Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in a child
Описание гипертрофической кардиомиопатии у ребенка
Gipertroficheskaya cardiomyopathy, or HCM, It is a form of cardiomyopathy. This condition, in which the heart muscle thickens because of genetic проблем со структурой мышц. When the muscle thickens, it must work more, to pump blood. Sometimes, thickening of the muscle prevents the blood leaving the heart and causes a blockage. This blockage can lead to “protekaniю” mitral valve. HCM can cause uneven heart muscle, and in rare cases it can cause abnormal heart rhythms, that may even lead to death.
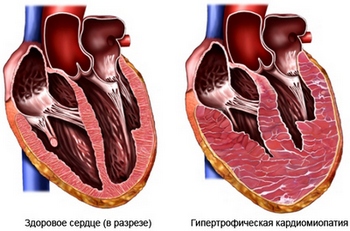
Причины гипертрофической кардиомиопатии у ребенка
ГКМ может быть вызвана геном, который вызывает нарушения в сердечной мышце. Он может передаваться по наследству, или это может произойти в результате изменения генов с течением времени.
Risk factors
Наличие члена семьи с ГКМ является основным фактором риска для ребенка.
Симптомы гипертрофической кардиомиопатии у ребенка
Symptoms may include:
- Chest pain;
- Fainting, особенно во время выполнения физических упражнений;
- Dizziness, especially after exercise;
- Cardiopalmus;
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing;
- General fatigue;
- Fatigue during exercise or activity, related to physical performance.
Эти симптомы могут быть вызваны побочными эффектами заболевания, в том числе ненормальным сердцебиением. Заблокированный или уменьшенный приток крови, usually, является причиной головокружения, обмороков и затрудненного дыхания. Младенцы с ГКМ могут иметь следующие симптомы:
- Fast, тяжелое дыхание во время кормления;
- Потоотделение во время кормления;
- Усталость или бездействие;
- Медленный набор веса.
Некоторые дети могут не иметь симптомов. Врач может заподозрить у ребенка заболевание, если у него есть шумы в сердце, хотя не каждый больной ГКМ имеет этот признак, и не все шумы возникают из-за ГКМ.
Диагностика гипертрофической кардиомиопатии у ребенка
The doctor asks about the symptoms and medical history, and performs a physical exam. Tests may include the following:
- Stress test – Tests on the body's response to physical exertion, which may help in detecting heart and lung problems;
- Echocardiography – It uses high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound), to examine the size, shape and motion of the heart;
- Transesophageal echocardiogram – for the detection of abnormalities of the heart is performed Photo;
- Холтеровский мониторинг – Portable ECG recorder attached to the patient (usually, on 24-72 o'clock), to record heart activity during normal daily activities;
- Heart catheterization – catheter inserted into an artery in the groin to study heart chambers;
- Coronary angiography – after administration of the radiopaque dye into the coronary artery is performed radiograph, that allows the doctor to look for abnormalities and to evaluate the function of the heart;
- Blood tests;
- Chest X-ray – used, to take a picture of structures inside the body.
Лечение гипертрофической кардиомиопатии у ребенка
Treatment focuses on, to control symptoms and prevent complications. Treatment options include:
Medication
Drugs may be used, to help maintain proper and regular heart function. Они также могут использоваться для удаления лишней жидкости из организма. При наличии аритмии ребенку может понадобиться прием антиаритмических препаратов и лекарств для разжижения крови.
Surgery
The thickened portion of the heart muscle is cut and removed. It may be necessary, если у ребенка заблокирован сердечный кровоток.
If the mitral valve is leaking, может быть сделана операция для ремонта или замены митрального клапана.
Implantable cardioverter defibrillator (Idk)
IIR is implanted, если ребенок подвержен повышенному риску внезапной смерти.
Профилактика гипертрофической кардиомиопатии у ребенка
Если у члена семьи была диагностирована ГКМ, ребенок должен быть проверен на данное заболевание.
