Hormonal study colpocytologic
Hormone cytologic diagnosis It allows you to specify the diagnosis of a variety of diseases (amenorrhea, dysfunctional uterine bleeding, pathological climax, hormonal forms of female infertility, and others.). With hormonal colpocytologic studies can determine the day of ovulation, which is crucial in determining the duration of pregnancy.
Hormone cytological diagnosis is based on the study rejects the epithelial cells of the vaginal mucosa and changes in their composition depending on the influence hormonal. Taking research material painless and can be done multiple times.
The methodology of the hormone cytological diagnosis
A glass pipette with a pear or an acute stomach take freely rejects (not scraping!) From verhnebokovoy of the vaginal vault, apply it to the edge of the slide and cut glass makes possible a thin smear. Then the smear is dried in air, the flame of the burner or fixed with a mixture of Nikiforov. When drying in air smears should be painted no later than 20-30 minutes.
For painting strokes applied monochrome or polychrome techniques. Monochrome painting techniques make it possible to determine the nature of the cells (value, form) and their location, the presence of other elements (leukocytes, Trichomonas, etc.). Polychrome staining methods allow a comprehensive cytologic analysis taking into account the hormonal influence on vaginal epithelium. Counting of cells is preferably carried out in different fields of view of the microscope in the middle portion of the glass, where the strokes thinner and the cells more visible.
The assessment data put colpocytologic changes the cellular composition, a degree of maturation of the vaginal epithelium.
Vaginal mucosa It is lined with stratified squamous epithelium neorogovevayuschy, including basal, parabasal, intermediate and superficial epithelial cells.
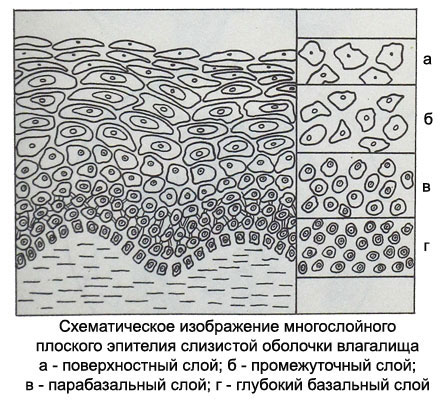
Basal epithelial cells not rejected and smear fall only when the vaginal mucosa injury or inflammation with damage to its wall.
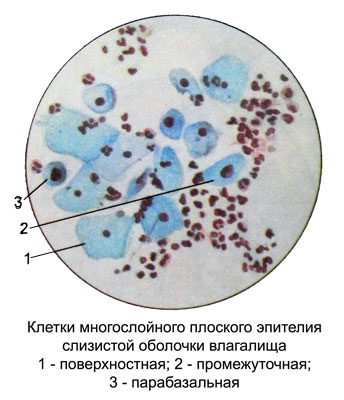
Parabasal cells of the lower layers of the vaginal epithelium small size, sometimes no more than a lymphocyte, round shape, with a large nucleus, occupying nearly the entire cell. Parabasal cells of the upper layers larger cells in the lower layer 2-3, oval or circular shape with a thickened rim of cytoplasm on edges. The core of their large, round or vesicular with fine chromatin network, sometimes with small nucleoli, Set in the heart of the cytoplasm. The higher the parabasal cells, the smaller the diameter of their kernels.
The presence of an independent department in a smear parabasal cells (without artificial scraping them) It constitutes a violation of the maturation of the vaginal epithelium, that may be due to the weak hormonal stimulation. The emergence of parabasal cells in inflammatory processes in the mucous membrane of the vagina accompanied by a large number of white blood cells.
Intermediate cells oval or triangular shaped characterized by a transparent cytoplasm. Cores of vesicular, often round or oval, with severe, often rough, chromatin network.
Superficial cells are large polygonal flat plate with a clear cytoplasm and small round pyknotic nucleus. The lower layers of the cells have a rounded shape and a larger core (prepiknoticheskie). Pyknosis of the nuclei of superficial cells indicates their maximum maturity, coming under the influence of estrogen stimulation.
For a more complete understanding of the morphological composition of the cells in the vaginal smear using the corresponding indices (maturation, eosinophilic, cariopyknotic, folding, crowding and other.).
Maturation index (IS) It is the percentage of in the vaginal smear parabasal, intermediate and surface cells. EC is determined by counting in several fields of 100- 200 cells and more. Designate it as a formula, where on the left write the number of parabasal cells, middle - Intermediate, Right - surface. In the absence of L for the cell type in the proper location figure give 0. There are various options of this index.
- A. Have smears only parabasal cells in the absence of intermediate and superficial - severe atrophy (eg, IS = 100/0/0).
- B. Increasing the number of cells in smears interlayer epithelium - moderate atrophy (eg, IS = 65/35/0).
- IN. The increase in the number of superficial cells in the absence of parabasal - umerennaya proliferation (eg, IS = 0/75/25). Increased proliferation indicated by an arrow, the right direction (eg, IS = 0/60/40).
