of hemoglobin as substrate.
The normal amount of activity of pepsin to be withdrawn in the study of donors in each laboratory, since they depend on the activity of crystalline pepsin, used to construct the calibration curve.
Normally, the content of pepsin in gastric contents after a test meal of cabbage is from 0,2 to 0,45 g / l.
To determine the activity of pepsin is also used Method Hunt, wherein it is using as a substrate plasma protein. The measurement is performed at the Medical colorimeter after the addition of the reagent Folin, used to evaluate the calibration table, built in the study of standard solutions of pepsin. In determining the amount of pepsin, vыdelyvshehosya during, take into account the hours of hard.
Pepsin content in healthy humans in a portion of the basal secretion of 50 to 300 mg / h, with a maximum of histamine stimulyatsii- 100 to 900 mg / h. There parallelism between the production of hydrochloric acid and pepsin content. In gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer, these high performance, in chronic gastritis with secretory insufficiency reduced, however the lack pepsin ahilii not observed.
Intragastric determining proteolytic activity of gastric juice
For intragastric study proteolytic activity of gastric juice administered through a tube PVC tube with substrate (Technical albumin or chicken protein, subjected to coagulation), I put on a metal cylinder, soldered to a rigid steel cable. After 1 hours after administration of the substrate tube it is removed from the stomach by gavage, administered parenterally submaximal or maximal dose of histamine and reintroduced to 1 hours to evaluate the severity of substrate proteolysis in the stomach, not only in the basal period, but also to stimulate the secretion of histamine.
The extent of intragastric proteolysis estimated volume of digested substrate and is expressed in micrograms per hour. After removing the tube from the stomach is determined by the amount of digested protein, then it is placed into 20 n. hydrochloric acid solution to evaluate additional digestion albumin, which occurs due to pepsin, penetrating the substrate from the gastric contents. The intensity of the additional proteolysis of albumin is due to the concentration of pepsin in the stomach. Hence, by the number of digested substrate, determined immediately after the time of your stay in the stomach, judged on the extent intragastric proteolysis, and additional data reflect the concentration of substrate proteolysis of pepsin in the gastric contents.
Both in terms of basal secretion, and after histamine submaximal stimulation in patients, suffering from duodenal ulcer, additional proteolysis above, than in healthy persons.
Intragastric study proteolytic activity of gastric juice has important diagnostic value, because it reflects the functional state of the secretory apparatus of the stomach in a, as close as possible to the physiological.
The total proteolytic activity of gastric juice can be determined by mikroekspress-A. A. Pokrovsky.
Determination of intrinsic factor
Intrinsic factor is a component of the mucus of the stomach. It is determined in a simplified manner (by the method of Glass-Boyd), based on protein precipitation step to precipitate and the hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide.
The concentration of intrinsic factor in normal fasting is 0-0.2 g / l, after test meal in healthy people is detected - 0.2-0.5 g / l.
Much increases the concentration of the internal factor in duodenal ulcer, which is especially pronounced in the interdigestive period.
Reducing the amount of intrinsic factor It is seen in chronic gastritis and indicates atrophy of gastric glands. The marked decrease in the secretion of intrinsic factor indicates the possibility of B12-deficiency anemia.
The findings of research of intrinsic factor have no independent value, they merely complement the results of the study of acid-forming function of the stomach.
