Atrioventricular block a child
Description atrioventricular blockade of the child
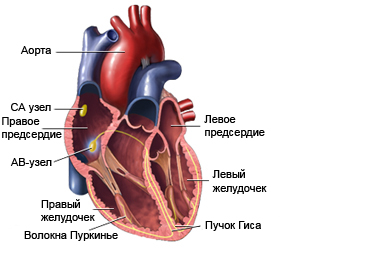
The heart has four chambers: two upper chambers (predserdiya) and the two lower chambers (ventricles). Sinoatrial (ARE) node, at the top part of the right atrium, generates electrical signals, are sent to the atrioventricular (AB) node. AV node sends the signals to reduce the ventricles, which are the main pumping chambers of the heart. When the heart is working properly, electrical signals are transmitted smoothly from the atria into the ventricles, causing rhythmic muscle contractions, which pumps blood to other parts of the body.
Heart block occurs, when the electrical signals do not pass through the AV node. Heart block does not mean, blood, leaving the heart, locked. It means, electrical signals, control the operation of the heart, transmitted correctly, which may lead to slow heartbeat.
There are three types of heart block:
- The first degree of blockade – This mild form of heart block. In this case, electrical signals are transmitted slowly, than usual, but still reach the ventricles. This usually no symptoms, and heartbeat and rhythm are normal;
- Second degree heart block – means, Some signals do not reach the ventricles. This leads to a reduced heart beat;
- Third degree, or complete blockade – this is the most serious type of heart block. In this state, the control signals are not able to reach the ventricles. The ventricles compensate for the absence of signals alone, but they are not able to fully perform this function, and patients observed a significant decrease in heart rate.
Reasons atrioventricular blockade of the child
Causes of heart block in children may include:
- Heart disease is inherited from parents;
- Taking certain medications;
- Effects of the operation;
- Infection, for example, such as Lyme disease;
- Lupus in the mother.
Symptoms atrioventricular blockade of the child
These symptoms may be caused by other serious diseases. When they occur, seek medical advice.
- Dizziness;
- Fainting;
- Chest pain;
- Breathlessness;
- Heartbeat;
- Slow heartbeat;
- Weakness and fatigue.
You need to know, the child may feel these symptoms, but can not tell or describe them. The child also may not have any symptoms.
Diagnosing atrioventricular blockade of the child
The doctor asks about the symptoms, observed the child, He is studying the medical history and doing a physical exam. It may also refer the child to a cardiologist for further examination.
Tests may include the following:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) – test, that records heart activity by measuring electrical current, passing through the heart muscle;
- Echocardiogram – test, which uses high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound), to examine the size, shape and motion of the heart.
Treatment of atrioventricular blockade of the child
The course of treatment depends on the type of heart block. Usually, treatment is not necessary for first-degree heart block. It is necessary to consult with your doctor about the best method of treatment for a child. Treatment may vklyucht install pacemaker. It can be installed in some cases, the second degree of blockade and in all cases the third degree heart block. Kardiostimuljator – device, which generates electrical signals for stimulating heart muscle contractions.
Prevention atrioventricular blockade of the child
Unfortunately, there is currently no way to prevent heart block in the child.