- T. The predominance of superficial cells in the smear - vыrazhennaya proliferation (eg, IS = 0/15/85 or 0/0/100). Reducing the proliferation indicated by an arrow, leftward (eg, in the initial EC = 0/0/100 reduction in proliferative changes it looks like a 0/30 ← / 70, then 0/50 → / 50 m. d.). Hence, changes in the degree of proliferation of the vaginal epithelium can be seen as a shift to the left or right shift, Why put an arrow, directed in the appropriate direction.
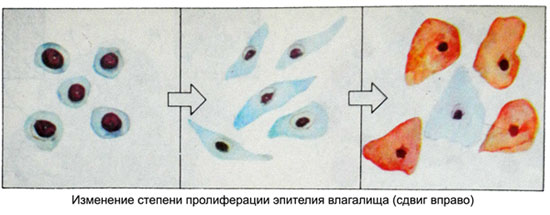
Thus, using IP vaginal epithelium can get an idea of the degree of influence as the endogenous hormone, and exogenous.
Cariopyknotic Index (THAT) is determined by counting the number of cells with the Office of Surface pyknotic nuclei (diameter less 6 m) with respect to the total number of cells with nuclei, the size of which more 6 m. Results are expressed as a percentage. The diameter of the core is measured in the same way, as the diameter of erythrocytes. It can be defined and visually - small pyknotic nuclei, compact, hyperchromic round or slightly oval.
Normally CI varies depending on the hormonal effect. Increasing estrogen stimulation causes an increase in CI, and, conversely, reduction of the effect of estrogen leads to a decrease in CI. According to this index can be judged on the duration of estrogen and synthetic analogues. Progesterone (hormone of the corpus luteum) and androgens have the ability to inhibit proliferation of the epithelium, estrogen-induced. The degree of suppression can be evaluated in terms of KI.
With the help of CI can determine the nature of the menstrual cycle, establish the presence of ovulation, detect excessive proliferation. High rates of CT in childhood and menopause lead to the conclusion of pathological proliferation, not characteristic of the age.
Thus, definition of nuclear pyknosis is one of the main diagnostic test hormone colpocytologic.
Eosinophilic Index (EI) - The percentage of mature cells with separated surface eosinophilic cytoplasm relative to the total number of cells in a smear. The size of the nuclei in the calculation of EI not taken into account. The cytoplasm of mature superficial cells in the vaginal epithelium is able to perceive different dye, Therefore, to determine EI polychrome staining methods used cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and basophilic. The more estrogen stimulation, the more superficial eosinophilic cell smears. Stimulation of progesterone and androgens are not capable of causing color cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm. These hormones are antagonists, vыzыvayuschymy Reduction EI.
In the normal menstrual cycle, the largest number of surface eosinophilic cells observed in the late follicular phase (preovulatory).
Established, what deep layers of cells of the vaginal epithelium - Parabasal and basal - painted in the blue and blue-green tones due to their content of protein SH groups.
Glycogen in the form of single granules contained only in the upper layer of parabasal cells. In the cells of the intermediate layer around the nuclei, glycogen is found, and a large number of protein SH groups located in a blue ring, surrounding the central core of glycogen. In the surface epithelial cells of the vagina in normal healthy menstruating woman glycogen is uniformly, occupying the entire surface of the cytoplasm. The amount of glycogen in the epithelial cells of the vagina varies depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle and hormonal activity of the ovaries. In girls before puberty vaginal epithelial cells glycogen poor. In normally menstruating women, the highest content of glycogen celebrated the 12th day of the menstrual cycle.
During the luteal phase of the cycle glycogen content decreases in the epithelial cells. The menopause is depleted glycogen vaginal mucosa; menopausal epithelial cells contained a significant amount of glycogen.
The appearance of eosinophilia of the cytoplasm of superficial cells of the vaginal epithelium in childhood or in deep menopause indicates the presence of pathological sources of estrogenic stimulation.
The content of glycogen in the epithelium of the vagina reflected in the degree of acidity of the contents of the vagina, and, Consequently, and the state of its flora. The basic conditions for the existence of rod-flora in the vagina of healthy women is a certain degree of acidity (pH 3,9—4,7), high levels of glucose and glycogen. Coccal flora occurs at low levels of glycogen, glucose content and low acidity of the vagina.
Index folding is determined by counting the number of folded mature superficial cells in relation to the total number of cells in a smear. While expressing progesterone stimulation. This is accompanied by twisting or folding the edges of the cytoplasm of cells, and they take the form of a rounded petal roses or folded in an envelope sheet. The index is given in the form of folding or describing expressed as a percentage, and the amount of nuclei and cytoplasm stain not taken into account.
Index crowding, or groups, cells characterizes the presence of groups of cells of the surface epithelium (4 and more) among the same, but located separately. Also it reflects the stimulation of progesterone vaginal epithelium, results in the sloughing of cells, their rejection and the location of groups and layers. This index is estimated at plus three-point system: severe overcrowding (+++), moderate (++), poor (+).
Each of these indices reflects the effect of a certain hormone, such as EI and CI - the degree of estrogen saturation, while the indices of folding and congestion - the effect of progesterone and androgens. With the IP can only establish the presence of atrophy or severe proliferation. Therefore, to determine the degree of hormonal abnormalities in the treatment of hormonal therapy is necessary to determine all indexes.
