Hirschsprung's disease
Description of Hirschsprung's disease
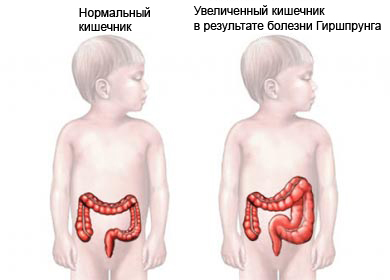
Hirschsprung's disease – a rare congenital disease. It affects nearly every 5000th neonate. Bowel obstruction disease ends and prevents normal bowel movements. Hirschsprung's disease occurs most often separately, but it can also be part of a syndrome.
Causes Hirschsprung's disease
Hirschsprung's disease is caused by the absence of certain nerve cells. These cells, called ganglia, They are found in the intestinal wall. They help relax the bowel wall, allowing feces to move through the colon. In children with this disease of the colon is nerasslablennoy, causing obstruction. The disease usually affects the past 30-50 centimeters of the colon, that ends with the rectum.
The absence of ganglia is due to a genetic defect. In some cases, Hirschsprung's disease is hereditary. It means, that parents can pass on to their children. This can occur, even if the parents do not have the disease.
Risk factors for Hirschsprung's disease
Factors, which increases the risk of Hirschsprung's disease:
- The presence of family members with Hirschsprung's disease;
- It is more common in men;
- The emergence of Hirschsprung's disease may be associated with other birth defects.
Symptoms of Hirschsprung's disease
Hirschsprung's disease is usually diagnosed in childhood, but it can also be detected later. Symptoms may vary with age.
Newborns
- Failure to pass meconium within the first 48 hours of life (Meconium – dark sticky substance, which is the first bowel movement);
- Vomiting after eating;
- Abdominal distention.
In young children,
- Severe constipation;
- Diarrhea;
- Anemia;
- Stunting.
Adolescents
- Severe constipation for most of life.
Diagnosis of Hirschsprung's disease
In most cases, Hirschsprung's disease are diagnosed in infancy, although some cases were discovered during adolescence or young adulthood.
Tests for diagnosis may include:
- Barium enema – injection barium salt solution into the rectum. At the same time the intestines become visible on x-ray, that allows us to consider possible defects;
- Biopsy – removal of a sample of intestinal tissue, to check for ganglia (or lack thereof);
- Anorectal manometry – measuring the pressure of internal and external sphincter with a rectal balloon or a special sensor.
Treatment of Hirschsprung's disease
The main method of treatment for Hirschsprung's disease – surgery, which removes the damaged part of the colon. There are three phases of surgery, but sometimes they do not need.
Phase surgery for Hirschsprung's disease:
- Colostomy – This phase involves the creation of surgical openings in the colon, which is brought to the abdominal surface. Feces and intestinal contents are allocated through the hole.
- Removal – the affected area of the colon is removed and the healthy part joins the rectum.
- Closure of colostomy – colostomy sutured, and bowel function gradually returns to normal.
Results
Symptoms are eliminated in 90% children after surgery. The best result is connected with the beginning of early treatment.
Complications
Complications may include:
- Enterobrosia;
- Enterocolitis;
- Short gut syndrome.
Prevention of Hirschsprung's disease
Methods of preventing this disease does not exist.
